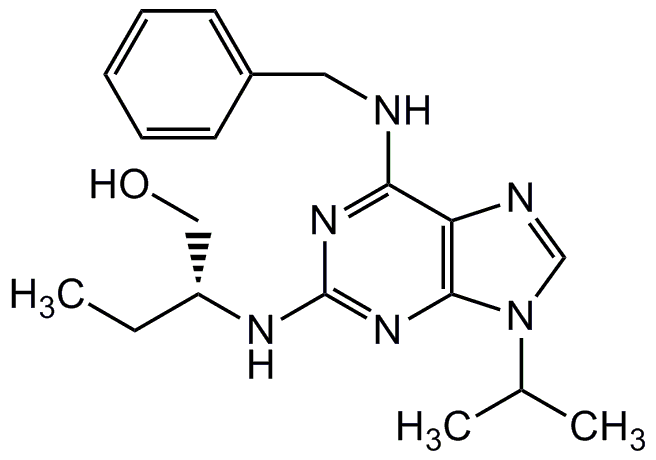
(R)-Roscovitine
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-CR1-0006-M001 | 1 mg | £30.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CR1-0006-M005 | 5 mg | £90.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CR1-0006-M050 | 50 mg | £250.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Storage:
-20°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
6-Benzylamino-2-(R)-[(1-ethyl)-2-hydroxyethylamino]-9-isopropylpurine
Appearance:
White to off-white solid.
CAS:
186692-46-6
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
InChi:
InChI=1S/C19H26N6O/c1-4-15(11-26)22-19-23-17(20-10-14-8-6-5-7-9-14)16-18(24-19)25(12-21-16)13(2)3/h5-9,12-13,15,26H,4,10-11H2,1-3H3,(H2,20,22,23,24)/t15-/m1/s1
InChiKey:
BTIHMVBBUGXLCJ-OAHLLOKOSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 186692-46-6. Formula: C19H26N6O. MW: 354.5. Potent and selective inhibitor of CDKs. More potent than olomoucine. Inhibits CDK1/cyclin B kinase (IC50 = 450 nM), CDK2 (IC50 = 700 nM) and CDK5/p35 (IC50 = 160 nM). Inhibits M phase promoting factor (MPF) kinase activity. Arrests human fibroblasts in G1 phase. Antitumor compound. Activates the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Targets both the p53 and NF-kappaB pathways[10]. Has effects on calcium channel gating. Prevents DNA damage-induced cyclin A1 upregulation. Apoptosis inducer. As CYC202 in phase I clinical trials. Reviews.
MDL:
MFCD02266401
Molecular Formula:
C19H26N6O
Molecular Weight:
354.5
Package Type:
Vial
Product Description:
Potent and selective inhibitor of CDKs [1, 2, 4, 16]. More potent than olomoucine [3]. Inhibits CDK1/cyclin B kinase (IC50 = 450 nM) [2], CDK2 (IC50 = 700 nM) [4] and CDK5/p35 (IC50 = 160 nM) [4,5]. Inhibits M phase promoting factor (MPF) kinase activity [2]. Arrests human fibroblasts in G1 phase [6]. Antitumor compound [8]. Activates the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway [9]. Targets both the p53 and NF-kappaB pathways[10]. Has effects on calcium channel gating [12, 17, 18]. Prevents DNA damage-induced cyclin A1 upregulation [13]. Apoptosis inducer [11, 15, 20]. As CYC202 in phase I clinical trials [14]. Reviews [3, 7, 19].
Purity:
>98% (HPLC)
SMILES:
CC[C@H](CO)NC1=NC2=C(N=CN2C(C)C)C(NCC2=CC=CC=C2)=N1
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO or 100% ethanol; only moderately soluble in water.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Biochemical Reagents
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
References
Activation of cyclin-dependent kinases by Myc mediates induction of cyclin A, but not apoptosis: B. Rudolph, et al.; EMBO J. 15, 3065 (1996) | Biochemical and cellular effects of roscovitine, a potent and selective inhibitor of the cyclin-dependent kinases cdc2, cdk2 and cdk5: L. Meijer, et al.; Eur. J. Biochem. 243, 527 (1997) | Chemical inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinases: L. Meijer and S.H. Kim; Meth. Enzymol. 283, 113 (1997) | Cytokinin-derived cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors: synthesis and cdc2 inhibitory activity of olomoucine and related compounds: L. Havlicek, et al.; J. Med. Chem. 40, 408 (1997) | Direct in vivo inhibition of the nuclear cell cycle cascade in experimental mesangial proliferative glomerulonephritis with Roscovitine, a novel cyclin-dependent kinase antagonist: J.W. Pippin, et al.; J. Clin. Invest. 100, 2512 (1997) | The cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors olomoucine and roscovitine arrest human fibroblasts in G1 phase by specific inhibition of CDK2 kinase activity: F. Alessi, et al.; Exp. Cell Res. 245, 8 (1998) | The specificities of protein kinase inhibitors: an update: J. Bain, et al.; Biochem. J. 371, 199 (2003) | In vitro and in vivo antitumor properties of the cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor CYC202 (R-roscovitine): S.J. McClue, et al.; Int. J. Cancer 102, 463 (2002) | The Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor CYC202 (R-roscovitine) inhibits retinoblastoma protein phosphorylation, causes loss of Cyclin D1, and activates the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway: S.R. Whittaker, et al.; Cancer Res. 64, 262 (2004) | R-Roscovitine simultaneously targets both the p53 and NF-kappaB pathways and causes potentiation of apoptosis: implications in cancer therapy: A. Dey, et al.; Cell Death Differ. 15, 263 (2008) | The CDK inhibitor, R-roscovitine, promotes eosinophil apoptosis by down-regulation of Mcl-1: R. Duffin, et al.; FEBS Lett. 583, 2540 (2009) | (R)-roscovitine prolongs the mean open time of unitary N-type calcium channel currents: N.R. DeStefino, et al.; Neuroscience 167, 838 (2010) | R-Roscovitine (Seliciclib) prevents DNA damage-induced cyclin A1 upregulation and hinders non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) DNA repair: M. Federico, et al.; Mol. Cancer 9,208 (2010) | Phase I evaluation of seliciclib (R-roscovitine), a novel oral cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, in patients with advanced malignancies: C. Le Tourneau, et al.; Eur. J. Cancer 46, 3243 (2010) | Roscovitine, olomoucine, purvalanol: inducers of apoptosis in maturing cerebellar granule neurons: E.A. Monaco, 3rd, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 67, 1947 (2004) | Roscovitine targets, protein kinases and pyridoxal kinase: S. Bach, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 280, 31208 (2005) | The effects of presynaptic calcium channel modulation by roscovitine on transmitter release at the adult frog neuromuscular junction: S. Cho & S.D. Meriney; Eur. J. Neurosci. 23, 3200 (2006) | Roscovitine differentially affects CaV2 and Kv channels by binding to the open state: Z. Buraei, et al.; Neuropharmacology 52, 883 (2007) | Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors as anticancer drugs: V. Krystof & S. Uldrijan; Curr. Drug Targets 11, 291 (2010) | Roscovitine induces cell death and morphological changes indicative of apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells: O.P. Mgbonyebi, et al.; Cancer Res. 59, 1903 (1999) | Polo-like kinase 4 transcription is activated via CRE and NRF1 elements, repressed by DREAM through CDE/CHR sites and deregulated by HPV E7 protein: M. Fischer, et al.; Nucleic Acids Res. 42, 163 (2014) (AdipoGen spec.) | Roscovitine is a proteostasis regulator that corrects the trafficking defect of F508del-CFTR by a CDK-independent mechanism: C. Norez, et al.; Br. J. Pharmacol. 171, 4831 (2014)
Related Products
| Product Name | Product Code | Supplier | (R)-CR8 | AG-CR1-0039 | AdipoGen Life Sciences | Summary Details | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|