Adiponectin (mouse) ELISA Kit (Twin Plex)
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-45A-0004YEK-KI01 | 96 wells | £430.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-45A-0004YTP-KI01 | 2 x 96 wells | £730.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Host Type: Mouse
Regulatory Status: RUO
Target Species: Mouse
Shipping:
Blue Ice
Storage:
+4°C
Images
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
ACRP30; AdipoQ; apM1; GBP28; Adipocyte Complement Related Protein of 30kDa
Assay Type:
Sandwich
Detection Type:
Colorimetric
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
Handling Advice:
After standard reconstitution, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C.Avoid freeze/thaw cycles.Plate and reagents should reach room temperature before use.
Long Description:
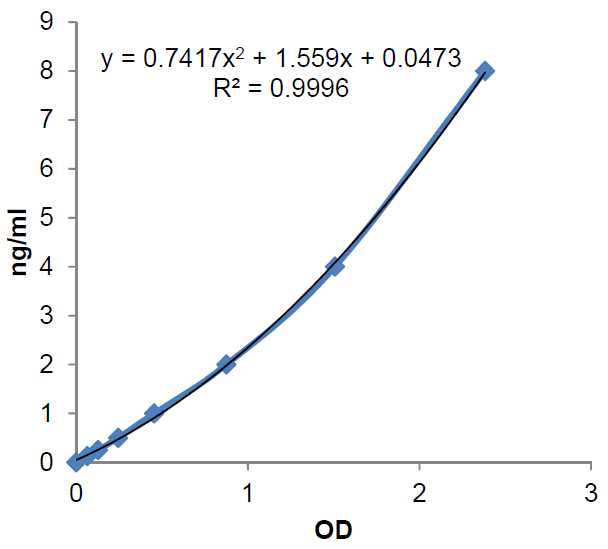
ELISA Assay. Detects mouse adiponectin. Does not cross-react with human adiponectin, rat adiponectin, mouse resistin, mouse RELM-beta or mouse leptin. Colorimetric assay. Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernatant, Plasma, Serum. Range: 0.125 to 8ng/ml. Sensitivity: 50pg/ml. Adiponectin is a promising biomarker of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) but also as a potential target for management of the metabolic syndrome. It is a very robust marker that is not prone to degradation or acute inflammatory challenges, is present in relatively high concentrations in the peripheral circulation, and can be collected by a variety of methods. The benefits of using adiponectin assays in clinical settings include, (a) prediction of risk of diabetes and metabolic status and (b) providing a tool to monitor metabolic improvements. Adiponectin exerts anti-atherogenic and anti-inflammatory properties and may be important as a biomarker for obesity-related cardiovascular disease (CVD). New findings showed urinary adiponectin excretion as an independent new biomarker of microvascular and macrovascular damage in T2DM and suggested it as a very promising tool for early cardiovascular disease risk assessment. Adiponectin serum level was also described as a good biomarker of colorectal adenoma, this being related to the positive correlation between obesity and increased risk of cancer at various sites (colorectal, breast, prostate and endometrium).
NCBI, Uniprot Number:
Q60994
Package Type:
Box
Product Description:
Adiponectin [ACRP30; AdipoQ] is a promising biomarker of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) but also as a potential target for management of the metabolic syndrome. It is a very robust marker that is not prone to degradation or acute inflammatory challenges, is present in relatively high concentrations in the peripheral circulation, and can be collected by a variety of methods. The benefits of using adiponectin assays in clinical settings include, (a) prediction of risk of diabetes and metabolic status and (b) providing a tool to monitor metabolic improvements. Adiponectin exerts anti-atherogenic and anti-inflammatory properties and may be important as a biomarker for obesity-related cardiovascular disease (CVD). New findings showed urinary adiponectin excretion as an independent new biomarker of microvascular and macrovascular damage in T2DM and suggested it as a very promising tool for early cardiovascular disease risk assessment. Adiponectin serum level was also described as a good biomarker of colorectal adenoma, this being related to the positive correlation between obesity and increased risk of cancer at various sites (colorectal, breast, prostate and endometrium).
Range:
0.125 to 8ng/ml
Sample Type:
Cell Culture Supernatant, Plasma, Serum
Sensitivity:
50pg/ml
Specificity:
Detects mouse adiponectin. Does not cross-react with human adiponectin, rat adiponectin, mouse resistin, mouse RELM-beta or mouse leptin.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
ELISA Kits
UNSPSC Number:
41116126
Use & Stability:
12 months after the day of manufacturing. See expiry date on ELISA Kit box.
References
Chop-deficient mice showed increased adiposity but no glucose intolerance: Y. Ariyama, et al.; Obesity 15, 1647 (2007) | Overexpression of human adiponectin in transgenic mice results in suppression of fat accumulation and prevention of premature death by highcalorie diet: S. Otabe, et al.; Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 293, E210 (2007) | Resveratrol inhibits TNF-alpha-induced changes of adipokines in 3T3-L1 adipocytes: J. Ahn, et al.; BBRC 364, 972 (2007) | Transgenic mice expressing nuclear sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c in adipose tissue exhibit liver histology similar to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: H. Nakayama, et al.; Metabolism 56, 470 (2007) | Anti-diabetic Effects of Compound K versus Metformin versus Compound K-Metformin Combination Therapy in Diabetic db/db Mice: S.H. Yoon, et al.; Biol. Pharm. Bull. 30, 2196 (2007) | Compound K Enhances Insulin Secretion with Beneficial Metabolic Effects in db/db Mice: G.C. Han, et al.; J. Agric. Food Chem. 55, 10641 (2007) | Expression of Src homology 2 domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase substrate-1 in pancreatic beta-Cells and its role in promotion of insulin secretion and protection against diabetes: M. Kobayashi, et al.; Endocrinology 149, 5662 (2008) | A Vinegar-processed Ginseng Radix (Ginsam) Ameliorates Hyperglycemia and Dyslipidemia in C57BL/KsJ db/db Mice: E.J. Han, et al.; Food Sci. Biotechnol. 17, 1228 (2008) | Effects of adiponectin transgenic expression in liver of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis model mice: H. Nakayama, et al.; Metabolism 58, 901 (2009) | Construction of adiponectin-encoding plasmid DNA and gene therapy of non-obese type 2 diabetes mellitus: M.H. Nan, et al.; J. Drug Target. 18, 67 (2010) | ER stress in adipocytes inhibits insulin signaling, represses lipolysis, and alters the secretion of adipokines without inhibiting glucose transport: L. Xu, et al.; Horm. Metab. Res. 42, 643 (2010) | Feeding silk protein hydrolysates to C57BL/KsJ-db/db mice improves blood glucose and lipid profiles: E.Y. Jung, et al.; Nutr. Res. 30, 783 (2010) | Hyperadiponectinemia enhances bone formation in mice: Y. Mitsui, et al.; BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 12, 18 (2011) | A promising culture model for analyzing the interaction between adipose tissue and cardiomyocytes: M. Anan, et al.; Endocrinology 152, 1599 (2011) | Hyperadiponectinemia protects against premature death in metabolic syndrome model mice by inhibiting AKT signaling and chronic inflammation: S. Otabe, et al.; J. Endocrinol. 213, 67 (2012) | Effects of Combining Linagliptin Treatment with BI-38335, A Novel SGLT2 Inhibitor, on Pancreatic Islet Function and Inflammation in db/db Mice: L. Chen, et al.; Curr. Mol. Med. 12, 995 (2012) | Chitooligosaccharide ameliorates diet-induced obesity in mice and affects adipose gene expression involved in adipogenesis and inflammation: E.H. Choi, et al.; Nutr. Res. 32, 218 (2012) | Anti-Hyperglycemic Effect of Fermented Ginseng in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Mouse Model: W.J. Jeon, et al.; Phytother. Res. 27, 166 (2013) | Anthocyanin increases adiponectin secretion and protects against diabetes-related endothelial dysfunction: Y. Liu, et al.; Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 306, E975 (2014) | Relation of circulating adiponectin level with epicardial adipose tissue thickness among overweight and obese indian patients: A cross sectional study: A.M. Chakraborty, et al.; Acta Sci. Med. Sci. 4, (2020) | Myeloid Cell?Specific IL-4 Receptor Knockout Partially Protects from Adipose Tissue Inflammation: J. Ackermann, et al.; J. Immunol. ahead of print (2021)
Related Products
| Product Name | Product Code | Supplier |
|---|