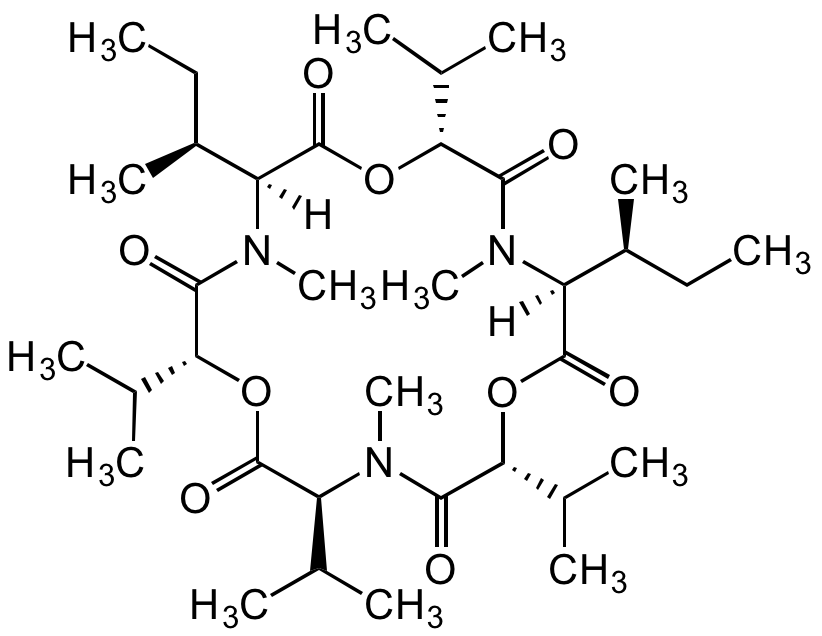
Enniatin A1
Product Code: AG-CN2-0478
Product Group: Natural Products and Extracts
Supplier: AdipoGen Life Sciences
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-CN2-0478-M001 | 1 mg | £280.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Storage:
Short Tem: +4°C Long Term: -20°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
2-(N-Methyl-L-valine) enniatin A
Appearance:
White to off-white solid.
CAS:
4530-21-6
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
solid
GHS Symbol:
GHS07
Handling Advice:
Keep cool and dry.Protect from light.
Hazards:
H302, H312, H332
InChi:
InChI=1S/C35H61N3O9/c1-16-22(11)25-34(43)46-27(19(5)6)30(39)36(13)24(18(3)4)33(42)45-28(20(7)8)31(40)37(14)26(23(12)17-2)35(44)47-29(21(9)10)32(41)38(25)15/h18-29H,16-17H2,1-15H3/t22-,23-,24-,25-,26-,27+,28+,29+/m0/s1
InChiKey:
OWUREPXBPJFMOK-CIRFPNLUSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 4530-21-6. Formula: C35H61N3O9. MW: 667.9. Isolated from fungus Fusarium sp. Cyclohexadepsipeptide mycotoxin. One of four major analogs in the enniatin complex. Commonly found food contaminant in cereals and their products. Ionophore antibiotic. Incorporation into the cell membrane forms dimeric structures that transport monovalent ions across the membrane (especially the mitochondrial membranes) affecting oxidative phosphorylation uncoupling. Anticancer compound. Triggers apoptosis in several cancer cell lines. Induced apoptosis in cancer cells (H4IIE rat hepatoma cells), decreasing the activation of the cell proliferation kinase, ERK (p44/p42) and inhibiting TNF-alpha-induced NF-kappaB activation. Moderate inhibitor of ACAT (acylcoenzyme A:cholesterolacyl transferase). Shown to have a variety of other biological activities such as antifungal, anthelmintic, insecticidal, immunomodulatory and phytotoxic activity.
MDL:
MFCD14635385
Molecular Formula:
C35H61N3O9
Molecular Weight:
667.9
Package Type:
Vial
Precautions:
P261, P280, P301, P312, P304, P340, P302, P352
Product Description:
Cyclohexadepsipeptide mycotoxin. One of four major analogs in the enniatin complex. Commonly found food contaminant in cereals and their products. Ionophore antibiotic. Incorporation into the cell membrane forms dimeric structures that transport monovalent ions across the membrane (especially the mitochondrial membranes) affecting oxidative phosphorylation uncoupling. Anticancer compound. Triggers apoptosis in several cancer cell lines. Induced apoptosis in cancer cells (H4IIE rat hepatoma cells), decreasing the activation of the cell proliferation kinase, ERK (p44/p42) and inhibiting TNF-alpha-induced NF-kappaB activation. Moderate inhibitor of ACAT (acylcoenzyme A:cholesterolacyl transferase). Shown to have a variety of other biological activities such as antifungal, anthelmintic, insecticidal, immunomodulatory and phytotoxic activity.
Purity:
>98% (HPLC)
Signal Word:
Warning
SMILES:
[H][C@@]1([C@@H](C)CC)N(C)C(=O)[C@H](OC(=O)[C@H](C(C)C)N(C)C(=O)[C@H](OC(=O)[C@]([H])([C@@H](C)CC)N(C)C(=O)[C@H](OC1=O)C(C)C)C(C)C)C(C)C
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO, ethanol, methanol or DMF. Almost insoluble in water.
Source / Host:
Isolated from fungus Fusarium sp.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Natural Products/Extracts
UNSPSC Number:
12352211
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
References
A comparison of beauvericin, enniatin and valinomycin as calcium transporting agents in liposomes and chromatophores: R.C. Prince, et al.; BBRC 59, 697 (1974) | Inhibition of acyl-CoA: Cholesterol acyltransferase activity by cyclodepsipeptide antibiotics: H. Tomoda, et al.; J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 45, 1626 (1992) | Investigation of the electrophysiological properties of enniatins: M. Kamyar, et al.; Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 429, 215 (2004) | Cytotoxicity of enniatins A, A1, B, B1, B2 and B3 from Fusarium avenaceum: L. Ivanova, et al.; Toxicon 47, 868 (2006) | Enniatin exerts p53-dependent cytostatic and p53-independent cytotoxic activities against human cancer cells: R. Dornetshuber, et al.; Chem. Res. Toxicol. 20, 465 (2007) | Emerging Fusarium-mycotoxins fusaproliferin, beauvericin, enniatins, and moniliformin - a review: M. Jestoi; Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 48, 21 (2008) | Oxidative stress and DNA interactions are not involved in Enniatin- and Beauvericin-mediated apoptosis induction: R. Dornetshuber, et al.; Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 53, 1112 (2009) | Enniatins A1, B and B1 from an endophytic strain of Fusarium tricinctum induce apoptotic cell death in H4IIE hepatoma cells accompanied by inhibition of ERK phosphorylation: W. Waetjen, et al.; Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 53, 431 (2009) | Toxigenicity of enniatins from Western Australian Fusarium species to brine shrimp (Artemia franciscana): D.C. Tan, et al.; Toxicon 57, 817 (2011) | Revisiting the enniatins: a review of their isolation, biosynthesis, structure determination and biological activities: A.A. Sy-Cordero, et al.; J. Antibiot. 65, 541 (2012) | Quantitative determination of the Fusarium mycotoxins beauvericin, enniatin A, A1, B and B1 in pig plasma using high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry: M. Devreese, et al.; Talanta 106, 212 (2013) | A preliminary study in Wistar rats with enniatin A contaminated feed: L. Manyes, et al.; Toxicol. Mech. Methods 24, 179 (2014) | Evaluation of immunologic effect of Enniatin A and quantitative determination in feces, urine and serum on treated Wistar rats: C. Juan, et al.; Toxicon 87, 45 (2014) | Enniatin A1, enniatin B1 and beauvericin on HepG2: Evaluation of toxic effects: A. Juan-Garcia, et al.; Food Chem. Toxicol. 84, 188 (2015)