CircuLex Mouse FABP5/E-FABP/mal1 ELISA Kit
Product Code:
MBL-CY-8056
MBL-CY-8056
Host Type:
Mouse
Mouse
Regulatory Status:
RUO
RUO
Application:
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
Shipping:
4°C
4°C
Storage:
4°C
4°C
No additional charges, what you see is what you pay! *
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| MBL-CY-8056 | 96 Assays | £602.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Stay in control of your spending. These prices have no additional charges, not even shipping!
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
Multibuy discounts available! Contact us to find what you can save.
This product comes from: United States.
Typical lead time: 10-14 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
Typical lead time: 10-14 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
- Further Information
- Documents
- References
- Show All
Further Information
Background:
Fatty acid-binding proteins (FABPs) are a class of cytoplasmic proteins that bind long chain fatty acids. FABPs are small intracellular proteins (~13-14 kDa) with a high degree of tissue specificity. They are abundantly present in various cell types and play an important role in the intracellular utilization of fatty acids, transport and metabolism. There are at least nine distinct types of FABP, each showing a specific pattern of tissue expression.
Human epidermal fatty acid binding protein (E-FABP, FABP5 and in mice called also mal1) belongs to the intracellular FABP family and is expressed in differentiated adipocytes, macrophages, skin, brain, mammary glands and so on. Mouse FABP5/E-FABP/mal1 has a high degree of homology to aP2 (mouse FABP4) and is also an important player in obesity-related disorders. FABP5/E-FABP/mal1 knockout mice exhibited enhanced insulin-stimulated glucose uptake and increased systemic insulin sensitivity, while transgenic overexpression of FABP5/E-FABP/mal1 aggravated insulin resistance and hyperglycaemia. Conversely, a marked compensatory up-regulation of adipocyte FABP5/E-FABP/mal1 expression was observed in FABP4/ aP2-deficient mice.
Description:
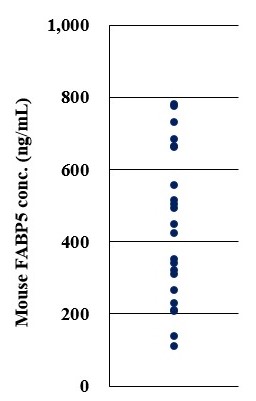
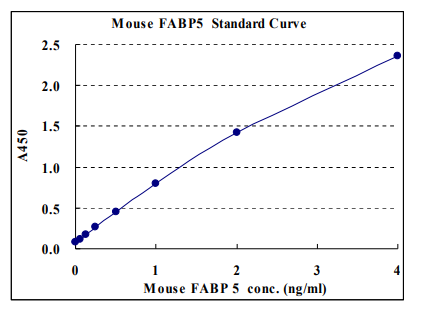
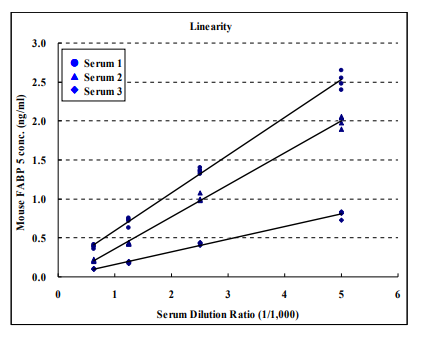
The CycLex Research Product CircuLex Mouse FABP5/E-FABP/mal1 ELISA kit is used for the quantitative measurement of mouse FABP5/E-FABP/mal1 in serum, plasma and other biological media.
Kit Components:
Microplate, 10X Wash Buffer, Dilution Buffer, Mouse FABP5/E-FABP/mal1 Standard, HRP conjugated Streptavidin, Biotinylated Detection Antibody, Substrate Reagent, Stop Solution
Sensitivity:
better than 6.91 pg/ml of sample.
Target:
FABP5/E-FABP/mal1
Documents
References
1. Furuhashi M. and Hotamisligil GS.; Fatty acid-binding proteins: role in metabolic diseases and potential as drug targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov., 7: 489, 2008
2. Chmurzynska A.; The multigene family of fatty acid-binding proteins (FABPs): function, structure and polymorphism. J Appl Genet., 47: 39-48, 2006
3. Storch J. and B Corsico B.; The emerging functions and mechanisms of mammalian fatty acid-binding proteins. Annu Rev Nutr., 28: 73-95, 2008
4. Krieg P, Feil S, Fu?rstenberger G, Bowden GT. Tumor-specific overexpression of a novel keratinocyte lipid-binding protein. Identification and characterization of a cloned sequence activated during multistage carcinogenesis in mouse skin. J Biol Chem., 268: 17362-17369, 1993
5. Siegenthaler C., Hotz R., Chatellard-Gruaz D., Didierjean L., Hellman and J H Saurat JH.; Purification and characterization of the human epidermal fatty acid-binding protein: localization during epidermal cell differentiation in vivo and in vitro. Biochem J., 302: 363, 1994
6. Maeda K, Uysal KT, Makowski L, Go?rgu?n CZ, Atsumi G, Parker RA, Bru?ning J, Hertzel AV, Bernlohr DA, Hotamisligil GS. Role of the fatty acid binding protein mal1 in obesity and insulin resistance. Diabetes, 52: 300-307, 2003
7. Hotamisligil GS, Johnson RS, Distel RJ, Ellis R, Papaioannou VE, Spiegelman BM. Uncoupling of obesity from insulin resistance through a targeted mutation in aP2, the adipocyte fatty acid bindingprotein. Science, 274: 1377-1379, 1996
8. Scheja L, Malowski L, Uysal KT, Wiesbrock SM, Shimshek DR, Meyers DS, Morgun M, Parker RA, Hotamisligil GS. Altered insulin secretion associated with reduced lipolytic efficiency in aP22/2 mice. Diabetes, 48: 1987-1994, 1999
9. Shaughnessy S, Smith ER, Kodukula S, Storch J, Fried SK. Adipocyte metabolism in adipocyte fatty acid binding protein knockout (aP22/2) mice after short-term high-fat feeding. Functional compensation by the keratinocyte fatty acid binding protein. Diabetes, 49: 904-911, 2000