Nampt (Visfatin/PBEF) (mouse) (rec.) (His)
Product Code:
AG-40A-0017
AG-40A-0017
Host Type:
E.coli
E.coli
Regulatory Status:
RUO
RUO
Target Species:
Mouse
Mouse
Shipping:
Blue Ice
Blue Ice
Storage:
-20°C
-20°C
No additional charges, what you see is what you pay! *
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-40A-0017-C050 | 50 ug | £330.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Stay in control of your spending. These prices have no additional charges, not even shipping!
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
Multibuy discounts available! Contact us to find what you can save.
This product comes from: Switzerland.
Typical lead time: 7-10 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
Typical lead time: 7-10 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
- Further Information
- Documents
- References
- Show All
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
Pre-B Cell Colony Enhancing Factor 1; PBEF1; Nicotinamide Phosphoribosyltransferase
Biological Activity:
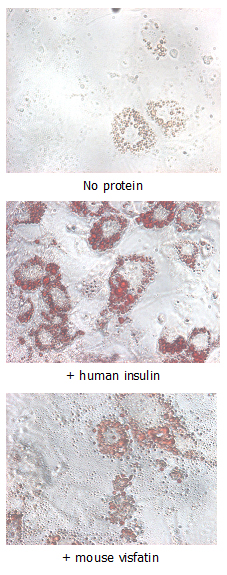
Shows adipogenic effects in stimulated differentiating 3T3-L1 cells.
EClass:
32160000
Endotoxin:
<1EU/µg purified protein (LAL test; Lonza).
Form (Short):
solid
Formulation:
Lyophilized from 0.2µm-filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.2.
Handling Advice:
After reconstitution, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C.Avoid freeze/thaw cycles.Centrifuge lyophilized vial before opening and reconstitution.PBS containing at least 0.1% BSA should be used for further dilutions.
Long Description:
Protein. Mouse Nampt (visfatin/PBEF) (aa 1-491) is fused at the C-terminus to a His-tag. Source: E. coli. Endotoxin content: <1EU/µg purified protein (LAL test; Lonza). Lyophilized from 0.2µm-filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.2. Purity: >90% (SDS-PAGE). Nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (Nampt; pre-B cell colony-enhancing factor; PBEF; Visfatin) is an adipokine that is localized to the bloodstream and has various functions, including the promotion of vascular smooth muscle cell maturation and inhibition of neutrophil apoptosis. It activates insulin receptor and has insulin-mimetic effects, lowering blood glucose and improving insulin sensitivity. The protein is highly expressed in visceral fat and serum levels of the protein correlate with obesity.
Molecular Weight:
~52kDa (SDS-PAGE)
NCBI, Uniprot Number:
Q99KQ4
Package Type:
Plastic Vial
Product Description:
Nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (Nampt; pre-B cell colony-enhancing factor; PBEF; Visfatin) is an adipokine that is localized to the bloodstream and has various functions, including the promotion of vascular smooth muscle cell maturation and inhibition of neutrophil apoptosis. It activates insulin receptor and has insulin-mimetic effects, lowering blood glucose and improving insulin sensitivity. The protein is highly expressed in visceral fat and serum levels of the protein correlate with obesity. Recently NAMPT extracellular (eNAMPT) has been shown to be secreted from macrophages in muscles and to triggers a proliferative signal of muscle stem cell (MusC) by binding to CCR5 located at the surface receptor of MusC.
Purity:
>90% (SDS-PAGE)
Sequence:
Mouse Nampt (visfatin/PBEF) (aa 1-491) is fused at the C-terminus to a His-tag.
Source / Host:
E. coli
TAGs:
His
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Other Proteins
UNSPSC Number:
12352202
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 6 months after receipt when stored at -20°C. Working aliquots are stable for up to 3 months when stored at -20°C.
Documents
References
Visfatin regulates insulin secretion, insulin receptor signalling and mRNA expression of diabetes-related genes in mouse pancreatic beta-cells: J.E. Brown, et al.; J. Mol. Endocrinol. 44, 171 (2010)