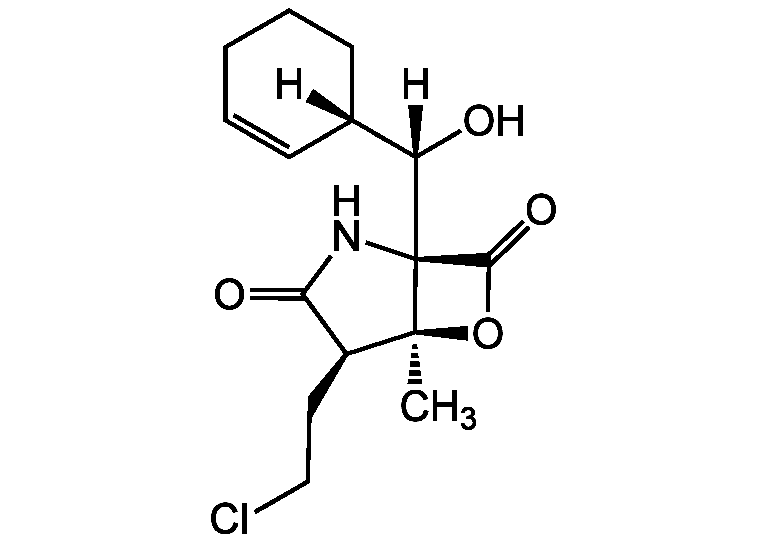
Salinosporamide A
Product Code: AG-CN2-0444
Product Group: Natural Products and Extracts
Supplier: AdipoGen Life Sciences
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-CN2-0444-M050 | 50 mg | Enquire |
Quantity:
| AG-CN2-0444-C100 | 100 ug | £125.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CN2-0444-M001 | 1 mg | £550.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CN2-0444-M005 | 5 mg | £1,810.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
Blue Ice
Storage:
+4°C
Images
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
SalA; Marizomib; NPI-0052
Appearance:
White solid.
CAS:
437742-34-2
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
GHS Symbol:
GHS07
Handling Advice:
Keep under inert gas.Protect from light.Protect from moisture and oxygen.
Hazards:
H302
InChi:
InChI=1S/C15H20ClNO4/c1-14-10(7-8-16)12(19)17-15(14,13(20)21-14)11(18)9-5-3-2-4-6-9/h3,5,9-11,18H,2,4,6-8H2,1H3,(H,17,19)/t9-,10+,11+,14+,15+/m1/s1
InChiKey:
NGWSFRIPKNWYAO-SHTIJGAHSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 437742-34-2. Formula: C15H20ClNO4. MW: 313.8. Isolated from Salinospora tropica. Potent, irreversible inhibitor of all the 3 proteolytic activities of the mammalian 20S proteasome. beta5 subunit: chymotrypsin-like (EC50 = 3.5nM) beta2 subunit: trypsin-like (EC50 = 28nM) beta1 subunit: caspase-like or peptidyl-glutamyl peptide-hydrolyzing (PGPH) (EC50 = 430nM) Potent anticancer compound. Triggers apoptosis, with distinct proteasome activity and mechanism of action compared to bortezomib (Velcade) (Prod. No. AG-CR1-3602). Most potent suppressor of NF-kappaB activation, compared with bortezomib, MG-132 (Prod. No. AG-CP3-0011), N-acetyl-leucyl-leucyl-norleucinal (ALLN) and lactacystin (Prod. No. AG-CN2-0104). Inhibitor of TNF-alpha, IL-1, IL-6, ICAM-1 and VEGF synthesis. Displays a longer inhibition duration than bortezomib. Potent antileukemic activity against bortezomib-resistant leukemia cells.
MDL:
MFCD16037703
Molecular Formula:
C15H20ClNO4
Molecular Weight:
313.8
Other data:
Note: We recommend to use fresh solutions. Aliquots should be prepared in DMSO and stored at -20°C.
Package Type:
Vial
Precautions:
P270, P301, P312, P330
Product Description:
Potent, irreversible inhibitor of all the 3 proteolytic activities of the mammalian 20S proteasome. beta5 subunit: chymotrypsin-like (EC50 = 3.5nM) beta2 subunit: trypsin-like (EC50 = 28nM) beta1 subunit: caspase-like or peptidyl-glutamyl peptide-hydrolyzing (PGPH) (EC50 = 430nM) Potent anticancer compound. Triggers apoptosis, with distinct proteasome activity and mechanism of action compared to bortezomib (Velcade) (Prod. No. AG-CR1-3602). Most potent suppressor of NF-kappaB activation, compared with bortezomib, MG-132 (Prod. No. AG-CP3-0011), N-acetyl-leucyl-leucyl-norleucinal (ALLN) and lactacystin (Prod. No. AG-CN2-0104). Inhibitor of TNF-alpha, IL-1, IL-6, ICAM-1 and VEGF synthesis. Displays a longer inhibition duration than bortezomib. Potent antileukemic activity against bortezomib-resistant leukemia cells.
Purity:
>95% (HPLC)
Signal word:
Warning
SMILES:
[H][C@](O)([C@@]1([H])CCCC=C1)[C@@]12NC(=O)[C@H](CCCl)[C@]1(C)OC2=O
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO. Do not dissolve in methanol or ethanol.
Source / Host:
Isolated from Salinospora tropica.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Natural Products/Extracts
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at -20°C.
References
Salinosporamide A: a highly cytotoxic proteasome inhibitor from a novel microbial source, a marine bacterium of the new genus salinospora: R.H. Feling, et al.; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 42, 355 (2003) | Structure-activity relationship studies of salinosporamide A (NPI-0052), a novel marine derived proteasome inhibitor: V.R. Macherla, et al.; J. Med. Chem. 48, 3684 (2005) | A novel orally active proteasome inhibitor induces apoptosis in multiple myeloma cells with mechanisms distinct from Bortezomib: D. Chauhan, et al.; Cancer Cell 8, 407 (2005) | Crystal structures of Salinosporamide A (NPI-0052) and B (NPI-0047) in complex with the 20S proteasome reveal important consequences of beta-lactone ring opening and a mechanism for irreversible binding: M. Groll, et al.; JACS 128, 5136 (2006) | NPI-0052 enhances tumoricidal response to conventional cancer therapy in a colon cancer model: J.C. Cusack, et al.; Clin. Cancer Res. 12, 6758 (2006) | Comparison of biochemical and biological effects of ML858 (salinosporamide A) and bortezomib: M.J. Williamson, et al.; Mol. Cancer Ther. 5, 3052 (2006) | Salinosporamide A (NPI-0052) potentiates apoptosis, suppresses osteoclastogenesis, and inhibits invasion through down-modulation of NF-kappaB-regulated gene products: K.S. Ahn, et al.; Blood 110, 2286 (2007) | A mechanistic and kinetic study of the beta-lactone hydrolysis of Salinosporamide A (NPI-0052), a novel proteasome inhibitor: N. Denora, et al.; J. Pharm. Sci. 96, 2037 (2007) | Combination of proteasome inhibitors bortezomib and NPI-0052 trigger in vivo synergistic cytotoxicity in multiple myeloma: D. Chauhan, et al.; Blood 111, 1654 (2008) | Discovery and development of the anticancer agent salinosporamide A (NPI-0052): W. Fenical, et al.; Bioorg. Med. Chem. 17, 2175 (2009) | Generating a generation of proteasome inhibitors: from microbial fermentation to total synthesis of salinosporamide a (marizomib) and other salinosporamides: B.C. Potts & K.S. Lam; Mar. Drugs 8, 835 (2010) (Review) | Salinosporamide natural products: Potent 20S proteasome inhibitors as promising cancer chemotherapeutics: T.A. Gulder & B.S. Moore; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 49, 9346 (2010) (Review) | Marizomib, a proteasome inhibitor for all seasons: preclinical profile and a framework for clinical trials: B.C. Potts, et al.; Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 11, 254 (2011) | Proteasome regulator marizomib (NPI-0052) exhibits prolonged inhibition, attenuated efflux, and greater cytotoxicity than its reversible analogs: A. Obaidat, et al.; J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 337, 479 (2011) | Molecular mechanisms of acquired proteasome inhibitor resistance: A.J. Kale & B.S. Moore; J. Med. Chem. 55, 10317 (2012) | Antileukemic activity and mechanism of drug resistance to the marine Salinispora tropica proteasome inhibitor salinosporamide A (Marizomib): D. Niewerth, et al.; Mol. Pharmacol. 86, 12 (2014) | NPI-0052 and gamma-radiation induce a synergistic apoptotic effect in medulloblastoma: E. Frisira, et al.; Cell Death Dis. 10, 785 (2019)