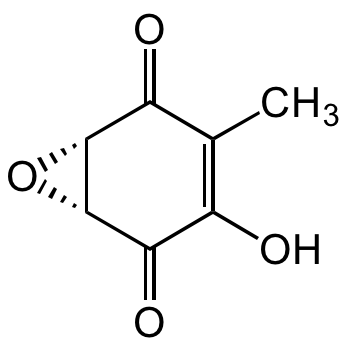
Terreic acid
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| BVT-0477-M001 | 1 mg | £70.00 |
Quantity:
| BVT-0477-M005 | 5 mg | £205.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Storage:
+4°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
TA; (1R,6S)-3-hydroxy-4-methyl-7-oxabicyclo[4.1.0]hept- 3-ene-2,5-dione; (-)-Terreic acid
Appearance:
White to off-white solid.
CAS:
121-40-4
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
GHS Symbol:
GHS07
Handling Advice:
Protect from light.
Hazards:
H302, H312
InChi:
InChI=1S/C7H6O4/c1-2-3(8)5(10)7-6(11-7)4(2)9/h6-8H,1H3/t6-,7+/m1/s1
InChiKey:
ATFNSNUJZOYXFC-RQJHMYQMSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 121-40-4. Formula: C7H6O4. MW: 154.1. Isolated from Aspergillus terreus.. Mycotoxin. Antibacterial and anticancer agent. A cell-permeable quinone epoxide antibiotic. Covalent inhibitor of the bacterial enzyme UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 1-carboxyvinyltransferase (MurA), which catalyzes the first committed step of bacterial cell wall biosynthesis. More potent than the known MurA inhibitor Fosphomycin. Reversible, substrate competitive and selective inhibitor of Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) catalytic activity, an important factor in B-cell and mast cell activation. Shown to bind to the BTK pleckstrin homology domain (BTK-PH) and block the interaction between the BTK-PH and PKC, affecting the catalytic activity of BTK but not of PKC. Has minimal effect on Lyn, Syk, PKA, casein kinase I, ERK1, ERK2, and p38 kinase activities. Antioxidant.
MDL:
MFCD01710762
Molecular Formula:
C7H6O4
Molecular Weight:
154.1
Package Type:
Plastic Vial
Precautions:
P280, P301+312, P302+352
Product Description:
Mycotoxin. Antibacterial and anticancer agent. A cell-permeable quinone epoxide antibiotic. Covalent inhibitor of the bacterial enzyme UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 1-carboxyvinyltransferase (MurA), which catalyzes the first committed step of bacterial cell wall biosynthesis. More potent than the known MurA inhibitor Fosphomycin. Reversible, substrate competitive and selective inhibitor of Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) catalytic activity, an important factor in B-cell and mast cell activation. Shown to bind to the BTK pleckstrin homology domain (BTK-PH) and block the interaction between the BTK-PH and PKC, affecting the catalytic activity of BTK but not of PKC. Has minimal effect on Lyn, Syk, PKA, casein kinase I, ERK1, ERK2, and p38 kinase activities. Antioxidant.
Purity:
>99% (HPLC)
Signal word:
Warning
SMILES:
O=C([C@@H]1[C@H]2O1)C(C)=C(O)C2=O
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO (10mg/ml), EtOH, MeOH, acetone, DCM or water (1mg/ml, warming and sonication might be necessary).
Source / Host:
Isolated from Aspergillus terreus.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Natural Products/Extracts
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at -20°C. Store solutions at -20°C in the dark.
References
Structure of terreic acid: J.C. Sheehan, et al.; JACS 80, 5536 (1958) | Studies on terreic acid: H. Yamamoto, et al.; J. Antibiot. 33, 320 (1980) | In vivo and in vitro studies on the binding nature of terreic acid with macromolecules such as protein and nucleic acids: T. Subramanian, et al.; Toxicol. Lett. 10, 249 (1982) | Terreic acid - a diabetogenic mycotoxin in rats: E.R.B. Shanmugasundaram, et al.; Curr. Sci. 53, 1290 (1984) | Terreic acid, a quinone epoxide inhibitor of Bruton's tyrosine kinase: Y. Kawakami, et al.; PNAS 96, 2227 (1999) | Regulation of protein kinase CbetaI by two protein-tyrosine kinases, Btk and Syk: Y. Kawakami, et al.; PNAS 97, 7423 (2000) | Modulation of the Fcepsilon receptor I signaling by tyrosine kinase inhibitors: search for therapeutic targets of inflammatory and allergy diseases: P. Luskova & P. Draber; Curr. Pharm. Des. 10, 1727 (2004) | The Fungal Product Terreic Acid Is a Covalent Inhibitor of the Bacterial Cell Wall Biosynthetic Enzyme UDP-N-Acetylglucosamine 1-Carboxyvinyltransferase (MurA): H. Han, et al.; Biochemistry 49, 4276 (2010) | Isolation of antioxidant compounds from Aspergillus terreus LS01: R.T. Dewi, et al.; J. Microb. Biochem. Techno. 4, 10 (2012) | Differential antibacterial properties of the MurA inhibitors terreic acid and fosfomycin: S. Olesen, et al.; J. Basic Microbiol. 54, 322 (2014) | Molecular Genetic Characterization of Terreic Acid Pathway in Aspergillus terreus: C.-J. Guo, et al.; Org. Lett. 16, 5250 (2014) | Escherichia coli N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphate-uridyltransferase/ glucosamine-1-phosphateacetyltransferase (GlmU) inhibitory activity of terreic acid isolated from Aspergillus terreus: R. Sharma, et al.; J. Biomol. Screen. 21, 342 (2016) | Heterologous pathway assembly reveals molecular steps of fungal terreic acid biosynthesis: C. Kong, et al.; Sci. Rep. 8, 1 (2018)