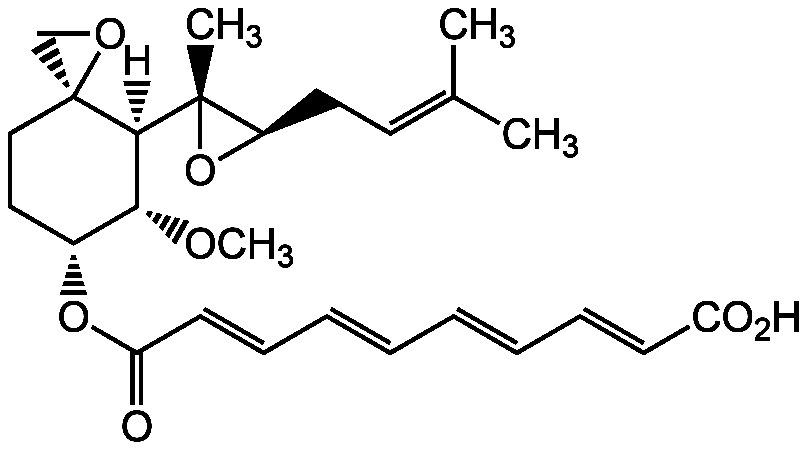
Fumagillin
Product Code: AG-CN2-0529
Product Group: Natural Products and Extracts
Supplier: AdipoGen Life Sciences
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-CN2-0529-M001 | 1 mg | £55.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CN2-0529-M005 | 5 mg | £140.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CN2-0529-M025 | 25 mg | £340.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Storage:
-20°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
Amebacilin; Fugilin; Fumidil; Fumadil B; NSC9168; U5762
Appearance:
Off-white solid.
CAS:
23110-15-8
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
GHS Symbol:
GHS07
Handling Advice:
Protect from light.
Hazards:
H302, H312, H319
InChi:
InChI=1S/C26H34O7/c1-18(2)13-14-20-25(3,33-20)24-23(30-4)19(15-16-26(24)17-31-26)32-22(29)12-10-8-6-5-7-9-11-21(27)28/h5-13,19-20,23-24H,14-17H2,1-4H3,(H,27,28)/b7-5+,8-6+,11-9+,12-10+/t19-,20-,23?,24-,25+,26+/m1/s1
InChiKey:
NGGMYCMLYOUNGM-IWMBURASSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 23110-15-8. Formula: C26H34O7. MW: 458.6. Isolated from Aspergillus fumigatus. Meroterpenoid antibiotic. Anticancer, antimicrobial, antimalarial and amoebicidal compound. Potent, selective and covalent inhibitor of methionine aminopeptidase-2 (MetAP2). Anti-angiogenic by impairing the growth of endothelial cells and altering gene expression. Inhibits endothelial cell proliferation in vitro and tumor-induced angiogenesis in vivo. Suppresses the HIV-1 infection of human macrophages through the inhibition of HIV-1 viral protein R (Vpr) activity. Inhibits neovascularization and might be useful in non-tumor diseases such as diabetic retinopathy, arthritis and psoriasis, which involve neovascularisation processes. Reduces diet-induced adipose tissue formation in mice, independent of its effects on angiogenesis.
MDL:
MFCD03990453
Molecular Formula:
C26H34O7
Molecular Weight:
458.6
Package Type:
Plastic Vial
Precautions:
P270, P280, P301, P312, P302, P352, P312
Product Description:
Meroterpenoid antibiotic. Anticancer, antimicrobial, antimalarial and amoebicidal compound. Potent, selective and covalent inhibitor of methionine aminopeptidase-2 (MetAP2). Anti-angiogenic by impairing the growth of endothelial cells and altering gene expression. Inhibits endothelial cell proliferation in vitro and tumor-induced angiogenesis in vivo. Suppresses the HIV-1 infection of human macrophages through the inhibition of HIV-1 viral protein R (Vpr) activity. Inhibits neovascularization and might be useful in non-tumor diseases such as diabetic retinopathy, arthritis and psoriasis, which involve neovascularisation processes. Reduces diet-induced adipose tissue formation in mice, independent of its effects on angiogenesis.
Purity:
>98% (1H-NMR)
Signal word:
Warning
SMILES:
[H][C@@]1([C@H](OC)[C@@H](CC[C@]11CO1)OC(=O)C=CC=CC=CC=CC(O)=O)[C@@]1(C)O[C@@H]1CC=C(C)C
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO, acetone or chloroform. Slightly soluble in methanol (5mg/ml) or ethanol. Insoluble in water.
Source / Host:
Isolated from Aspergillus fumigatus.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Natural Products/Extracts
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. Store solutions at -20°C in the dark.
References
Antibiotic substance produced by Aspergillus fumigatus: T.E. Eble, et al.; Antibiot. Chemother. 1, 54 (1951) | Synthetic analogues of fumagillin that inhibit angiogenesis and suppress tumour growth: D. Ingber, et al.; Nature 348, 555 (1990) | The anti-angiogenic agent fumagillin covalently binds and inhibits the methionine aminopeptidase, MetAP-2: N. Sin, et al.; PNAS 94, 6099 (1997) | Inhibition of Angiogenesis In Vivo by ets-1 Antisense Oligonucleotides-Inhibition of Ets-1 Transcription Factor Expression by the Antibiotic Fumagillin: N. Wernert, et al.; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 38, 3228 (1999) | Structure elucidation of fumagillin-related natural products: J. Halasz, et al.; Tetrahedron 56, 10081 (2000) | A re-evaluation of fumagillin selectivity towards endothelial cells: S. Rodriguez-Nieto, et al.; Anticancer Res. 21, 3457 (2001) | Fumagillin treatment of intestinal microsporidiosis: J. Molina, et al.; N. Engl. J. Med. 346, 1963 (2002) | Early genetic mechanisms underlying the inhibitory effects of endostatin and fumagillin on human endothelial cells: C.M. Mazzanti, et al.; Genome Res. 14, 1585 (2004) | Fumagillin suppresses HIV-1 infection of macrophages through the inhibition of Vpr activity: N. Watanabe, et al.; FEBS Lett. 580, 2598 (2006) | Fumagillin: an anti-infective as a parent molecule for novel angiogenesis inhibitors: B. Lefkove, et al.; Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 5, 573 (2007) | Fumagillin and fumarranol interact with P. falciparum methionine aminopeptidase 2 and inhibit malaria parasite growth in vitro and in vivo: X. Chen, et al.; Chem. Biol. 16, 193 (2009) | Fumagillin inhibits colorectal cancer growth and metastasis in mice: in vivo and in vitro study of anti-angiogenesis: L. Hou, et al.; Pathol. Int. 59, 448 (2009) | Syntheses of fumagillin and ovalicin: J. Yamaguchi & Y. Hayashi; Chem. Eur. J. 16, 3884 (2010) | Fumagillin reduces adipose tissue formation in murine models of nutritionally induced obesity: H.R. Lijnen, et al.; Obesity 18, 2241 (2010) | Inhibition of neutrophil function following exposure to the Aspergillus fumigatus toxin fumagillin: J.P. Fallon, et al.; J. Med. Microbiol. 59, 625 (2010) | Fumagillin and structurally related molecules as source of new drugs: D. Gamba-Sanches; Mini-Rev. Org. Chem. 9, 126 (2012) | Stimulation of suicidal erythrocyte death by fumagillin: M. Zbidah, et al.; Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 112, 346 (2013)