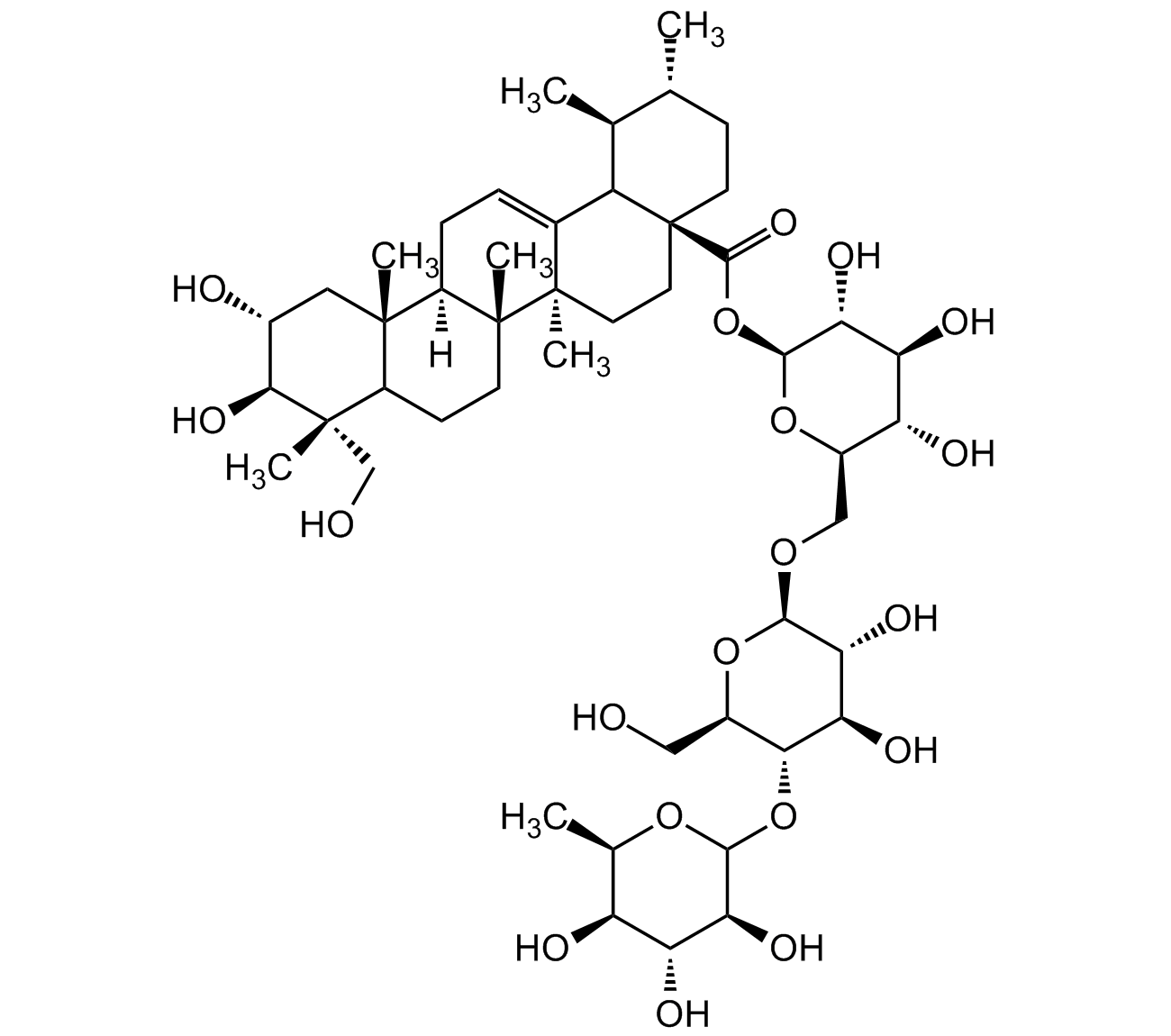
Asiaticoside
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| CDX-A0575-M025 | 25 mg | £145.00 |
Quantity:
| CDX-A0575-M100 | 100 mg | £413.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Host Type: Plant
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
AMBIENT
Storage:
+4°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
Blastostimulina; Centelase; Emdecassol; Madecassol; Marticassol; FK1080; BRN 0078195; NSC 166062
Appearance:
White creamy powder.
CAS:
16830-15-2
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
Handling Advice:
Protect from light and moisture.
InChi:
InChI=1S/C48H78O19/c1-20-10-13-48(15-14-46(6)23(29(48)21(20)2)8-9-28-44(4)16-24(51)39(60)45(5,19-50)27(44)11-12-47(28,46)7)43(61)67-42-36(58)33(55)31(53)26(65-42)18-62-40-37(59)34(56)38(25(17-49)64-40)66-41-35(57)32(54)30(52)22(3)63-41/h8,20-22,24-42,49-60H,9-19H2,1-7H3/t20-,21+,22-,24-,25-,26-,27?,28-,29?,30+,31-,32-,33+,34-,35+,36-,37-,38-,39+,40-,41?,42+,44+,45+,46-,47-,48+/m1/s1
InChiKey:
WYQVAPGDARQUBT-NXDSUYQXSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 16830-15-2. Formula: C48H78O19. MW: 959.133. Asiaticoside is the main saponin constituent of C. asiatica, a plant long used in the Ayurvedic system of medicine to treat dermatitis, diabetes, cough, cataract, hypertension, as well as for wound healing and improving memory. It is a human collagen I synthesis inducer with anti-wrinkle activity. It shows wound healing activity, enhancing normal human skin cell migration, attachment and growth. Asiaticoside is an anti-inflammatory compound that inibits MAPKs, NF-kappa, COX-2 and iNOS expression, and production of TNF-alpha and IL-6. Also shown to induce apoptosis and autophagy in cancer cells. Described to have also antibacterial, antioxidant, anxiolytic, antidepressant-like, hepatoprotective, neuroprotective and antileishmanial activity.
MDL:
MFCD06642601
Molecular Formula:
C48H78O19
Molecular Weight:
959.133
Package Type:
Vial
Product Description:
Asiaticoside is the main saponin constituent of C. asiatica, a plant long used in the Ayurvedic system of medicine to treat dermatitis, diabetes, cough, cataract, hypertension, as well as for wound healing and improving memory. It is a human collagen I synthesis inducer with anti-wrinkle activity. It shows wound healing activity, enhancing normal human skin cell migration, attachment and growth. Asiaticoside is an anti-inflammatory compound that inibits MAPKs, NF-kappa, COX-2 and iNOS expression, and production of TNF-alpha and IL-6. Also shown to induce apoptosis and autophagy in cancer cells. Described to have also antibacterial, antioxidant, anxiolytic, antidepressant-like, hepatoprotective, neuroprotective and antileishmanial activity.
Purity:
>95% (NMR)
SMILES:
O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@](C)(CO)C(CC[C@]2(C)[C@]3([H])CC=C4[C@@]2(C)CC[C@]5(C(O[C@@H]6O[C@H](CO[C@@H]7O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](OC8O[C@H](C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]8O)[C@H](O)[C@H]7O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]6O)=O)C4[C@@H](C)[C@H](C)CC5)[C@]3(C)C1
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO or ethanol. Slightly soluble in methanol.
Source / Host:
Plant
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Natural Products/Extracts
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at +4°C.
References
(1) A. Shukla, et al.; J. Ethnopharmacol. 65, 1 (1999) | (2) J.H. Sampson, et al.; Phytomedicine 8, 230 (2001) | (3) J.S. Guo, et al.; Planta Med. 70, 1150 (2004) | (4) J.S. Ryu, et al.; Skin Res. Technol. 11, 157 (2005) | (5) S.W. Chen, et al.; Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 85, 339 (2006) | (6) X. Liang, et al.; Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 89, 444 (2008) | (7) C.L. Xu, et al.; Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 100, 413 (2012) | (8) S.K. Bhaumik, et al.; J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 67, 910 (2012) | (9) J.H. Lee, et al.; Phytomedicine 19, 1223 (2012) | (10) J. Wan, et al.; Phytother. Res. 27, 1136 (2013) | (11) F.Y. Qi, et al.; Neural. Regen. Res. 9, 1275 (2014) | (12) Y. Luo, et al.; Mol. Med. Rep. 12, 8294 (2015) | (13) Q. Hou, et al.; Exp. Ther. Med. 12, 1269 (2016) | (14) X. Wang, et al.; Mol. Med. Rep. 17, 2893 (2018) | (15) L. Jing, et al.; Cytotechnology 70, 855 (2018) | (16) L. Yingchun, et al.; Med. Sci. Monit. 25, 1355 (2019)