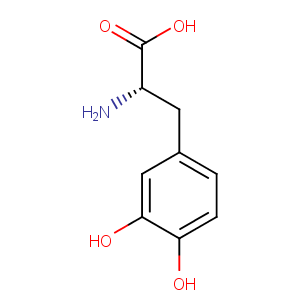
L-DOPA
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| TAR-T0848-200mg | 200mg | £111.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special offer! Add £1 to your order to get a TargetMol CCK-8 Kit. Read more here. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
cool pack
Storage:
-20℃
Images
Documents
Further Information
Bioactivity:
Levodopa is an amino acid precursor of dopamine with antiparkinsonian properties. Levodopa is a prodrug that is converted to dopamine by DOPA decarboxylase and can cross the blood-brain barrier. When in the brain, levodopa is decarboxylated to dopamine and stimulates the dopaminergic receptors, thereby compensating for the depleted supply of endogenous dopamine seen in Parkinson's disease. To assure that adequate concentrations of levodopa reach the central nervous system, it is administered with carbidopa, a decarboxylase inhibitor that does not cross the blood-brain barrier, thereby diminishing the decarboxylation and inactivation of levodopa in peripheral tissues and increasing the delivery of dopamine to the CNS.
CAS:
59-92-7
Formula:
C9H11NO4
Molecular Weight:
197.19
Pathway:
GPCR/G Protein; Metabolism; Neuroscience
Purity:
0.9999
SMILES:
N[C@@H](Cc1ccc(O)c(O)c1)C(O)=O
Target:
Dopamine Receptor; Endogenous Metabolite
References
1. Mena MA, et al. Neuroreport, 1993, 4(4), 438-440.
2. Garcia-Effron G, et al. J Antimicrob Chemother, 2004, 53(6), 1086-1089.
3. Bordet R, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 1997, 94(7), 3363-3367.
4. Ferrer B, et al. Eur J Neurosci, 2003, 18(6), 1607-1614.
5. Murer MG, et al. Ann Neurol, 1998, 43(5), 561-575.
6. Perez-Pardo P, et al. Additive Effects of Levodopa and a Neurorestorative Diet in a Mouse Model of Parkinson's Disease. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018 Aug 3;10:237.