MEBSTAIN Apoptosis TUNEL Kit Direct
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| MBL-8445 | FCM:66 Tests, Stain: 40 Tests | £535.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
4°C
Storage:
-20°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Background:
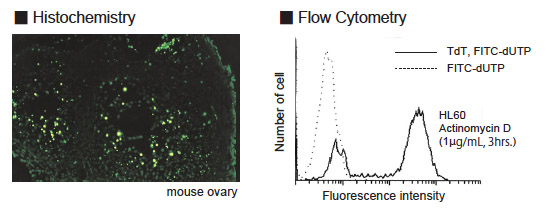
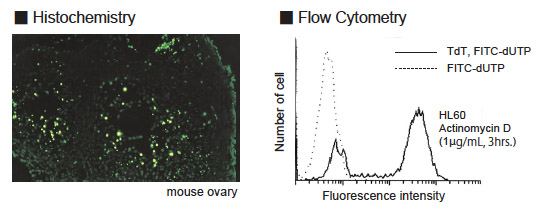
Programmed cell death is a selective process of physiological cell deletion. It plays a major role in developmental biology and in maintenance of homeostasis in vertebrates (1-4). For example, during maturation, T cells recognizing self antigens are destroyed by programmed cell death (5). Programmed cell death is morphologically known as apoptosis. Apoptosis is accompanied by condensation of cytoplasm, loss of plasma membrane microvilli, condensation and fragmentation of nuclei, and extensive degradation of chromosomal DNA into oligomers of about 180 bp. Fragmentation of nuclear DNA is a biochemical hallmark of apoptosis. The TdT-mediated dUTP-biotin nick end labeling method (TUNEL method) developed by Gavrieli et al (6) has enabled in situ visualization of DNA fragmentation at the single cell level and is a more sensitive method than conventional morphological techniques(7). The MEBSTAIN Apoptosis Kit Direct is an apoptosis detection kit based on the TUNEL method. The main advantage of this rapid and simple procedure is the use of fluorescein-dUTP to label DNA strand breaks. This allows the direct detection of DNA fragmentation.
Description:
In cells in which apoptosis occurs, the chromatin DNA is cut by endonuclease at linker DNA site between nucleosomes. Then, DNA fragments, which are a number of multimers of nucleosomal units exit in nuclei. In TUNEL method, 3?-OH DNA ends generated by DNA fragmentation is nick end labeled with fluorescein-dUTP, mediated by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT). This method allows specific staining.
Kit Components:
Proteinase K (PK), TdT, TdT buffer II, FITC-dUTP, TB buffer
Target:
Apoptosis
References
Dinnen RD, et al., J Biol Chem, 282, 26675 (2007)
Goga Y, et al., J Dent Res, 85, 240 (2006)
Negoro S, et al., Circulation, 103, 555 (2001)
Numata K, et al., J Immunol, 178, 3777 (2007)
Pati D, et al., Mol Cell Biol, 22, 8267 (2002)
Sanematsu F, J Biol Chem, 281, 13817 (2006)
Vaccari S, et al., J Endocrinol, 191, 287 (2006)
Yano T, et al., Mol Cell Biol, 26, 4474 (2006)
Yoshikawa R, et al., Cancer Res, 61, 1029 (2001)