CycLex Polo-like kinase 1 Assay/Inhibitor Screening Kit
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| MBL-CY-1163 | 96 Assays | £602.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
4°C
Storage:
4°C. Please refer to datasheet for additional information
Images
Documents
Further Information
Applications:
Other - 1) Screening inhibitors or activators of Plk1.
2) Detecting the effects of pharmacological agents on Plk1 activity.
Background:
Polo-like kinases (Plk) have been shown to be important contributors to several cell-cycle events (1,2).
Genetic and biochemical experiments in various organisms indicate that polo-like kinases regulate
diverse cellular events at multiple mitotic stages. Genetic studies in Drosophila and yeast indicate Plks
function in centrosome assembly and separation during the formation of the bipolar spindle. Drosophila
polo mutants reveal phenotypes of hyper-condensed chromosomes, monopolar spindles, disorganized
spindle poles, and abnormal chromosome segregation (3). Schizosaccharomyces pombe plo1 displays
similar phenotypes, such as the formation of monopolar spindles or a failure in septum formation after
nuclear division (4). The budding yeast polo-like kinase homolog, Cdc5, seems to play an important role
in actin ring formation and cytokinesis (5). In mammalian cells, antibody microinjection suggests a role
for Plk1 in centrosome maturation (6). Mammalian Plk1 was further shown to phosphorylate specifically
at least three components of APC, and to activate APC to ubiquitinate cyclin B using an in
vitro-reconstituted system (7). More recent studies demonstrated that polo kinase activity plays a pivotal
role in the separation of sister chromatids during mitosis (8).
Elevated expression of Plk1 occurs in many different types of cancer, and Plk1 has been proposed as a
diagnostic marker for several tumors. Liu and Erikson (9) used the vector-based small interfering RNA
(siRNA) technique to specifically deplete Plk1 in cancer cells. They found that such depletion
dramatically inhibited cell proliferation, decreased viability, and resulted in cell-cycle arrest with a 4 N
DNA content. The formation of a dumbbell-like chromatin structure suggested the inability of these cells
to completely separate the sister chromatids at the onset of anaphase. Plk1 depletion induced apoptosis,
as indicated by the appearance of sub-genomic DNA in FACS profiles, the activation of caspase-3, and
the formation of fragmented nuclei. The p53 pathway was shown to be involved in Plk1
depletion-induced apoptosis. DNA damage occurred in Plk1-depleted cells and inhibition of ATM
strongly potentiated the lethality of Plk1 depletion. The data supported the notion that disruption of Plk1
function could be an important application in cancer therapy.
Description:
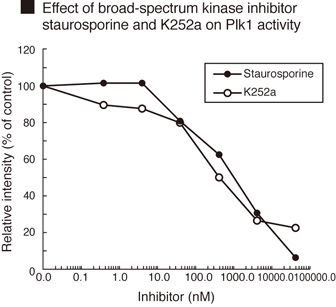
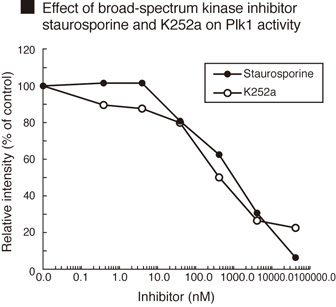
The Polo-like kinase 1 Assay/Inhibitor Screening kit is designed to measure the activity of purified
polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1) and for the rapid and sensitive evaluation of inhibitors using recombinant Plk1.
The phospho-serine/threonine specific polyclonal antibody used in this assay kit specifically recognizes
a phosphorylated threonine in a proprietary protein that is specifically phosphorylated by Plk1.
Gene IDs:
Human: 5347 Mouse: 18817
Kit Components:
Microplate (coated with recombinant Protein-X as Polo-like kinase 1 substrate), 10X Wash Buffer Kinase Buffer, 20X ATP, Anti-Phospho-Serine/Threonine Monoclonal Antibody(PTS-07) Substrate Reagent, HRP conjugated Anti-mouse IgG, Stop Solution
Target:
Plk1
References
1. Lane, H. A. & Nigg, E. A. Trends Cell Biol. 7, 63-68, 1997
2. Glover, D. M., Hagan, I. M. & Tavares, A. A. M. Genes Dev. 12, 3777-3787, 1998
3. Sunkel, C. E. & Glover, D. M. J. Cell Sci. 89, 25-38, 1988
4. Ohkura, H., Hagan, I. & Glover, D. M. Genes Dev. 9, 1059-1073, 1995
5. Song, S. & Lee, K. S. J. Cell Biol. 152, 451-469, 2001
6. Lane, H. A. & Nigg, E. A. J. Cell Biol. 135, 1701-1713, 1996
7. Kotani, S., Tugendreich, S., Fujii, M., Jorgensen, P., Watanabe, N., Hoog, C., Hieter, P. & Todokoro, K.
Mol. Cell 1, 371-380, 1998
8. Alexandru, G., Uhlmann, F., Mechtler, K., Poupart, M. & Nasmyth, K. Cell 105, 459-472, 2001
9. Liu, X.; Erikson, R. L: Polo-like kinase (Plk1) depletion induces apoptosis in cancer cells. Proc. Nat.
Acad. Sci. 100, 5789-5794, 2003.