CycLex CK2(Casein kinase II) Kinase Assay/Inhibitor Screening Kit
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| MBL-CY-1170 | 96 Assays | £602.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
4°C
Storage:
4°C. Please refer to datasheet for additional information
Images
Documents
Further Information
Applications:
Other - 1) Screening inhibitors or activators of CK2.
2) Detecting the effects of pharmacological agents on CK2 activity.
Background:
Protein kinase CK2 is a ubiquitous and pleiotropic serine/threonine protein kinase, which appears to interact with different signaling pathways and therefore represents the prototype of a multifunctionalprotein kinase. The holoenzyme is generally composed of two catalytic (alpha and/or alpha') and two regulatory (beta) subunits (1-3). Although the beta subunits deeply affect many properties of CK2, both the free alpha/alpha' catalytic subunits and the holoenzyme are constitutively active. The enzyme is highly expressed in most cancers (4) and this higher expression has been tentatively correlated with the involvement of CK2 in the promotion of specific phases of the cell cycle (5). Unlike the majority of protein kinases, which are tightly regulated enzymes, CK2 is endowed with high constitutive activity, a feature that is suspected to underlie its oncogenic potential (6, 7) and possible implication in viral infections. This makes CK2 an attractive target for anti-neoplastic and antiviral drugs. Experimental studies suggest that dysregulated expression of the alpha subunit of CK2 imparts an oncogenic potential in the cells such that in cooperation with certain oncogenes (8, 9), it produces a profound enhancement of the tumor phenotype. Recent studies have provided evidence that overexpression of CK2 in tumor cells is not simply a reflection of tumor cell proliferation alone but additionally may reflect the pathobiological characteristics of the tumor. Of considerable interest is the possibility that CK2 dysregulation in tumors may influence the apoptotic activity in those cells (10-12). Approaches to interfering with the CK2 signal may provide a useful means for inducing tumor cell death (13).
Description:
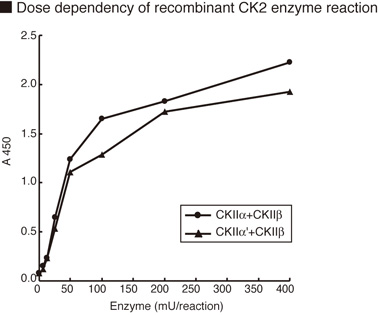
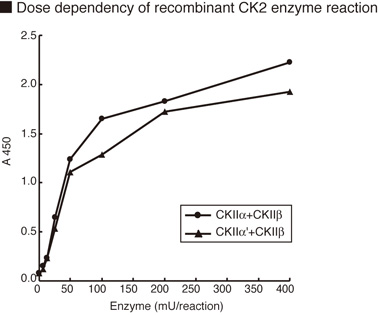
The CycLex® CK2 Assay/Inhibitor Screening kit is designed to measure the activity of purified
Casein Kinase-2 (CK2) for the rapid and sensitive evaluation of CK2 inhibitors or activators. The
phospho-specific monoclonal antibody used in this assay kit specifically recognizes the
phospho-serine46 residue in p53, which is phosphorylated by CK2 in vitro.
Gene IDs:
Human: 1457 Mouse: 12995
Kit Components:
Microplate, 10x Wash Buffer, Kinase Buffer, 20x ATP, HRP conjugated Detection Antibody, Substrate Reagent, Stop Solution
Target:
CK2
References
1. Lozeman, F.J., Litchfield, D.W., Piening, C., Takio, K., Walsh, K.A. and Krebs, E.G. (1990) Isolation
and characterization of human cDNA clones encoding the ? and ?? subunits of CK2. Biochemistry 29,
8436?8447
2. Litchfield, D.W., Lozeman, F.J., Piening, C., Sommercorn, J., Takio, K., Walsh, K.A. and Krebs, E.G.
(1990) Subunit structure of CK2 from bovine testis: demonstration that the ? and ?? subunits are
distinct polypeptides. J. Biol. Chem. 265, 7638?7644
3. Maridor, G., Park, W., Krek, W. and Nigg, E.A. (1991) CK2. cDNA sequences, developmental
expression and tissue distribution of mRNAs for ?, ?? and ? subunits of the chicken enzyme. J. Biol.
Chem. 266, 2362?2368
4. Munstermann, U., Fritz, G., Seitz, G., Lu, Y.P., Schneider, H.R. and Issinger, O.-G. (1990) CK2 is
elevated in solid human tumors and rapidly proliferating non-neoplastic tissue. Eur. J. Biochem. 189,
251?257
5. Pepperkok, R., Lorenz, P., Ansorge, W. and Pyerin, W. (1994) CK2 is required for transition of G0/G1,
early G1, and G1/S phases of the cell cycle. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 6986?6991
6. Landesman-Bollag, E., Romieu-Mourez, R., Song, D.H., Sonenshein, G.E., Cardiff, R.D. and Seldin, D.C. (2001) Protein kinase CK2 in mammary gland tumorigenesis. Oncogene 20, 3247?3257
7. Seldin, D.C. and Leder, P. (1995) CK2 alpha transgene-induce murine lymphoma: relation to
theileriosis in cattle. Science 267, 894?897
8. Landesman-Bollag, E., Channavajhala, P.L., Cardiff, R.D. and Seldin, D.C. (1998) p53 deficiency and
mis-expression of protein kinase CK2a collaborate in the development of thymic lymphomas in mice.
Oncogene 16, 2965?2974
9. Channavajhala, P. and Seldin, D.C. (2002) Functional interaction of protein kinase CK2 and c-Myc in
lymphomagenesis. Oncogene 21, 5280?5288
10. Sayed, M., Pelech, S., Wong, C., Marotta, A. and Salh, B. (2001) Protein kinase CK2 is involved in
G2 arrest and apoptosis following spindle damage in epithelial cells. Oncogene 20, 6994?7005
11. Desagher, S., Osen-Sand, A., Montessuit, S., Magnenat, E., Vilbois, F., Hochmann, A., Journot, L.,
Antonsson, B. and Martinou, J.C. (2001) Phosphorylation of bid by casein kinases I and II regulates
its cleavage by caspase 8. Mol. Cell 8, 601?611
12. Li, P., Li, J., Muller, E., Otto, A., Dietz, R. and von Harsdorf, R. (2002) Phosphorylation by protein
kinase CK2. A signaling switch for the caspase-inhibiting protein ARC. Mol. Cell 10, 247?258
13. Wang, H., Davis, A., Yu, S. and Ahmed, K. (2001) Response of cancer cells to molecular interruption
of the CK2 signal. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 227, 167?174