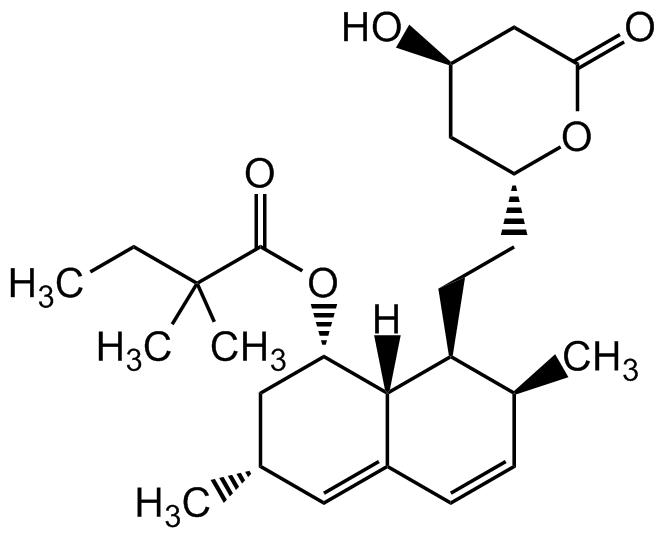
Simvastatin
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-CN2-0052-M010 | 10 mg | £35.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CN2-0052-M050 | 50 mg | £50.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Storage:
-20°C
Images
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
MK-733; Synvinolin; BRN 4768037
Appearance:
White powder.
CAS:
79902-63-9
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
Handling Advice:
After reconstitution, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C.
InChi:
InChI=1S/C25H38O5/c1-6-25(4,5)24(28)30-21-12-15(2)11-17-8-7-16(3)20(23(17)21)10-9-19-13-18(26)14-22(27)29-19/h7-8,11,15-16,18-21,23,26H,6,9-10,12-14H2,1-5H3/t15-,16-,18+,19+,20-,21-,23-/m0/s1
InChiKey:
RYMZZMVNJRMUDD-HGQWONQESA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 79902-63-9. Formula: C25H38O5. MW: 418.6. Synthetic. Synthetic analog of Lovastatin (Prod. No. AG-CN2-0051 http://www.adipogen.com/ag-cn2-0051/lovastatin.html ). Potent competitive HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor. Anti-hypercholesterolemic agent. Cholesterol/isoprenoid biosynthesis inhibitor. Blocks the production of mevalonate, a critical compound in the production of cholesterol and isoprenoids. Inhibits the isoprenylation of Ras and Rho family GTPases. Smooth muscle cell proliferation inhibitor. Anti-adhesive, immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory compound. Proteasome modulator. Stimulates bone formation. Apoptosis inducer. Anticancer compound. Increases cellular resistance to anticancer agents such as doxorubicin and etoposides (Prod. No. AG-CR1-3572 http://www.adipogen.com/ag-cr1-3572/etoposide.html ). Suppresses ICAM-1-LFA-1 interactions, which blocks virus replication and infection. Anti-hypertensive agent. Suppresses TNF-induced NF-kappaB activation.
MDL:
MFCD00072007
Molecular Formula:
C25H38O5
Molecular Weight:
418.6
Package Type:
Vial
Product Description:
Synthetic analog of Lovastatin (Prod. No. AG-CN2-0051 http://www.adipogen.com/ag-cn2-0051/lovastatin.html ). Potent competitive HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor. Anti-hypercholesterolemic agent. Cholesterol/isoprenoid biosynthesis inhibitor. Blocks the production of mevalonate, a critical compound in the production of cholesterol and isoprenoids. Inhibits the isoprenylation of Ras and Rho family GTPases . Anticancer compound that causes cell cycle arrest in G1 and G2/M phases through modulation of proteasome in cancer cell lines. SKP2 E3 ligase inhibitor. Decreases the expression of Skp2 and results in the inhibition of Skp2-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of p27 and p21, leading to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Smooth muscle cell proliferation inhibitor. Anti-adhesive, immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory compound that stimulates bone formation. Suppresses TNF-induced NF-kappaB activation. Increases cellular resistance to anticancer agents such as doxorubicin and etoposides (Prod. No. AG-CR1-3572 http://www.adipogen.com/ag-cr1-3572/etoposide.html ). Suppresses ICAM-1-LFA-1 interactions, which blocks virus replication and infection. Anti-hypertensive agent.
Purity:
>98% (HPLC)
SMILES:
[H][C@]12[C@H](C[C@@H](C)C=C1C=C[C@H](C)[C@@H]2CC[C@@H]1C[C@@H](O)CC(=O)O1)OC(=O)C(C)(C)CC
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO, ethanol or methanol. Insoluble in water.
Source / Host:
Synthetic.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Biochemical Reagents
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
References
Effects of synvinolin (MK-733) on plasma lipids in familial hypercholesterolaemia: M.J. Mol, et al.; Lancet 2, 936 (1986) | All ras proteins are polyisoprenylated but only some are palmitoylated: J.F. Hancock, et al.; Cell 57, 1167 (1989) | Inhibition of proliferation of human smooth muscle cells by various HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors; comparison with other human cell types: P. Negre-Aminou, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1345, 259 (1997) | Statins as a newly recognized type of immunomodulator: B. Kwak, et al.; Nat. Med. 6, 1399 (2000) | Lovastatin and simvastatin are modulators of the proteasome: C. Wojcik, et al.; Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 32, 957 (2000) | Statins and bone formation: I.R. Garrett, et al.; Curr. Pharm. Des. 7, 715 (2001) | HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors as immunomodulators: potential use in transplant rejection: L.J. Raggatt & N.C. Partridge; Drugs 62, 2185 (2002) (Review) | HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors and the malignant cell: the statin family of drugs as triggers of tumor-specific apoptosis: W.W. Wong, et al.; Leukemia 16, 508 (2002) | The statins as anticancer agents: K.K. Chan, et al.; Clin. Cancer Res. 9,10 (2003) | Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects of statins: L.M. Blanco-Colio, et al.; Kidney Int. 63, 12 (2003) | Statin compounds reduce human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication by preventing the interaction between virion-associated host intercellular adhesion molecule 1 and its natural cell surface ligand LFA-1: J.F. Giguere & M.J. Tremblay; J. Virol. 78, 12062 (2004) | HMG CoA reductase inhibitors (statins) to treat Epstein-Barr virus-driven lymphoma: J.I. Cohen; Br. J. Canc. 92, 1593 (2005) | Beyond lipid lowering: the anti-hypertensive role of statins: V. Chopra, et al.; Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 21, 161 (2007) | Reversal of chemoresistance and enhancement of apoptosis by statins through down-regulation of the NF-kappaB pathway: K.S. Ahn, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 75, 907 (2008) | Simvastatin-induced cell cycle arrest through inhibition of STAT3/SKP2 axis and activation of AMPK to promote p27 and p21 accumulation in hepatocellular carcinoma cells: S.-T. Wang, et al.; Cell Death Dis. 8, e2626 (2017)