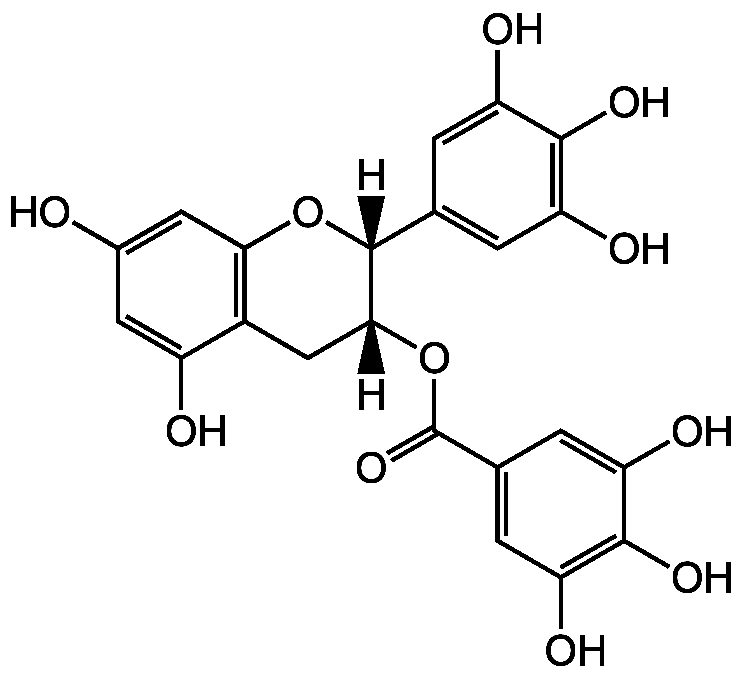
(-)-Epigallocatechin gallate
Product Code: AG-CN2-0063
Product Group: Natural Products and Extracts
Supplier: AdipoGen Life Sciences
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-CN2-0063-M025 | 25 mg | £30.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CN2-0063-M100 | 100 mg | £70.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Storage:
-20°C
Images
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate; EGCG; CCRIS 3729; Teavigo; NVP-XAA 723
Appearance:
Off-white to white powder.
CAS:
989-51-5
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
Handling Advice:
Keep cool and dry.Keep under inert gas.Protect from light.
InChi:
InChI=1S/C22H18O11/c23-10-5-12(24)11-7-18(33-22(31)9-3-15(27)20(30)16(28)4-9)21(32-17(11)6-10)8-1-13(25)19(29)14(26)2-8/h1-6,18,21,23-30H,7H2/t18-,21-/m1/s1
InChiKey:
WMBWREPUVVBILR-WIYYLYMNSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 989-51-5. Formula: C22H18O11. MW: 458.4. Isolated from green tea. Potent anticancer compound. Anti-angiogenic. VEGF, VE-cadherin phosphorylation, matrix metalloproteinase and urokinase-plasminogen activator (uPA) inhibitor. Anti-inflammatory. NF-kappaB inhibitor. Modulates chronic inflammatory diseases, such as type 2 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease. COX-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS; NOS II) inhibitor. Potent antioxidant. Protects cells from lipid peroxidation and DNA damage induced by reactive free radicals. Regulates cancer cell growth, proliferation, transformation, survival, angiogenesis, apoptosis, invasion and metastasis. Chemopreventive. Apoptosis inducer. Promotes cell cycle arrest. Modulates signal transduction pathways including JAK/STAT, MAPK, PI3K/AKT, Wnt and Notch. EGFR and HER-2 receptor signaling inhibitor. MAPKs and activator protein-1 inhibitor. mTOR suppressor. IGF-I signaling inhibitor. Proteasome inhibitor. Telomerase and DNA methyltransferase inhibitor. Selective and noncompetitive HAT inhibitor. Topoisomerase I and II inhibitor. Hedgehog signaling (Hh) modulator. PTCH and Gli1 inhibitor. Wnt signaling inhibitor. Neuroprotective. Activates HO-1 by the ARE/Nrf2 pathway, protecting neurons against oxidative damage. STAT-1 inhibitor. Shows preventive cardiovascular and metabolic (obesity, insulin resistance, hypertension and hypercholesterolemia) effects. Inhibits extracellular signal-related kinases (ERK), activates AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), modulates adipocyte marker proteins and down-regulates lipogenic enzymes as well as other potential targets. Fatty acid synthase (FAS) inhibitor. Autophagy stimulator.
MDL:
MFCD00075940
Molecular Formula:
C22H18O11
Molecular Weight:
458.4
Package Type:
Vial
Product Description:
Potent anticancer compound. Anti-angiogenic. VEGF, VE-cadherin phosphorylation, matrix metalloproteinase and urokinase-plasminogen activator (uPA) inhibitor. Anti-inflammatory. NF-kappaB inhibitor. Modulates chronic inflammatory diseases, such as type 2 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease. COX-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS; NOS II) inhibitor. Potent antioxidant. Protects cells from lipid peroxidation and DNA damage induced by reactive free radicals. Regulates cancer cell growth, proliferation, transformation, survival, angiogenesis, apoptosis, invasion and metastasis. Chemopreventive. Apoptosis inducer. Promotes cell cycle arrest. Modulates signal transduction pathways including JAK/STAT, MAPK, PI3K/AKT, Wnt and Notch. EGFR and HER-2 receptor signaling inhibitor. MAPKs and activator protein-1 inhibitor. Potent DYRK1A inhibitor (IC50=330nM). mTOR suppressor. IGF-I signaling inhibitor. Proteasome inhibitor. Telomerase and DNA methyltransferase inhibitor. Selective and noncompetitive HAT inhibitor. Topoisomerase I and II inhibitor. Hedgehog signaling (Hh) modulator. PTCH and Gli1 inhibitor. Wnt signaling inhibitor. Neuroprotective. Activates HO-1 by the ARE/Nrf2 pathway, protecting neurons against oxidative damage. STAT-1 inhibitor. Shows preventive cardiovascular and metabolic (obesity, insulin resistance, hypertension and hypercholesterolemia) effects. Inhibits extracellular signal-related kinases (ERK), activates AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), modulates adipocyte marker proteins and down-regulates lipogenic enzymes as well as other potential targets. Fatty acid synthase (FAS) inhibitor. Autophagy stimulator.
Purity:
>98% (HPLC)
SMILES:
[H][C@]1(CC2=C(O[C@]1([H])C1=CC(O)=C(O)C(O)=C1)C=C(O)C=C2O)OC(=O)C1=CC(O)=C(O)C(O)=C1
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO, ethanol, dimethylformamide and water.
Source / Host:
Isolated from green tea.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Natural Products/Extracts
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. After reconstitution, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C.
References
Molecular mechanisms underlying chemopreventive activities of anti-inflammatory phytochemicals: down-regulation of COX-2 and iNOS through suppression of NF-kappa B activation: Y.J. Surh, et al.; Mutat. Res. 480-481, 243 (2001) (Review) | The specificities of protein kinase inhibitors : an update: J. Bain, et al.; Biochem. J. 371, 199 (2003) | Targeting multiple signaling pathways by green tea polyphenol (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate: N. Khan, et al.; Cancer Res. 66, 2500 (2006) (Review) | Inhibition of fatty acid synthase by polyphenols: W.X. Tian; Curr. Med. Chem. 13, 967 (2006) (Review) | Green tea polyphenols as a natural tumour cell proteasome inhibitor: Q.P. Dou, et al.; Inflammopharmacology 16, 208 (2008) (Review) | Chemoprevention with phytochemicals targeting inducible nitric oxide synthase: A. Murakami; Forum Nutr. 61, 193 (2009) (Review) | Molecular basis for cancer chemoprevention by green tea polyphenol EGCG: H. Tachibana; Forum Nutr. 61, 156 (2009) (Review) | Apoptosis by dietary agents for prevention and treatment of prostate cancer: N. Khan, et al.; Endocr. Relat. Cancer 17, R39 (2010) (Review) | Targeting polyamines and biogenic amines by green tea epigallocatechin-3-gallate: E. Melgarejo, et al.; Amino Acids 38, 519 (2010) (Review) | Green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate: inflammation and arthritis: R. Singh, et al.; Life Sci. 86, 907 (2010) (Review) | Regulation of survival, proliferation, invasion, angiogenesis, and metastasis of tumor cells through modulation of inflammatory pathways by nutraceuticals: S.C. Gupta, et al.; Cancer Metastasis Rev. 29, 405 (2010) (Review) | Updates of mTOR inhibitors: H. Zhou, et al.; Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 10, 571 (2010) (Review) | The role of nutraceuticals in the regulation of Wnt and Hedgehog signaling in cancer: F.H. Sarkar, et al.; Cancer Metastasis Rev. 29, 383 (2010) (Review) | Use of STAT1 inhibitors in the treatment of brain I/R injury and neurodegenerative diseases: F.H. Ebner, et al.; Cent. Nerv. Syst. Agents Med. Chem. 11, 2 (2011) (Review) | Weight control and prevention of metabolic syndrome by green tea: S. Sae-tan, et al.; Pharmacol. Res. 64, 146 (2011) (Review) | Targeting cell signaling and apoptotic pathways by dietary agents: role in the prevention and treatment of cancer: M.K. Shanmugam, et al.; Nutr. Cancer 63, 161 (2011) (Review) | Implications of cancer stem cell theory for cancer chemoprevention by natural dietary compounds: Y. Li, et al.; J. Nutr. Biochem. 22, 799 (2011) (Review) | Modulation of Nrf2/ARE pathway by food polyphenols: a nutritional neuroprotective strategy for cognitive and neurodegenerative disorders: G. Scapagnini, et al.; Mol. Neurobiol. 44, 192 (2011) (Review) | Nutritional approaches to modulate oxidative stress in Alzheimer's disease: C.B. Pocernich, et al.; Curr. Alzheimer Res. 8, 452 (2011) (Review) | Possible involvement of programmed cell death pathways in the neuroprotective action of polyphenols: S. Bastianetto, et al.; Curr. Alzheimer Res. 8, 445 (2011) (Review) | Green tea catechin, epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG): mechanisms, perspectives and clinical applications: B.N. Singh, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 82, 1807 (2011) (Review) | Epigenetic diet: impact on the epigenome and cancer: T.M. Hardy & T.O. Tollefsbol; Epigenomics 3, 503 (2011) (Review) | Green tea EGCG, T cells, and T cell-mediated autoimmune diseases: D. Wu, et al.; Mol. Aspects Med 33, 107 (2012) (Review) | Epigallocatechin-3-gallate, a DYRK1A inhibitor, rescues cognitive deficits in Down syndrome mouse models and in humans: R. De la Torre, et al.; Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 58, 278 (2014)
Related Products
| Product Name | Product Code | Supplier | Purvalanol A | AG-CR1-2903 | AdipoGen Life Sciences | Summary Details | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AZ191 | AG-CR1-3657 | AdipoGen Life Sciences | Summary Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SB415286 | AG-CR1-3658 | AdipoGen Life Sciences | Summary Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SB216763 | AG-CR1-3659 | AdipoGen Life Sciences | Summary Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||