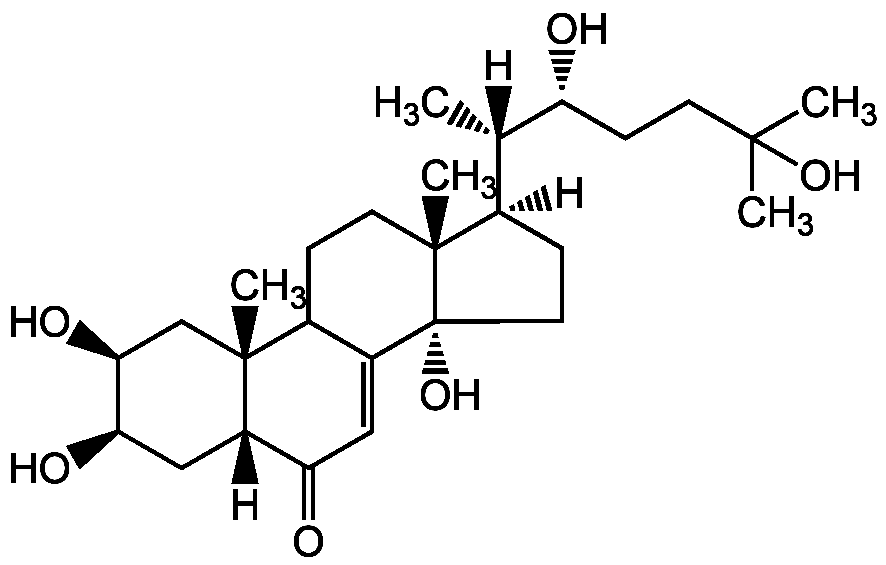
Ecdysone
Product Code: AG-CN2-0071
Product Group: Natural Products and Extracts
Supplier: AdipoGen Life Sciences
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-CN2-0071-M001 | 1 mg | £65.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CN2-0071-M005 | 5 mg | £160.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CN2-0071-M010 | 10 mg | £265.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Storage:
-20°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
alpha-Ecdysone; BRN 2422986; CCRIS 6931; 2beta,3beta,14alpha,22R,25-Pentahydroxy-5beta-cholest-7-en-6-one
Appearance:
White to off-white solid.
CAS:
3604-87-3
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
InChi:
InChI=1S/C27H44O6/c1-15(20(28)8-9-24(2,3)32)16-7-11-27(33)18-12-21(29)19-13-22(30)23(31)14-25(19,4)17(18)6-10-26(16,27)5/h12,15-17,19-20,22-23,28,30-33H,6-11,13-14H2,1-5H3/t15-,16+,17?,19-,20+,22+,23-,25+,26+,27+/m0/s1
InChiKey:
UPEZCKBFRMILAV-DBDKQAFGSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 3604-87-3. Formula: C27H44O6. MW: 464.6. Isolated from Ipomoea hederacea. Steroidal prohormone of the major insect molting hormone 20-hydroxyecdysone. A member of the ecdysteroid family. Ecdysone receptor (EcR) agonist. Induces the expression of genes coding for proteins that the larva requires, and it causes chromosome puffs (sites of high expression) to form in polytene chromosomes. Plays a key role in insect development, cell proliferaton, growth and apoptosis by controlling gene expression involved in moulting and metamorphosis. It acts through a heterodimeric receptor comprising the ecdysone receptor and the ultraspiracle proteins (USP). Appears in many plants mostly as a protection agent (toxins or antifeedants) against herbivorous insects. Used for controlled gene expression in scientific research, agriculture and medicine. Used for the development of selective insect growth regulators for use as environmentally benign insecticides.
MDL:
MFCD00042683
Molecular Formula:
C27H44O6
Molecular Weight:
464.6
Package Type:
Vial
Product Description:
Steroidal prohormone of the major insect molting hormone 20-hydroxyecdysone. A member of the ecdysteroid family. Ecdysone receptor (EcR) agonist. Induces the expression of genes coding for proteins that the larva requires, and it causes chromosome puffs (sites of high expression) to form in polytene chromosomes. Plays a key role in insect development, cell proliferaton, growth and apoptosis by controlling gene expression involved in moulting and metamorphosis. It acts through a heterodimeric receptor comprising the ecdysone receptor and the ultraspiracle proteins (USP). Appears in many plants mostly as a protection agent (toxins or antifeedants) against herbivorous insects. Used for controlled gene expression in scientific research, agriculture and medicine. Used for the development of selective insect growth regulators for use as environmentally benign insecticides.
Purity:
>95% (NMR)
SMILES:
[H][C@@](C)([C@H](O)CCC(C)(C)O)[C@@]1([H])CC[C@@]2(O)C3=CC(=O)[C@]4([H])C[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)C[C@]4(C)C3CC[C@]12C
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in acetic acid, ethanol, methanol or DMSO. Sparingly soluble in chloroform. Insoluble in water.
Source / Host:
Isolated from Ipomoea hederacea.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Natural Products/Extracts
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
References
Ecdysone, an insect steroid hormone, and its mode of action: P. Karlson & C.E. Sekeris; Recent Prog. Horm. Res. 22, 473 (1966) | Ecdysone, the molting hormone of insects: P. Karlson; Naturwissenschaften 53, 445 (1966) (German) | Puffs and gene regulation-molecular insights into the Drosophila ecdysone regulatory hierarchy: C.S. Thummel; Bioessays 12, 561 (1990) | Hormones, puffs and flies: the molecular control of metamorphosis by ecdysone: A.J. Andres & C.S. Thummel; Trends Genet. 8, 132 (1992) (Review) | The IVth Karlson Lecture: ecdysone-responsive genes: P. Cherbas; Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 23, 3 (1993) | Ecdysone signaling cascade and regulation of Drosophila metamorphosis: E.H. Baehrecke; Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 33, 231 (1996) (Review) | Nuclear hormone receptors and the Drosophila ecdysone response: S.R. Russell; Biochem. Soc. Symp. 62, 111 (1996) | Ecdysone receptors and their biological actions: L.M. Riddiford, et al.; Vitam. Horm. 60, 1 (2000) | Ecdysone-regulated puff genes 2000: C.S Thummel; Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 32, 113 (2002) | Ecdysone-controlled expression of transgenes: L.D. Graham; Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2, 525 (2002) | Non-genomic ecdysone effects and the invertebrate nuclear steroid hormone receptor EcR-new role for an "old" receptor? U. Schlattner, et al.; Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 247, 64 (2006) | Ecdysone and the cell cycle: investigations in a mosquito cell line: A.M. Fallon & A. Gerenday; J. Insect. Physiol. 56, 1396 (2010)
Related Products
| Product Name | Product Code | Supplier | Ponasterone A | AG-CN2-0053 | AdipoGen Life Sciences | Summary Details | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|