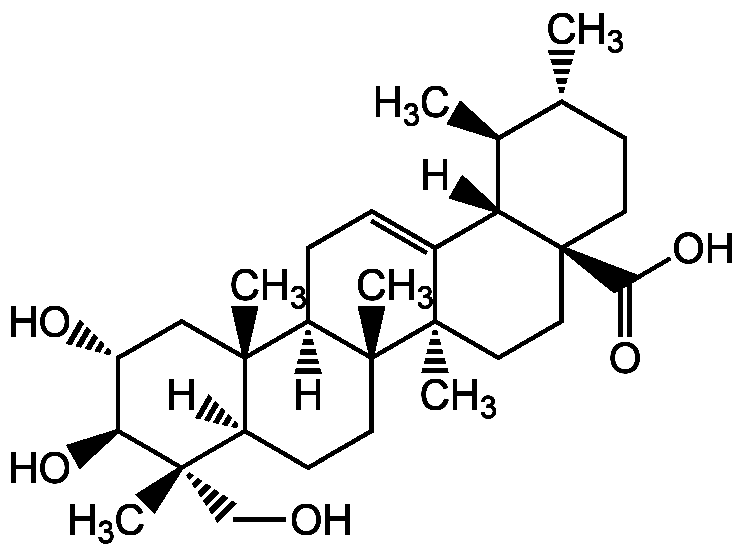
Asiatic acid
Product Code: AG-CN2-0400
Product Group: Natural Products and Extracts
Supplier: AdipoGen Life Sciences
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-CN2-0400-M005 | 5 mg | £45.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CN2-0400-M025 | 25 mg | £115.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Storage:
+4°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
2alpha,23-Dihydroxyursolic acid; Dammarolic acid; NSC166063
Appearance:
White to off-white powder.
CAS:
464-92-6
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
Handling Advice:
Protect from light.Protect from moisture.
InChi:
InChI=1S/C30H48O5/c1-17-9-12-30(25(34)35)14-13-28(5)19(23(30)18(17)2)7-8-22-26(3)15-20(32)24(33)27(4,16-31)21(26)10-11-29(22,28)6/h7,17-18,20-24,31-33H,8-16H2,1-6H3,(H,34,35)/t17-,18+,20-,21-,22-,23+,24+,26+,27+,28-,29-,30+/m1/s1
InChiKey:
JXSVIVRDWWRQRT-UYDOISQJSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 464-92-6. Formula: C30H48O5. MW: 488.7. Isolated from Centella asiatica. Apoptosis inducer. Cell cycle arrest inducer. Anticancer compound Antioxidant. Hepatoprotective. Inhibits TGF-beta/Smad-mediated fibrogenesis. Stimulates wound healing. Anti-diabetic. Glycogen phosphorylase inhibitor. Neuroprotective. Modulates multiple targets associated with amyloid-beta precursor protein processing and amyloid-beta protein clearance. Down regulates BACE1 and increases ADAM10 maturation. Anti-hyperglycemic compound. Anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive compound. Antiangiogenic. Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitor. PPARgamma inhibitor through a C/EBPbeta-independent mechanisms. Anti-osteoporotic. Inhibits adipogenic differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells (BMSC).
MDL:
MFCD00238541
Molecular Formula:
C30H48O5
Molecular Weight:
488.7
Package Type:
Vial
Product Description:
Apoptosis inducer [1, 3]. Cell cycle arrest inducer [1]. Anticancer compound [1, 5] Antioxidant. Hepatoprotective [2]. Inhibits TGF-beta/Smad-mediated fibrogenesis [12]. Stimulates wound healing [4]. Anti-diabetic. Glycogen phosphorylase inhibitor [6]. Neuroprotective [13]. Modulates multiple targets associated with amyloid-beta precursor protein processing and amyloid-beta protein clearance. Down regulates BACE1 and increases ADAM10 maturation [7]. Anti-hyperglycemic compound [8, 14]. Anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive compound [9]. Antiangiogenic [10]. Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitor [11]. PPARgamma inhibitor through a C/EBPbeta-independent mechanisms [15]. Anti-osteoporotic. Inhibits adipogenic differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells (BMSC) [15].
Purity:
>95% (NMR)
SMILES:
[H][C@@]12CC[C@]3(C)[C@]([H])(CC=C4[C@]5([H])[C@@H](C)[C@H](C)CC[C@@]5(CC[C@@]34C)C(O)=O)[C@@]1(C)C[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@]2(C)CO
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO, ethanol or dimethylformamide. Sparingly soluble in water.
Source / Host:
Isolated from Centella asiatica.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Natural Products/Extracts
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
References
Asiatic acid, a triterpene, induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest through activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in human breast cancer cells: Y.L. Hsu, et al.; J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 313, 333 (2005) | Mechanism underlying mitochondrial protection of asiatic acid against hepatotoxicity in mice: J. Gao, et al.; J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 58, 227 (2006) | Disruption of the endoplasmic reticulum and increases in cytoplasmic calcium are early events in cell death induced by the natural triterpenoid Asiatic acid: G.M. Gurfinkel, et al.; Apoptosis 11, 1463 (2006) | Structure-activity relationship study of asiatic acid derivatives for new wound healing agent: B.S. Jeong; Arch. Pharm. Res. 29, 556 (2006) | Asiatic acid induces colon cancer cell growth inhibition and apoptosis through mitochondrial death cascade: X.L. Tang, et al.; Biol. Pharm. Bull. 32, 1399 (2009) | Synthesis and biological evaluation of asiatic acid derivatives as inhibitors of glycogen phosphorylases: L. Zhang, et al.; Chem. Biodivers. 6, 864 (2009) | Withanolide A and asiatic acid modulate multiple targets associated with amyloid-beta precursor protein processing and amyloid-beta protein clearance: S.P. Patil, et al.; J. Nat. Prod. 73, 1196 (2010) | Asiatic acid preserves beta cell mass and mitigates hyperglycemia in streptozocin-induced diabetic rats: J. Liu, et al.; Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 26, 448 (2010) | Antinociceptive activities and the mechanisms of anti-inflammation of asiatic Acid in mice: S.S. Huang, et al.; Evid. Based Complement Alternat. Med. 2011, 895857 (2011) | Asiatic acid inhibits pro-angiogenic effects of VEGF and human gliomas in endothelial cell culture models: C.V. Kavitha, et al.; PLoS One 6, e22745 (2011) | Inhibitory effect of asiatic acid on acetylcholinesterase, excitatory post synaptic potential and locomotor activity: M.N. Nasir, et al.; Phytomedicine 19, 311 (2012) | Asiatic acid inhibits liver fibrosis by blocking TGF-beta/Smad signaling in vivo and in vitro: L.X. Tang, et al.; PLoS One 7, e31350 (2012) | Asiatic acid attenuates infarct volume, mitochondrial dysfunction, and matrix metalloproteinase-9 induction after focal cerebral ischemia: K.Y. Lee, et al.; Stroke 43, 1632 (2012) | Efficacy of asiatic acid, a pentacyclic triterpene on attenuating the key enzymes activities of carbohydrate metabolism in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: V. Ramachandran & R. Saravanan; Phytomedicine 20, 230 (2013) | Asiatic Acid Inhibits Adipogenic Differentiation of Bone Marrow Stromal Cells: Z.W. Li, et al.; Cell Biochem. Biophys. 68, 437 (2014)
Related Products
| Product Name | Product Code | Supplier | Asiaticoside | AG-CN2-0080 | AdipoGen Life Sciences | Summary Details | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|