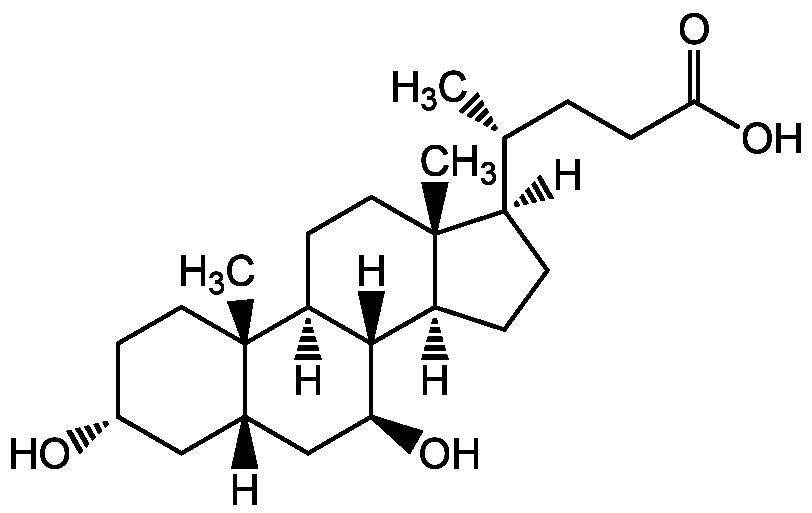
Ursodeoxycholic acid
Product Code: AG-CN2-0411
Product Group: Natural Products and Extracts
Supplier: AdipoGen Life Sciences
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-CN2-0411-G001 | 1 g | £45.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CN2-0411-G005 | 5 g | £115.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Storage:
+4°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
UDCA; USAN; BRN 3219888; NSC 657950; NSC 683769
Appearance:
White to off-white powder.
CAS:
128-13-2
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
GHS Symbol:
GHS07
Handling Advice:
Protect from light.Protect from moisture.
Hazards:
H302
InChi:
InChI=1S/C24H40O4/c1-14(4-7-21(27)28)17-5-6-18-22-19(9-11-24(17,18)3)23(2)10-8-16(25)12-15(23)13-20(22)26/h14-20,22,25-26H,4-13H2,1-3H3,(H,27,28)/t14-,15+,16-,17-,18+,19+,20+,22+,23+,24-/m1/s1
InChiKey:
RUDATBOHQWOJDD-UZVSRGJWSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 128-13-2. Formula: C24H40O4. MW: 392.6. Synthetic. Endogenous hydrophilic bile acid. Antioxidant. Cytoprotective against oxidative stress and cell death. Hepatoprotective at cellular and molecular level, including stabilization of membranes. Protects hepatocytes against bile acid-induced apoptosis. Antiapoptotic and antinecrotic. Targets the mitochondrial function and integrity, reduction of endoplasmatic stress and interactions with survival signals in cAMP, Akt, NF-kappaB, MAPK and PI3K signaling pathways. Modulator and finetuner of the p53-Mdm-2 complex. Chemopreventive against colorectal cancer by countering the tumor-promoting effects of secondary bile acids. Shows also effects on epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling and COX-2 expression. Immunomodulator and anti-inflammatory compound. Modifies TLR4 and TLR9 signaling pathways and downregulates the production of proinflammatory tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha). Pregnane X receptor agonist. Neuroprotective. Inhibits neuronal apoptosis. Glucocorticoid Receptor (GR) agonist. Anticholestatic agent. Used to reduce cholesterol absorption and for cholesterol gallstone dissolution. Used to treat primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC). Interferes with the progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)/NASH. Reduces CXCR3 expression. TIMP-1 inducer. ADAM17 inhibitor.
MDL:
MFCD00065453
Molecular Formula:
C24H40O4
Molecular Weight:
392.6
Package Type:
Vial
Precautions:
P264, P301, P312, P330
Product Description:
Endogenous hydrophilic bile acid. Antioxidant. Cytoprotective against oxidative stress and cell death. Hepatoprotective at cellular and molecular level, including stabilization of membranes. Protects hepatocytes against bile acid-induced apoptosis. Antiapoptotic and antinecrotic. Targets the mitochondrial function and integrity, reduction of endoplasmatic stress and interactions with survival signals in cAMP, Akt, NF-kappaB, MAPK and PI3K signaling pathways. Modulator and finetuner of the p53-Mdm-2 complex. Chemopreventive against colorectal cancer by countering the tumor-promoting effects of secondary bile acids. Shows also effects on epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling and COX-2 expression. Immunomodulator and anti-inflammatory compound. Modifies TLR4 and TLR9 signaling pathways and downregulates the production of proinflammatory tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha). Pregnane X receptor agonist. Neuroprotective. Inhibits neuronal apoptosis. Glucocorticoid Receptor (GR) agonist. Anticholestatic agent. Used to reduce cholesterol absorption and for cholesterol gallstone dissolution. Used to treat primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC). Interferes with the progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)/NASH. Reduces CXCR3 expression [11]. TIMP-1 inducer [12]. ADAM17 inhibitor [12].
Purity:
>95% (NMR)
Signal word:
Warning
SMILES:
[H][C@@]1(CC[C@@]2([H])[C@]3([H])[C@@H](O)C[C@]4([H])C[C@H](O)CC[C@]4(C)[C@@]3([H])CC[C@]12C)[C@H](C)CCC(O)=O
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO, ethanol or dimethylformamide. Sparingly soluble in water.
Source / Host:
Synthetic.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Natural Products/Extracts
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at +4°C.
References
Antioxidant properties of ursodeoxycholic acid: D. Lapenna, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 64, 1661 (2002) (Review) | Ursodeoxycholic acid in cholestatic liver disease: mechanisms of action and therapeutic use revisited: G. Paumgartner, et al.; Hepatology 36, 525 (2002) (Review) | Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: an overview of current insights in pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatmen. T.C. Schreuder, et al.; World J. Gastroenterol. 14, 2474 (2008) (Review) | p53 and the regulation of hepatocyte apoptosis: implications for disease pathogenesis: J.D. Amaral, et al.; Trends Mol. Med. 15, 531 (2009) (Review) | Bile acids: regulation of apoptosis by ursodeoxycholic acid: J.D. Amaral, et al.; J. Lipid. Res. 50, 1721 (2009) (Review) | Bile acids as regulators of hepatic lipid and glucose metabolism: M. Trauner, et al.; Dig. Dis. 28, 220 (2010) (Review) | Targeting the p53 pathway of apoptosis: J.D. Amaral, et al.; Curr. Pharm. Des. 16, 2493 (2010) (Review) | Ursodeoxycholic acid and chemoprevention of colorectal cancer: L. Serfaty, et al.; Gastroenterol. Clin. Biol. 34, 516 (2010) (Review) | Ursodeoxycholic acid and bile-acid mimetics as therapeutic agents for cholestatic liver diseases: an overview of their mechanisms of action: R. Poupon; Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 36, S3 (2012) (Review) | Ursodeoxycholic acid in cholestasis: linking action mechanisms to therapeutic applications: M.G. Roma, et al.; Clin. Sci. (Lond). 121, 523 (2011) (Review) | CXCR3 axis in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis: a possible novel mechanism of the effect of ursodeoxycholic acid: P. Manousou, et al.; Clin. Exp. Immunol. 172, 9 (2013) | Liver protective effect of ursodeoxycholic acid includes regulation of ADAM17 activity: H. Buryova, et al.; BMC Gastroenterol. 13, 155 (2013)
Related Products
| Product Name | Product Code | Supplier | Chenodeoxycholic acid | AG-CN2-0410 | AdipoGen Life Sciences | Summary Details | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|