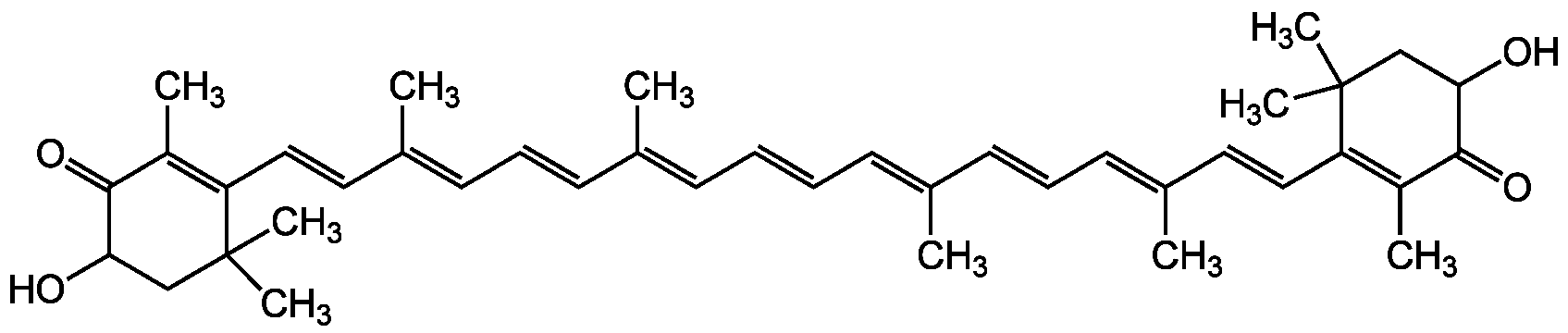
Astaxanthin
Product Code:
AG-CN2-0055
AG-CN2-0055
Regulatory Status:
RUO
RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Ambient
Storage:
Short term: +4°C. Long term: -20°C
Short term: +4°C. Long term: -20°C
No additional charges, what you see is what you pay! *
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-CN2-0055-M005 | 5 mg | £51.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CN2-0055-M025 | 25 mg | £131.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Stay in control of your spending. These prices have no additional charges to UK mainland customers, not even shipping!
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
Multibuy discounts available! Contact us to find what you can save.
This product comes from: Switzerland.
Typical lead time: 7-10 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
Typical lead time: 7-10 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
- Further Information
- Documents
- References
- Related Products
- Show All
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
3,3'-Dihydroxy-beta-carotene-4,4'-dione; all-trans-Astaxanthin; Ovoester; NSC635689; CCRIS 7118; HSDB 7468
Appearance:
Dark violet red solid.
CAS:
472-61-7
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
Handling Advice:
Keep cool and dry.
InChi:
InChI=1S/C40H52O4/c1-27(17-13-19-29(3)21-23-33-31(5)37(43)35(41)25-39(33,7)8)15-11-12-16-28(2)18-14-20-30(4)22-24-34-32(6)38(44)36(42)26-40(34,9)10/h11-24,35-36,41-42H,25-26H2,1-10H3/b12-11+,17-13+,18-14+,23-21+,24-22+,27-15+,28-16+,29-19+,30-20+
InChiKey:
MQZIGYBFDRPAKN-QISQUURKSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 472-61-7. Formula: C40H52O4. MW: 596.8. Synthetic. Potent antioxidant carotenoid. Free radical scavenger. Reduces oxidative stress. Anticancer compound. Anti-inflammatory. Blocks NF-kappaB activation. Anti-hypertensive. Cardiovascular protective. Improves neuronal stem cell potential. Neuroprotective. Inhibits tumor invasion. Apoptosis inducer . Increases insulin sensitivity. Attenuates diabetes associated coagulatory, oxidative and inflammatory stress. PPARalpha agonist and PPARgamma antagonist. Shows positive effects on obesity and insulin resistance Hepatoprotective. Reviews.
MDL:
MFCD00672621
Molecular Formula:
C40H52O4
Molecular Weight:
596.8
Other data:
Solubility in aqueous buffers: Further dilutions of the organic solvent solution into aqueous or isotonic saline should be made prior to
Package Type:
Vial
Product Description:
Potent antioxidant carotenoid [1]. Free radical scavenger [1, 3]. Reduces oxidative stress [1, 3]. Anticancer compound [2]. Anti-inflammatory. Blocks NF-kappaB activation [3, 18]. Anti-hypertensive. Cardiovascular protective [4, 6]. Improves neuronal stem cell potential [7, 9]. Neuroprotective [10]. Inhibits tumor invasion [11]. Apoptosis inducer [14]. Increases insulin sensitivity [12]. Attenuates diabetes associated coagulatory, oxidative and inflammatory stress [17]. PPARalpha agonist and PPARgamma antagonist [19, 20]. Shows positive effects on obesity and insulin resistance [17, 19, 20] Hepatoprotective [21]. Reviews [5, 6, 15, 16].
Purity:
>98% (HPLC)
SMILES:
CC(C=CC=C(/C)C=CC1=C(C)C(=O)C(O)CC1(C)C)=C/C=C/C=C(C)/C=C/C=C(C)/C=C/C1=C(C)C(=O)C(O)CC1(C)C
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO, chloroform or DMF. Soluble in ethanol or methanol if heated. Insoluble in water.
Source / Host:
Synthetic.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Natural Products/Extracts
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
Documents
References
Antioxidant activities of astaxanthin and related carotenoids: Y.M. Naguib; J. Agric. Food Chem. 48, 1150 (2000) | Antitumor activity of astaxanthin and its mode of action: H. Jyonouchi, et al.; Nutr. Cancer 36, 59 (2000) | Astaxanthin inhibits nitric oxide production and inflammatory gene expression by suppressing I(kappa)B kinase-dependent NF-kappaB activation: S.J. Lee, et al.; Mol. Cells 16, 97 (2003) | Antihypertensive potential and mechanism of action of astaxanthin: II. Vascular reactivity and hemorheology in spontaneously hypertensive rats: G. Hussein, et al.; Biol. Pharm. Bull. 28, 967 (2005) | Astaxanthin: a novel potential treatment for oxidative stress and inflammation in cardiovascular disease: F.J. Pashkow, et al.; Am. J. Cardiol. 101, 58D (2008) (Review) | Astaxanthin, oxidative stress, inflammation and cardiovascular disease: R.G. Fassett & J.S. Coombes; Future Cardiol. 5, 333 (2009) (Review) | Astaxanthin Improves Stem Cell Potency via an Increase in the Proliferation of Neural Progenitor Cells: J.H. Kim, et al.; Int. J. Mol. Sci. 11, 5109 (2010) | Astaxanthin decreased oxidative stress and inflammation and enhanced immune response in humans: J.S. Park, et al.; Nutr. Metab. (Lond). 7, 18 (2010) | Astaxanthin improves the proliferative capacity as well as the osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation potential in neural stem cells: J.H. Kim, et al.; Food Chem. Toxicol. 48, 1741 (2010) | Neuroprotective effect of astaxanthin on H(2)O(2)-induced neurotoxicity in vitro and on focal cerebral ischemia in vivo: Y.P. Lu, et al.; Brain Res. 1360, 40 (2010) | Astaxanthin inhibits tumor invasion by decreasing extracellular matrix production and induces apoptosis in experimental rat colon carcinogenesis by modulating the expressions of ERK-2, NFkB and COX-2: P. Nagendraprabhu & G. Sudhandiran; Invest. New Drugs. 29, 207 (2011) | High dose astaxanthin lowers blood pressure and increases insulin sensitivity in rats: are these effects interdependent?: H.G. Preuss, et al.; Int. J. Med. Sci. 8, 126 (2011) | Ameliorative effect of astaxanthin on endothelial dysfunction in streptozotocin-induced diabetes in male rats: Z.W. Zhao, et al.; Arzneimittelforschung 61, 239 (2011) | Astaxanthin induces mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in rat hepatocellular carcinoma CBRH-7919 cells: X.D. Song, et al.; Biol. Pharm. Bull. 34, 839 (2011) | Astaxanthin, cell membrane nutrient with diverse clinical benefits and anti-aging potential: P. Kidd; Altern. Med. Rev. 16, 355 (2011) (Review) | Astaxanthin: a potential therapeutic agent in cardiovascular disease: R.G. Fassett & J.S. Coombes; Mar. Drugs 9, 447 (2011) (Review) | Anticoagulatory and antiinflammatory effects of astaxanthin in diabetic rats: K.C. Chan, et al.; J. Food Sci. 77, H76 (2012) | Astaxanthin Treatment Reduced Oxidative Induced Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Secretion in U937: SHP-1 as a Novel Biological Target: L. Speranza, et al.; Mar. Drugs 10, 890 (2012) | The natural carotenoid astaxanthin, a PPAR-a agonist and PPAR-g antagonist, reduces hepatic lipid accumulation by rewiring the transcriptome in lipid-loaded hepatocytes: Y. Jai, et al.; Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 56, 878 (2012) | Astaxanthin functions differently as a selective peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor g modulator in adipocytes and macrophages: M. Inoue, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 84, 692 (2012) | Hepatoprotective potential of astaxanthin against 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in cultured rat hepatocytes: H. Turkez, et al.; Toxicol. Ind. Health. 30, 101 (2012)