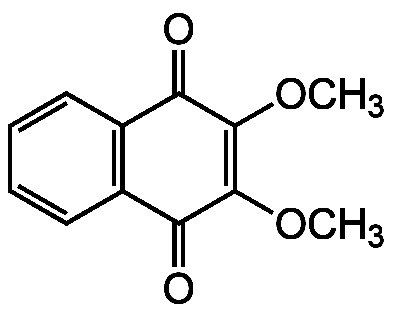
DMNQ
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-CR1-3598-M005 | 5 mg | £75.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CR1-3598-M010 | 10 mg | £105.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CR1-3598-M025 | 25 mg | £200.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
-20°C
Storage:
-20°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
2,3-Dimethoxy-1,4-naphthoquinone; 2,3-diOMe-1,4-NQ
Appearance:
Yellow crystalline solid.
CAS:
6956-96-3
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
GHS Symbol:
GHS07
Handling Advice:
Protect from light and moisture.
Hazards:
H315, H319, H335
InChi:
InChI=1S/C12H10O4/c1-15-11-9(13)7-5-3-4-6-8(7)10(14)12(11)16-2/h3-6H,1-2H3
InChiKey:
ZEGDFCCYTFPECB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 6956-96-3. Formula: C12H10O4. MW: 218.2. Cell permeable, non-alkylating, non-thiol, adduct-forming, redox cycling quinone. Intracellular superoxide anion formation/ROS generation inducer. Anticancer agent. Shown to induce cell proliferation, apoptosis, necrosis and necroptosis in vitro, dependent on concentration, time, temperature and cell type. Valuable tool for the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in order to study the role of ROS in cell toxicity, apoptosis and necrosis. Useful as reference compound in characterizing the effects of oxidative stress. Can be used to eliminate any mechanistic ambiguity involving redox cycling quinoids as the source of reactive oxidant species/oxidative stress in biological studies.
MDL:
MFCD00184331
Molecular Formula:
C12H10O4
Molecular Weight:
218.2
Package Type:
Vial
Precautions:
P261, P271, P280, P312
Product Description:
Cell permeable, non-alkylating, non-thiol, adduct-forming, redox cycling quinone. Intracellular superoxide anion formation/ROS generation inducer. Anticancer agent. Shown to induce cell proliferation, apoptosis, necrosis and necroptosis in vitro, dependent on concentration, time, temperature and cell type. Valuable tool for the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in order to study the role of ROS in cell toxicity, apoptosis and necrosis. Useful as reference compound in characterizing the effects of oxidative stress. Can be used to eliminate any mechanistic ambiguity involving redox cycling quinoids as the source of reactive oxidant species/oxidative stress in biological studies.
Purity:
>99% (NMR)
Signal word:
Warning
SMILES:
COC1=C(OC)C(=O)C2=C(C=CC=C2)C1=O
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO or methanol.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Biochemical Reagents
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
References
The role of oxidative processes in the cytotoxicity of substituted 1,4-naphthoquinones in isolated hepatocytes: D. Ross, et al.; Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 248, 460 (1986) | Redox cycling and sulphydryl arylation; their relative importance in the mechanism of quinone cytotoxicity to isolated hepatocytes: T.W. Gant, et al.; Chem. Biol. Interact. 65, 157 (1988) | Quinone-induced DNA single strand breaks in rat hepatocytes and human chronic myelogenous leukaemic K562 cells: W.A. Morgan, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 44, 215 (1992) | Quinone-induced oxidative stress elevates glutathione and induces gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase activity in rat lung epithelial L2 cells: M.M. Shi, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 269, 26512 (1994) | Different prooxidant levels stimulate growth, trigger apoptosis, or produce necrosis of insulin-secreting RINm5F cells: J.M. Dypbukt, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 269, 30553 (1994) | DNA single-strand breakage in mammalian cells induced by redox cycling quinones in the absence of oxidative stress: W.A. Morgan; J. Biochem. Toxicol. 10, 227 (1995) | Naphthoquinone-induced DNA damage in the absence of oxidative stress: W.A. Morgan; Biochem. Soc. Trans. 23, 225S (1995) | Differential mechanisms of cell killing by redox cycling and arylating quinones: T.R. Henry & K.B. Wallace; Arch. Toxicol. 70, 482 (1996) | Naphthazarin derivatives: synthesis, cytotoxic mechanism and evaluation of antitumor activity: Y.J. You, et al.; Arch. Pharm. Res. 21, 595 (1998) | Temperature-dependent quinone cytotoxicity in platelets involves arylation: Y.A. Kang, et al.; J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 65, 1367 (2002) | Superoxide targets calcineurin signaling in vascular endothelium: D. Namgaladze, et al.; BBRC 334, 1061 (2005) | Oxidative stress promotes polarization of human T cell differentiation toward a T helper 2 phenotype: M.R. King, et al.; J. Immunol. 176, 2765 (2006) | Caspase-2 activation in neural stem cells undergoing oxidative stress-induced apoptosis: C. Tamm, et al.; Apoptosis 13, 354 (2008) | A Receptor-interacting Protein 1 (Rip1) Independent Necrotic Death Under The Control Of Protein Phosphatase Pp2a That Involves The Reorganization Of Actin Cytoskeleton And The Action Of Cofilin-1: A. Tomasella, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 289, 25699 (2014)
Related Products
| Product Name | Product Code | Supplier | Colchicine | AG-CN2-0048 | AdipoGen Life Sciences | Summary Details | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIN-1 chloride | AG-CR1-0027 | AdipoGen Life Sciences | Summary Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||