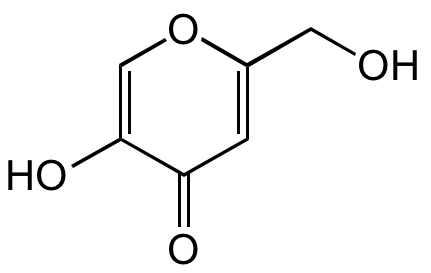
Kojic acid
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| BVT-0019-M010 | 10 mg | £60.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Storage:
+4°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
5-Hydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)-4H-pyran-4-one; KOJ
Appearance:
White solid.
CAS:
501-30-4
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
solid
Handling Advice:
Protect from light when in solution.
InChi:
InChI=1S/C6H6O4/c7-2-4-1-5(8)6(9)3-10-4/h1,3,7,9H,2H2
InChiKey:
BEJNERDRQOWKJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 501-30-4. Formula: C6H6O4. MW: 142.1. Isolated from Aspergillus sp. Mycotoxin. Chelation agent with polyfunctional skeleton for development of biologically active compounds. Moderate antibacterial agent. Tyrosinase inhibitor. Inhibits catecholase activity of tyrosinase. Anti-melanogenic. Skin whitening agent. Antioxidant. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenger. D-Amino acid oxidase (DAAO) inhibitor. Shown to inhibit NF-kB activation. Inducer of macrophage activation. Radioprotectant activity. Antileishmanial agent. Insecticidal. Antifungal chemosensitizer. Used in cosmetics and as food additive.
MDL:
MFCD00006580
Molecular Formula:
C6H6O4
Molecular Weight:
142.1
Package Type:
Plastic Vial
Product Description:
Mycotoxin. Chelation agent with polyfunctional skeleton for development of biologically active compounds. Moderate antibacterial agent. Tyrosinase inhibitor. Inhibits catecholase activity of tyrosinase. Anti-melanogenic. Skin whitening agent. Antioxidant. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenger. D-Amino acid oxidase (DAAO) inhibitor. Shown to inhibit NF-kB activation. Inducer of macrophage activation. Radioprotectant activity. Antileishmanial agent. Insecticidal. Antifungal chemosensitizer. Used in cosmetics and as food additive.
Purity:
>99% (NMR)
SMILES:
OCC1=CC(=O)C(O)=CO1
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO, methanol or water.
Source / Host:
Isolated from Aspergillus sp.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Natural Products/Extracts
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at +4°C.
References
The contitution of kojic acid, a gamma-pyrone derivative of Aspergillus oryzae from carbohydrates: T. Yabuta; J. Chem. Soc. 125, 575 (1924) | Toxicity and Antibiotic Activity of Kojic Acid Produced by Aspergillus luteo-virescens: H.E. Morton, et al.; J. Bacteriol. 50, 579 (1945) | Kojic acid scavenges free radicals while potentiating leukocyte functions including free radical generation: Y. Niwa & H. Akamatsu; Inflammation 15, 303 (1991) | Kojic acid, a cosmetic skin whitening agent, is a slow-binding inhibitor of catecholase activity of tyrosinase: J. Cabanes, et al.; J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 46, 982 (1994) | The combination of glycolic acid and hydroquinone or kojic acid for the treatment of melasma and related conditions: A. Garcia & J.E. Fulton Jr.; Dermatol. Surg. 22, 443 (1996) | Kojic acid--a new leading molecule for a preparation of compounds with an anti-neoplastic potential: L. Novotny, et al.; Neoplasma 46, 89 (1999) (Review) | Kojic acid, a potential inhibitor of NF-kappaB activation in transfectant human HaCaT and SCC-13 cells: K.Y. Moon, et al.; Arch. Pharm. Res. 24, 307 (2001) | Effects of mycotoxins, kojic acid and oxalic acid, on biological fitness of Lygus hesperus (Heteroptera: Miridae): J. Alverson; J. Invertebr. Pathol. 83, 60 (2003) | From miso, sake and skoyu to cosmetics: a century of science for kojic acid: R. Bentley; Nat. Prod. Rep. 23, 1046 (2006) (Review) | Kojic acid and its manganese and zinc complexes as potential radioprotective agents: S. Emami, et al.; Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 17, 45 (2007) | Kojic acid, a secondary metabolite from Aspergillus sp. acts as an inducer of macrophage activation: A.P. Rodrigues, et al.; Cell Biol. Int. 35, 335 (2011) | Synthesis of kojic acid derivatives as secondary binding site probes of D-amino acid oxidase: M. Raje, et al.; Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 23, 3910 (2013) | Synergism of antifungal activity between mitochondrial respiration inhibitors and kojic acid: J.H. Kim, et al.; Molecules 18, 1564 (2013) | A novel function for kojic acid, a secondary metabolite from Aspergillus fungi, as antileishmanial agent: A.P. Rodrigues, et al.; PLoS One 9, e91259 (2014) | A tyrosinase inhibitor from Aspergillus niger: K.Y. Vasantha, et al.; J. Food Sci. Tech. 51, 2877 (2014) | Application of FTIR microspectroscopy for characterization of biomolecular changes in human melanoma cells treated by sesamol and kojic acid: M. Srisayam, et al.; J. Dermatol. Sci. 73, 241 (2014) | Feeding Deterrence, acute toxicity and sublethal growth effects of kojic acid isolated from Aspergillus funiculosus: S. Busi, et al.; Nat. Prod. J. 4, 18 (2014)