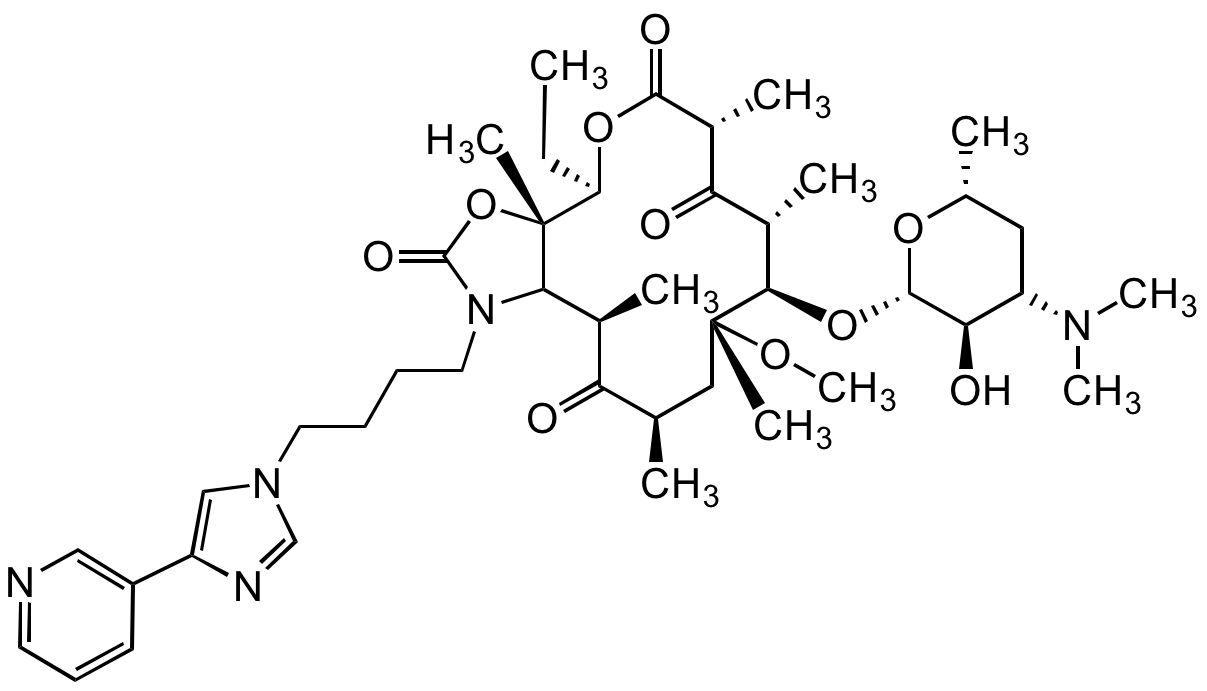
Telithromycin
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| BVT-0456-M001 | 1 mg | £55.00 |
Quantity:
| BVT-0456-M010 | 10 mg | £140.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Storage:
+4°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
RU 66647; Ketek; HMR 3647
Appearance:
White solid.
CAS:
191114-48-4
Class:
9
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
GHS Symbol:
GHS05,GHS08
Handling Advice:
Protect from light when in solution.
Hazards:
H315, H319, H335, H400, H410
InChi:
InChI=1S/C43H65N5O10/c1-12-33-43(8)37(48(41(53)58-43)19-14-13-18-47-23-31(45-24-47)30-16-15-17-44-22-30)27(4)34(49)25(2)21-42(7,54-11)38(28(5)35(50)29(6)39(52)56-33)57-40-36(51)32(46(9)10)20-26(3)55-40/h15-17,22-29,32-33,36-38,40,51H,12-14,18-21H2,1-11H3/t25-,26-,27+,28+,29-,32+,33-,36-,37?,38-,40+,42-,43-/m1/s1
InChiKey:
LJVAJPDWBABPEJ-XLSPMWLOSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 191114-48-4. Formula: C43H65N5O10. MW: 812. Semi-synthetic. Ketolide type macrolide antibiotic. Antibacterial compound used to treat mild to moderate respiratory infections. Protein synthesis inhibitor, by binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit and subsequently blocking the progression of the growing polypeptide chain. Binds to domains II and V of the 23S rRNA of the 50S ribosomal subunit. Has a higher affinity for these ribosomal targets than conventional macrolides due to the additional interactions and increased binding at domain II. Retains activity against Gram-positive cocci in the presence of resistance mediated by methylases (erm genes) that alter the binding site at domain V. May inhibit the formation of ribosomal subunits 50S and 30S.
MDL:
MFCD04117983
Molecular Formula:
C43H65N5O10
Molecular Weight:
812
Package Type:
Plastic Vial
PG:
III
Precautions:
P273, P280, P302, P352, P304, P340, P305, P351, P338, P312
Product Description:
Ketolide type macrolide antibiotic. Antibacterial compound used to treat mild to moderate respiratory infections. Protein synthesis inhibitor, by binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit and subsequently blocking the progression of the growing polypeptide chain. Binds to domains II and V of the 23S rRNA of the 50S ribosomal subunit. Has a higher affinity for these ribosomal targets than conventional macrolides due to the additional interactions and increased binding at domain II. Retains activity against Gram-positive cocci in the presence of resistance mediated by methylases (erm genes) that alter the binding site at domain V. May inhibit the formation of ribosomal subunits 50S and 30S.
Purity:
>98% (NMR, TLC)
Signal word:
Warning
SMILES:
CC[C@H]1OC(=O)[C@H](C)C(=O)[C@H](C)[C@@H](O[C@@H]2O[C@H](C)CC([C@H]2O)N(C)C)[C@@](C)(C[C@@H](C)C(=O)[C@H](C)C2N(CCCCN3C=NC(=C3)C3=CN=CC=C3)C(=O)O[C@]12C)OC
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO, ethanol, methanol, acetone or methylene chloride. Sparingly soluble in water (0.3mg/ml).
Source / Host:
Semi-synthetic.
Transportation:
Excepted Quantity
UN Nummer:
UN 3077
UNSPSC Category:
Natural Products/Extracts
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at +4°C.
References
The ketolide antibiotics HMR-3647 and HMR 3004 are active against Toxoplasma gondii in vitro and in murine models of infection: F.G. Araujo, et al.; Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 41, 2137 (1997) | The in-vitro activity of HMR 3647, a new ketolide antimicrobial agent: F.J. Boswell, et al.; J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 42, 703 (1998) | Drugs of the 21st century: telithromycin (HMR 3647) - the first ketolide: G. Ackermann & A.C. Rodloff; J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 51, 497 (2003) | Telithromycin: K. Wellington & S. Noble; Drugs 64, 1683 (2004) | Telithromycin: A ketolide antibiotic for treatment of respiratory tract infections: J.R. Lonks & D.A. Goldmann; Clin. Inf. Dis. 40, 1657 (2005) | Antibacterial drug discovery-Then, now and the genomics future: R. Monaghan & J.F. Barrett; Biochem. Pharmacol. 71, 901 (2006) | Telithromycin in the treatment of pneumococcal community-acquired respiratory tract infections: a review: C.M. Fogarty, et al.; Int. J. Infect. Dis. 10, 136 (2006) | Benefit-risk assessment of telithromycin in the treatment of community-acquired pneumonia: S.D. Brown; Drug Safety 31, 561 (2008) | Time-dependent effects of Klebsiella pneumonia endotoxin on the telithromycin pharmacokinetics in rats; restoration of the parameters in 96-hour KPLPS rats to the control levels: J.H. Lee, et al.; Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 21, 860 (2008) | Ketolides - the modern relatives of macrolides: the pharmacokinetic perspective: M. Zeitlinger, et al.; Clin. Pharmacokinet. 48, 23 (2009) | Inducible expression of erm(B) by the ketolides telithromycin and cethromycin: P. Byoungduck & M. Yu-Hong; Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 46, 226 (2015) | ClpP-independent function of ClpX interferes with telithromycin resistance conferred by msr(A) in Staphylococcus aureus: V. Vimberg, et al.; Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 59, 3611 (2015)
Related Products
| Product Name | Product Code | Supplier |
|---|