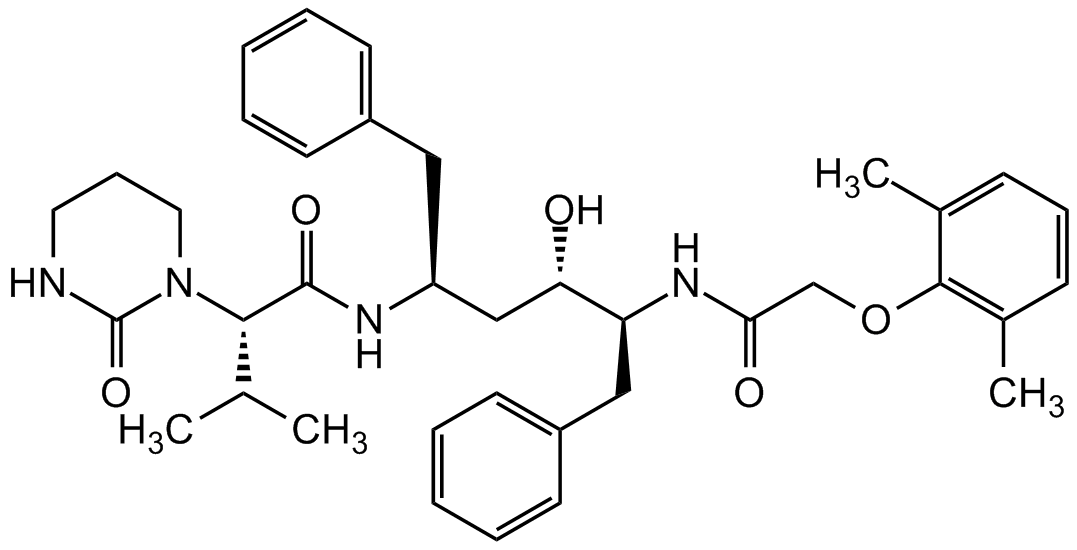
Lopinavir
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-CR1-3715-M025 | 25 mg | £40.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CR1-3715-M100 | 100 mg | £100.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CR1-3715-M250 | 250 mg | £180.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Storage:
-20°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
A-157378.0; ABT-378; Aluviran
Appearance:
White to off-white solid.
CAS:
192725-17-0
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
Handling Advice:
Keep cool and dry.
InChi:
InChI=1S/C37H48N4O5/c1-25(2)34(41-20-12-19-38-37(41)45)36(44)39-30(21-28-15-7-5-8-16-28)23-32(42)31(22-29-17-9-6-10-18-29)40-33(43)24-46-35-26(3)13-11-14-27(35)4/h5-11,13-18,25,30-32,34,42H,12,19-24H2,1-4H3,(H,38,45)(H,39,44)(H,40,43)/t30-,31-,32-,34-/m0/s1
InChiKey:
KJHKTHWMRKYKJE-SUGCFTRWSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 192725-17-0. Formula: C37H48N4O5. MW: 628.8. The antiviral agent Lopinavir is a potent inhibitor of HIV-1 protease (Ki=1.3pM for wild-type enzyme) and has been shown to block the replication of clinical isolates of HIV (EC50s=5-52nM). Lopinavir is an antiretroviral of the protease inhibitor class. It is used against HIV infections as a fixed-dose combination with another protease inhibitor, ritonavir (lopinavir/ritonavir). Lopinavir/ritonavir inhibits the HIV protease enzyme by forming an inhibitor-enzyme complex thereby preventing cleavage of the gag-pol polyproteins. Immature, non- infectious viral particles are subsequently produced. Lopinavir also has an ability to inhibit ZMPSTE24 (zinc metallopeptidase STE24). HIV-PIs block prelamin A processing by directly affecting the enzymatic activity of ZMPSTE24, and in this way they may contribute to lipodystrophy in individuals undergoing HIV-PI treatment. It also has been shown to inhibit meningioma cell proliferation, induce apoptosis on lymphoma cells and inhibit insulin signaling. Shown in a SARS-CoV-2 protease structure model study to potentially bind and inhibit the coronavirus endopeptidase C30 (CEP_C30) of SARS-CoV-2. A initial randomized trial study was not successful.
MDL:
MFCD22628840
Molecular Formula:
C37H48N4O5
Molecular Weight:
628.8
Package Type:
Vial
Product Description:
The antiviral agent Lopinavir is a potent inhibitor of HIV-1 protease (Ki=1.3pM for wild-type enzyme) and has been shown to block the replication of clinical isolates of HIV (EC50s=5-52nM). Lopinavir is an antiretroviral of the protease inhibitor class. It is used against HIV infections as a fixed-dose combination with another protease inhibitor, ritonavir (lopinavir/ritonavir). Lopinavir/ritonavir inhibits the HIV protease enzyme by forming an inhibitor-enzyme complex thereby preventing cleavage of the gag-pol polyproteins. Immature, non- infectious viral particles are subsequently produced. Lopinavir also has an ability to inhibit ZMPSTE24 (zinc metallopeptidase STE24). HIV-PIs block prelamin A processing by directly affecting the enzymatic activity of ZMPSTE24 and in this way they may contribute to lipodystrophy in individuals undergoing HIV-PI treatment. It also has been shown to inhibit meningioma cell proliferation, induce apoptosis on lymphoma cells and inhibit insulin signaling. Shown in a SARS-CoV-2 protease structure model study to potentially bind and inhibit the coronavirus endopeptidase C30 (CEP_C30) of SARS-CoV-2. A initial randomized trial study was not successful.
Purity:
>98% (1H-NMR)
SMILES:
O=C1NCCCN1[C@@H](C(C)C)C(N[C@@H](CC2=CC=CC=C2)C[C@H](O)[C@H](CC3=CC=CC=C3)NC(COC4=C(C)C=CC=C4C)=O)=O
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in ethanol (20mg/ml), DMSO (15mg/ml) or dimtheylformamide (15mg/ml).
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Biochemical Reagents
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
References
ABT-378, a highly potent inhibitor of the human immunodeficiency virus protease: H.L. Sham, et al.; Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 42, 3218 (1998) | Synthesis and antiviral activities of the major metabolites of the HIV protease inhibitor ABT-378 (Lopinavir): H.L. Sham, et al.; Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 11, 1351 (2001) | In vitro antiviral interaction of lopinavir with other protease inhibitors: A. Molla, et al.; Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 46, 2249 (2002) | In vitro hypersusceptibility of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 subtype C protease to lopinavir: L.M. Gonzalez, et al.; Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 47, 2817 (2003) | Role of lopinavir/ritonavir in the treatment of SARS: initial virological and clinical findings: C.M. Chu, et al.; Thorax 59, 252 (2004) | HIV-protease inhibitors block the enzymatic activity of purified Ste24p: S.E. Hudon, et al.; BBRC 374, 365 (2008) | Lopinavir inhibits meningioma cell proliferation by Akt independent mechanism: M.D. Johnson, et al.; J. Neurooncol. 101, 441 (2011) | HIV protease inhibitor Lopinavir induces apoptosis of primary effusion lymphoma cells via suppression of NF-kappaB pathway: R. Kariya, et al.; Cancer Lett. 342, 52 (2014) | Lopinavir inhibits insulin signaling by promoting protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B expression: T. Kitazawa, et al.; Exp. Ther. Med. 8, 851 (2014) | A systematic review of lopinavir therapy for SARS coronavirus and MERS coronavirus-A possible reference for coronavirus disease-19 treatment option: T.T. Yao, et al.; J. Med. Virol. (Epub ahead of print) (2020) (Review) | Molecular Modeling Evaluation of the Binding Effect of Ritonavir, Lopinavir and Darunavir to Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Proteases: S. Lin, et al.; (Epub ahead of print) (2020) | A Trial of Lopinavir-Ritonavir in Adults Hospitalized with Severe Covid-19: B. Cao, et al.; N. Engl. J. Med. (Epub ahead of print) (2020)