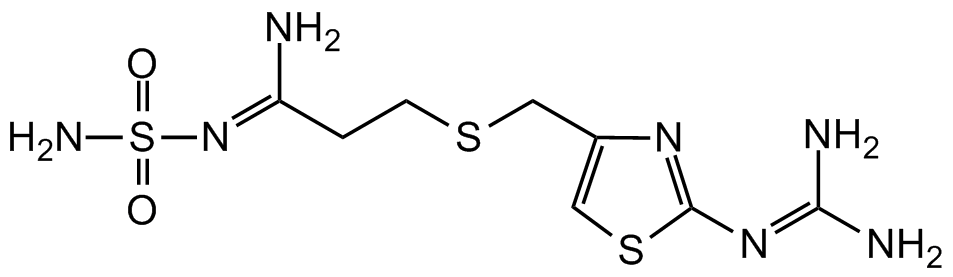
Famotidine
Product Code: AG-CR1-3730
Product Group: Natural Products and Extracts
Supplier: AdipoGen Life Sciences
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-CR1-3730-G001 | 1 g | £40.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CR1-3730-G005 | 5 g | £105.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
MK-208; YM-11170; Pepcid; N'-(Aminosulfonyl)-3-([2-(diaminomethyleneamino)-4-thiazolyl]methylthio)propanamidine
Appearance:
White to off-white solid.
CAS:
76824-35-6
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
InChi:
InChI=1S/C8H15N7O2S3/c9-6(15-20(12,16)17)1-2-18-3-5-4-19-8(13-5)14-7(10)11/h4H,1-3H2,(H2,9,15)(H2,12,16,17)(H4,10,11,13,14)
InChiKey:
XUFQPHANEAPEMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 76824-35-6. Formula: C8H15N7O2S3. MW: 337.5. Famotidine is a histamine H2 receptor antagonist. It is selective for H2 over H1 and muscarinic receptors (Kis = 4 and 28 µM, respectively, in bovine cerebral cortex).
Famotidine blocks the action of histamine in the parietal cells, ultimately blocking acid secretion in the stomach. It inhibits histamine-induced acid secretion in isolated canine parietal cells (IC50 = 0.6µM) and suppresses histamine-induced gastric acid secretion in dogs when administered orally and in anesthetized rats when administered intraduodenally (ID50s = 10 and 400µg/kg, respectively).
Famotidine is used to treat ulcers, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and heartburn and it decreases the risk of gastrointestinal toxicity associated with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Potential inhibitor of the viral enzyme papain-like protease (PLpro), important for SARS-CoV-2 replication and being tested in COVID-19 clinical trials.
MDL:
MFCD00079297
Molecular Formula:
C8H15N7O2S3
Molecular Weight:
337.5
Package Type:
Vial
Product Description:
Famotidine is a histamine H2 receptor antagonist. It is selective for H2 over H1 and muscarinic receptors (Kis = 4 and 28 µM, respectively, in bovine cerebral cortex). Famotidine blocks the action of histamine in the parietal cells, ultimately blocking acid secretion in the stomach. It inhibits histamine-induced acid secretion in isolated canine parietal cells (IC50 = 0.6µM) and suppresses histamine-induced gastric acid secretion in dogs when administered orally and in anesthetized rats when administered intraduodenally (ID50s = 10 and 400µg/kg, respectively). Famotidine is used to treat ulcers, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and heartburn and it decreases the risk of gastrointestinal toxicity associated with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Potential inhibitor of the viral enzyme papain-like protease (PLpro), important for SARS-CoV-2 replication and being tested in COVID-19 clinical trials.
Purity:
>98% (HPLC)
SMILES:
N/C(N)=N/C1=NC(CSCC/C(N)=N/S(=O)(N)=O)=CS1
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO (30mg/ml) or DMF (30mg/ml).
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Natural Products/Extracts
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
References
Pharmacokinetics of famotidine, a new H2-receptor antagonist, in relation to renal function: T. Takabatake, et al.; Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 28, 327 (1985) | Antimuscarinic effects of antihistamines: Quantitative evaluation by receptor-binding assay: N. Kubo, et al.; Jap. J. Pharmacol 43, 277 (1987) | Famotidine. An updated review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic use in peptic ulcer disease and other allied diseases: H.D. Langtry, et al.; Drugs 38, 551 (1989) (Review) | Differences in the antisecretory actions of the proton pump inhibitor AG-1749 (lansoprazole) and the histamine H2-receptor antagonist famotidine in rats and dogs: H. Nagaya, et al.; Jap. J. Pharmacol. 55, 425 (1991) | Clinical pharmacokinetics of famotidine: H. Echizen & T. Ishizaki; Clin. Pharmacokinet. 21, 178 (1991) (Review) | Famotidine, the new antiulcero-genic agent, a potent ligand for metal ions: H. Kozlowski, et al.; J. Inorg. Biochem. 48, 233 (1992) | Famotidine in gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD): I.C. Wesdorp; Hepatogastroenterology 1, 24 (1992) (Review) | Analysis of therapeutic targets for SARS-CoV-2 and discovery of potential drugs by computational methods: C. Wu, et al.; Acta Pharm. Sin. B. (Epub ahea of print) (2020)