anti-beta-Tubulin (beta-monoE) pAb (IN115)
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-25B-0039-C050 | 50 ug | £350.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Host Type: Rabbit
Antibody Clonality: Polyclonal
Regulatory Status: RUO
Target Species:
- Human
- Mouse
Applications:
- Immunocytochemistry (ICC)
- Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
- Immunoprecipitation (IP)
- Western Blot (WB)
Shipping:
BLUE ICE
Storage:
Short Term Storage: +4?C. Long Term Storage: -20?C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Concentration:
1mg/ml
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
Formulation:
Liquid. In PBS containing 0.02% Proclin 300.
Handling Advice:
After opening, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C.Avoid freeze/thaw cycles.
Immunogen:
Synthetic peptide corresponding to D431EQGEFE(E-COOH*)EEEG441-NH2 of human tubulin beta-2A chain (*secondary glutamate branched from gamma-carboxyl group of glutamate as isopeptide bond).
Long Description:
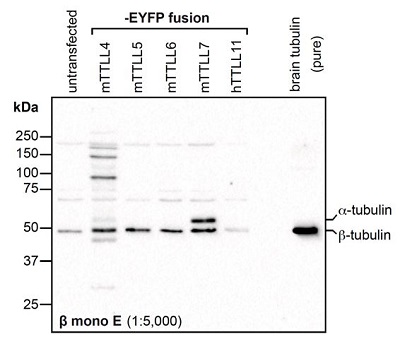
Polyclonal Antibody. Recognizes the posttranslational modification glutamylation with specific reactivity for the GE(*-E)F motive. Because the sequence GEF is specific to several beta-tubulin isotypes, the antibody selectively detects mono-glutamylated beta-tubulin. Applications: ICC, IHC, IP, WB. Source: Rabbit. Polyglutamylation is an evolutionarily conserved protein post-translational modification in which glutamate side chains of variable lengths are formed on the modified protein. The most prominent substrate is tubulin, the building block of microtubules (MTs). Polyglutamylation has been found on both, alpha- and beta-tubulin. It is catalyzed by multiple enzymes that belong to the family of tubulin tyrosine-ligase like (TTLL) enzymes. These TTLLs have substrate (alpha- vs beta-tubulin) as well as reaction (initiation vs elongation) specificities. These subtle changes in levels of polyglutamylation on specific tubulin isoforms could in turn be influencing the diverse MT functions that are regulated by polyglutamylation. The beta-monoE antibody selectively labels glutamylation of beta-tubulin due to its specificity to a sequence motif (GE(*-E)F) that only exists in beta-tubulin isotypes. It allows to specifically detect beta-tubulin glutamylation in brain tubulin, where other antibodies predominantly detect alpha-tubulin glutamylation.
NCBI, Uniprot Number:
Q13885
Other data:
Recognizes predominantly mono-glutamylated beta-tubulin. However, in cells overexpressing enzymes that can modify both alpha- and beta-tubulin, it might detect glutamylation on alpha-tubulin as well. Requires GE(*-E)F motive, which is present in several beta-tubulin isotypes. No other specificity to particular tubulin isotypes nor to tubulin from particular species are observed. The use of the antibody at too high concentrations obscures its specificity in immunofluorescence.
Package Type:
Plastic Vial
Product Description:
Polyglutamylation is an evolutionarily conserved protein post-translational modification in which glutamate side chains of variable lengths are formed on the modified protein. The most prominent substrate is tubulin, the building block of microtubules (MTs). Polyglutamylation has been found on both, alpha- and beta-tubulin. It is catalyzed by multiple enzymes that belong to the family of tubulin tyrosine-ligase like (TTLL) enzymes. These TTLLs have substrate (alpha- vs beta-tubulin) as well as reaction (initiation vs elongation) specificities. These subtle changes in levels of polyglutamylation on specific tubulin isoforms could in turn be influencing the diverse MT functions that are regulated by polyglutamylation. The beta-monoE antibody selectively labels glutamylation of beta-tubulin due to its specificity to a sequence motif (GE(*-E)F) that only exists in beta-tubulin isotypes. It allows to specifically detect beta-tubulin glutamylation in brain tubulin, where other antibodies predominantly detect alpha-tubulin glutamylation.
Purity:
>95% (SDS-PAGE)
Source / Host:
Rabbit
Specificity:
Recognizes the posttranslational modification glutamylation with specific reactivity for the GE(*-E)F motive. Because the sequence GEF is specific to several beta-tubulin isotypes, the antibody selectively detects mono-glutamylated beta-tubulin.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Primary Antibodies
UNSPSC Number:
12352203
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at -20°C.
References
Distinct roles of alpha- and beta-tubulin polyglutamylation in controlling axonal transport and in neurodegeneration: S. Bodakuntla, et al.; EMBO J. 40, e108498 (2021)