Recombinant SARS-CoV-2, Trimeric Spike (S) Protein
Product Code:
LEI-S848
LEI-S848
Host Type:
Virus
Virus
Regulatory Status:
RUO
RUO
Storage:
This recombinant protein may be stored as received at 2-8°C for up to one month. For longer term storage aseptically aliquot in working volumes without diluting and store at -80°C. Avoid Repeated Freeze Thaw Cycles.
This recombinant protein may be stored as received at 2-8°C for up to one month. For longer term storage aseptically aliquot in working volumes without diluting and store at -80°C. Avoid Repeated Freeze Thaw Cycles.
No additional charges, what you see is what you pay! *
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| LEI-S848-100ug | 100 ug | £673.00 |
Quantity:
| LEI-S848-500ug | 500 ug | £2,661.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Stay in control of your spending. These prices have no additional charges, not even shipping!
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
Multibuy discounts available! Contact us to find what you can save.
This product comes from: US.
Typical lead time: 14-21 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
Typical lead time: 14-21 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
- Further Information
- References
- Related Products
- Show All
Further Information
Conjugate/Tag/Label:
Purified No Carrier Protein
Format:
This recombinant protein is aseptically packaged and formulated in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline (PBS) pH 7.2 - 7.4, 150 mM NaCl with no carrier protein, potassium, calcium or preservatives added.
Formulation:
This recombinant protein is aseptically packaged and formulated in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline (PBS) pH 7.2 - 7.4, 150 mM NaCl with no carrier protein, potassium, calcium or preservatives added.
Long Description:
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the causative agent of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), is an enveloped, single-stranded, positive-sense RNA virus that belongs to the Coronaviridae family 1. The SARS-CoV-2 genome, which shares 79.6% identity with SARS-CoV, encodes four essential structural proteins: the spike (S), envelope (E), membrane (M), and nucleocapsid protein (N) 2. The S protein is a transmembrane, homotrimeric, class I fusion glycoprotein that mediates viral attachment, fusion, and entry into host cells 3. Each ~180 kDa monomer contains two functional subunits, S1 (~700 a.a) and S2 (~600 a.a), that mediate viral attachment and membrane fusion, respectively. S1 contains two major domains, the N-terminal (NTD) and C-terminal domains (CTD). The CTD contains the receptor-binding domain (RBD), which binds to the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor on host cells 3-5. Although both SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 bind the ACE2 receptor, the RBDs only share ~73% amino acid identity, and the SARS-CoV-2 RBD binds with a higher affinity compared to SARS-CoV 3, 6. The RBD is dynamic and undergoes hinge-like conformational changes, referred to as the ?down? or ?up? conformations, which hide or expose the receptor-binding motifs, respectively 7. Following receptor binding, S1 destabilizes, and TMPRSS2 cleaves S2, which undergoes a pre- to post-fusion conformation transition, allowing for membrane fusion 8, 9. The S protein has been the main focus of therapeutic and vaccine design as it is highly immunogenic. Both neutralizing antibodies 10,11 and memory T cells 12,13 targeting the S protein are present in the sera of convalescent COVID-19 patients.
NCBI Gene:
43740568
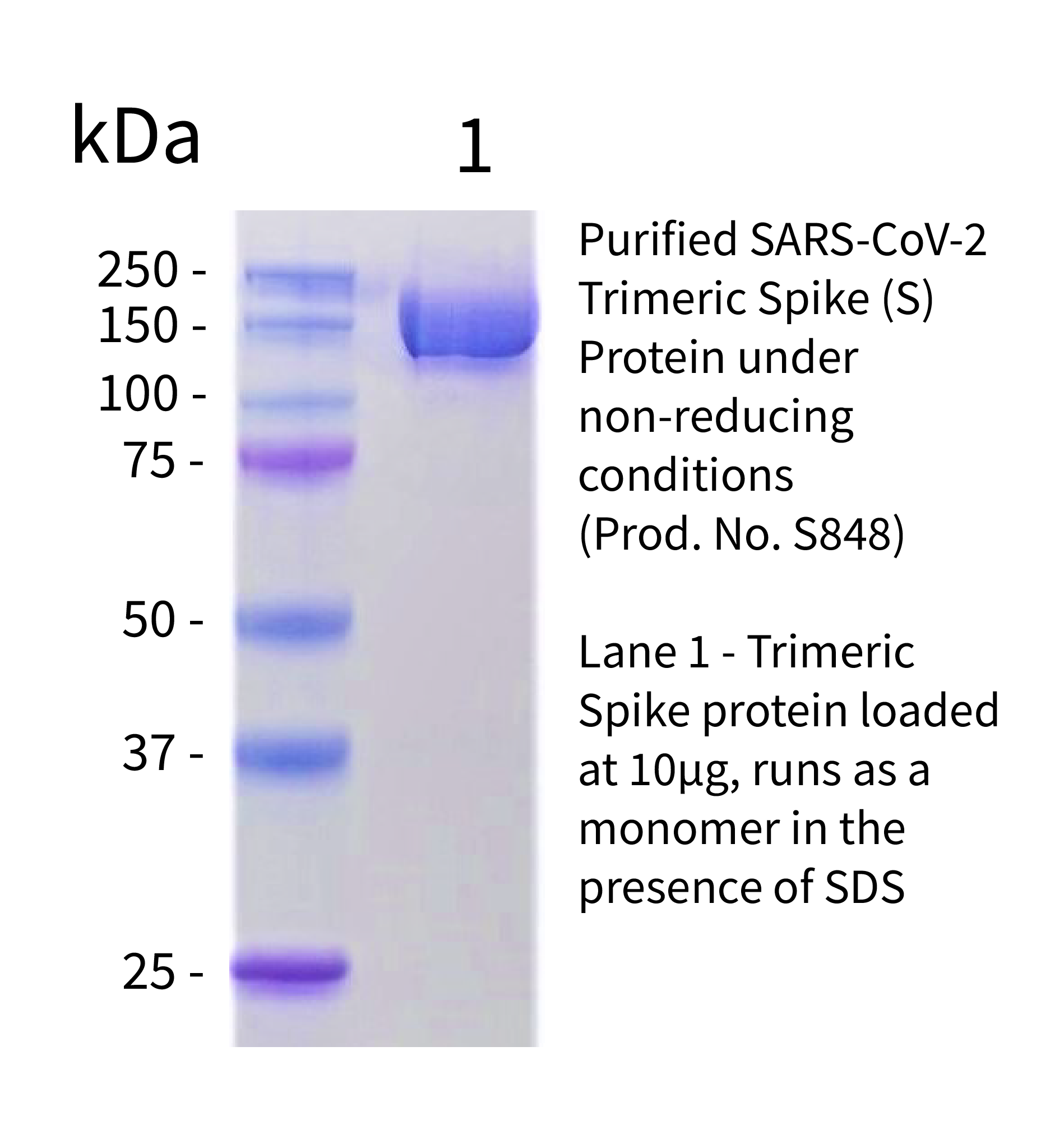
Purity:
>95% by SDS Page
Target:
SARS-CoV-2
References
1. Zhou, P., Yang, X., Wang, X. et al. Nature 579, 270?273. 2020.
2. Wu, F., Zhao, S., Yu, B. et al. Nature 579, 265?269. 2020.
3. Wrapp D, Wang N, Corbett KS, et al. bioRxiv. 2020.02.11.944462. 2020.
4. Walls AC, Park YJ, Tortorici MA, et al. Cell. 181(2):281-292.e6. 2020.
5. Li W, Zhang C, Sui J, et al. EMBO J. 24(8):1634-1643. 2005.
6. Shang, J., Ye, G., Shi, K. et al. Nature 581, 221?224. 2020.
7. Gui M, Song W, Zhou H, et al. Cell Res. 27(1):119-129. 2017.
8. Walls AC, Tortorici MA, Snijder J, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 114(42):11157-11162. 2017.
9. Hoffmann M, Kleine-Weber H, Schroeder S, et al. Cell. 181(2):271-280.e8. 2020.
10. Cao Y, Su B, Guo X, et al. Cell. 182(1):73-84.e16. 2020.
11. Ju, B., Zhang, Q., Ge, J. et al. Nature. 2020.
12. Grifoni A, Weiskopf D, Ramirez SI, et al. Cell. 181(7):1489-1501.e15. 2020.
13. Ni L, Ye F, Cheng ML, et al. Immunity. 52(6):971-977.e3. 2020.