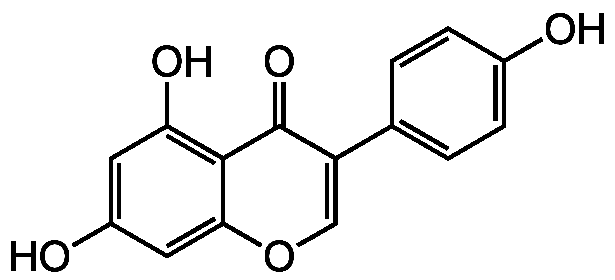
Genistein
Product Code: AG-CN2-0427
Product Group: Natural Products and Extracts
Supplier: AdipoGen Life Sciences
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-CN2-0427-M010 | 10 mg | £35.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CN2-0427-M050 | 50 mg | £45.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CN2-0427-M250 | 250 mg | £80.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Storage:
-20°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
NSC 36586; Baichanin A; Differenol A; 4',5,7-Trihydroxyisoflavone; 5,7-Dihydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one
Appearance:
White to off-white solid.
CAS:
446-72-0
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
GHS Symbol:
GHS07
Handling Advice:
Keep cool and dry.Protect from light.
Hazards:
H302
InChi:
InChI=1S/C15H10O5/c16-9-3-1-8(2-4-9)11-7-20-13-6-10(17)5-12(18)14(13)15(11)19/h1-7,16-18H
InChiKey:
TZBJGXHYKVUXJN-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 446-72-0. Formula: C15H10O5. MW: 270.2. Synthetic. Cell-permeable, reversible, substrate competitive tyrosine kinase inhibitor (including EGFR phosphorylation), implicated in almost all cell growth and proliferation signal cascades. Inhibitor of mammalian DNA topoisomerase II. Anticancer agent, inducing cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Antiangiogenic agent, down-regulates the transcription of genes involved in controlling angiogenesis. Binds estrogen receptor beta. Can increase the rate of growth of some ER expressing breast cancers. Potent alpha-glucosidase inhibitor. Anthelmintic. Anti-diabetic. Activates nuclear receptors, oestrogen receptors and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (all PPAR isoforms) and it inhibits various enzyme activities. Inhibitor of GLUT4-mediated glucose uptake in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Stimulator of autophagy vacuolization. Antioxidant. TRAIL sensitizer. Acts as an agonist at the GPR30 receptor. MALT1 inhibitor DNA methyltransferase inhibitor. Genistein exhibits synergistic antibacterial effects on MRSA.
MDL:
MFCD00016952
Molecular Formula:
C15H10O5
Molecular Weight:
270.2
Package Type:
Vial
Precautions:
P270, P301, P312, P330
Product Description:
Cell-permeable, reversible, substrate competitive tyrosine kinase inhibitor (including EGFR phosphorylation), implicated in almost all cell growth and proliferation signal cascades [1]. Inhibitor of mammalian DNA topoisomerase II [2]. Anticancer agent, inducing cell cycle arrest and apoptosis [3]. Antiangiogenic agent, down-regulates the transcription of genes involved in controlling angiogenesis [12]. Binds estrogen receptor beta. Can increase the rate of growth of some ER expressing breast cancers [4, 10]. Potent alpha-glucosidase inhibitor [5]. Anthelmintic [6]. Anti-diabetic. Activates nuclear receptors, oestrogen receptors and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (all PPAR isoforms) and it inhibits various enzyme activities [7, 8, 14]. Inhibitor of GLUT4-mediated glucose uptake in 3T3-L1 adipocytes [9]. Stimulator of autophagy vacuolization [12]. Antioxidant [13]. TRAIL sensitizer [15]. Acts as an agonist at the GPR30 receptor [16]. MALT1 inhibitor [17] DNA methyltransferase inhibitor [18]. Genistein exhibits synergistic antibacterial effects on MRSA [19].
Purity:
>99%
Signal word:
Warning
SMILES:
OC1=CC=C(C=C1)C1=COC2=CC(O)=CC(O)=C2C1=O
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO; slightly soluble in ethanol. Insoluble in water.
Source / Host:
Synthetic.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Natural Products/Extracts
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
References
Genistein, a specific inhibitor of tyrosine-specific protein kinases: T. Akiyama, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 262, 5592 (1987) | Inhibitory effects of the tyrosine kinase inhibitor genistein on mammalian DNA topoisomerase II: J. Markovits, et al.; Cancer Res. 49, 5111 (1989) | Genistein inhibition of the growth of human breast cancer cells: independence from estrogen receptors and the multi-drug resistance gene: G. Peterson & S. Barnes; BBRC 179, 661 (1991) | Interaction of estrogenic chemicals and phytoestrogens with estrogen receptor beta: G.G. Kuiper, et al.; Endocrinology 139, 4252 (1998) | Genistein, a soy isoflavone, is a potent alpha-glucosidase inhibitor: DS. Lee & SH. Lee; FEBS Lett. 501, 84 (2001) | Anthelmintic efficacy of Flemingia vestita: genistein-induced effect on the activity of nitric oxide synthase and nitric oxide in the trematode parasite, Fasciolopsis buski: P.K. Kar, et al.; Parasitol. Int. 51, 249 (2002) | Soy isoflavones exert antidiabetic and hypolipidemic effects through the PPAR pathways in obese Zucker rats and murine RAW 264.7 cells: O. Mezei, et al.; J. Nutr. 133, 1238 (2003) | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma ) as a molecular target for the soy phytoestrogen genistein: Z.C. Dang, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 278, 962 (2003) | Genistein directly inhibits GLUT4-mediated glucose uptake in 3T3-L1 adipocytes: M. Bazuine, et al.; BBRC 326, 511 (2005) | Genistein stimulates growth of human breast cancer cells in a novel, postmenopausal animal model, with low plasma estradiol concentrations Y.H. Ju, et al.; Carcinogenesis 27, 1292 (2006) | Phytochemical genistein in the regulation of vascular function: new insights: H. Si & D. Liu; Curr. Med. Chem. 14, 2581 (2007) | Diet, autophagy, and cancer: a review: K. Singletary & J. Milner; Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 17, 1596 (2008) (Review) | Comparison of flavonoids and isoflavonoids as antioxidants: RM. Han, et al.; J. Agric. Food Chem. 57, 3780 (2009) | Dose-dependent effects of soy phyto-oestrogen genistein on adipocytes: mechanisms of action: Z.C. Dang; Obes. Rev. 10, 342 (2009) (Review) | Novel HTS strategy identifies TRAIL-sensitizing compounds acting specifically through the caspase-8 apoptotic axis: D. Finlay, et al.; PLoS One 5, e13375 (2010) | Genistein regulates the IL-1 beta induced activation of MAPKs in human periodontal ligament cells through G protein-coupled receptor 30: L.J. Luo, et al.; Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 522, 9 (2012) | MALT1 small molecule inhibitors specifically suppress ABC-DLBCL in vitro and in vivo: L. Fontan, et al.; Cancer Cell 22, 812 (2012) | DNA methyltransferase-1 inhibitors as epigenetic therapy for cancer: V. Singh, et al.; Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 13, 379 (2013) | Flavonoids from Sophora moorcroftiana and their synergistic antibacterial effects on MRSA: SY. Wang, et al.; Phytother. Res. 28, 1071 (2014) | Anti-estrogenic and anti-aromatase activities of citrus peels major compounds in breast cancer: D.M. El-Kersh, et al.; Nature Sci. Rep. 11, 7121 (2021)