Clinical Diagnosis of Autoimmune Diseases
MBL provides IVD & RUO ELISAs for the diagnosis of autoantibodies commonly encountered in specific autoimmune diseases.
See the Products Available for the Detection of:
Detection of Autoimmune Blistering Diseases
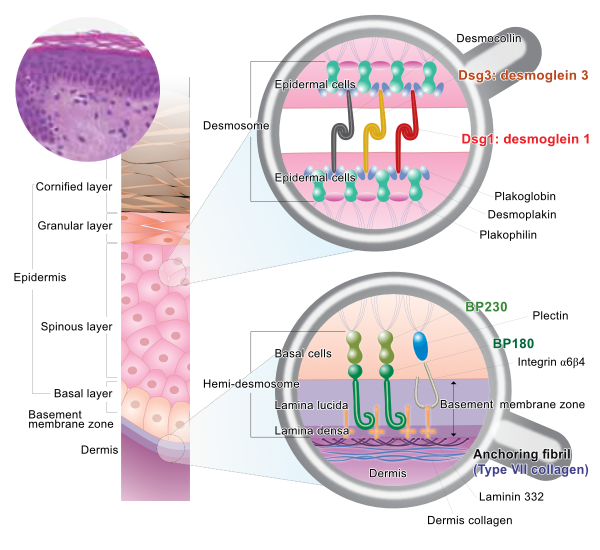
Autoimmune Blistering Diseases are a group of disorders associated with autoantibodies that are directed against desmosomal structural proteins (pemphigus) or hemidesmosomal proteins (Bullous Pemphigoid and Epidermolysis Bullosa Acquisita).
MBL offers ELISA kits for detection and monitoring of autoantibodies for these diseases.
- Highly Specific
- Parallel fluctuation with disease activity
- High Sensitivity
- Economical breakaway strips
Pemphigus vulgaris (PV)/Pemphigus foliaceus (PF)
Pemphigus is a group of autoimmune blistering diseases of the skin and mucous membranes which are characterised by intraepidermal blisters due to acantholysis (i.e. disruption of the intracellular connections between keratinocytes of the epidermis) and immunopathologically by in vivo bound and circulating immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies directed against the cell surface of keratinocytes. The target antigens in pemphigus are Dsg1 and 3, members of the cadherin super family. Pemphigus can be classified into pemphigus vulgaris (PV), pemphigus foliaceus (PF), paraneoplastic pemphigus (PNP), and others. The blisters in PV and PF occur in the deeper region of the epidermis (just above the basal layer) and the upper layer respectively.
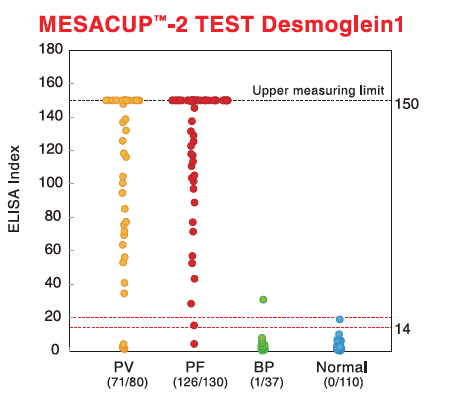
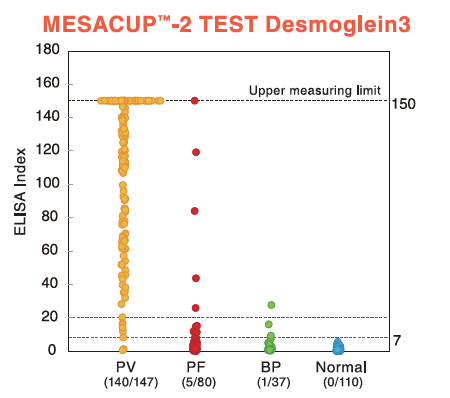
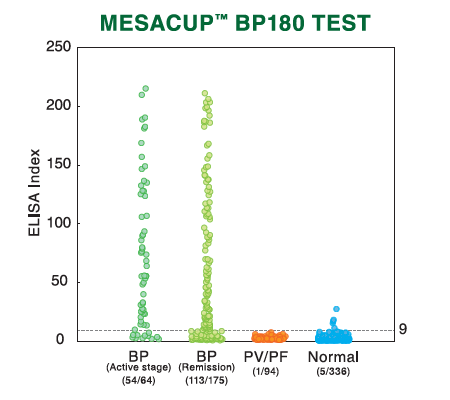
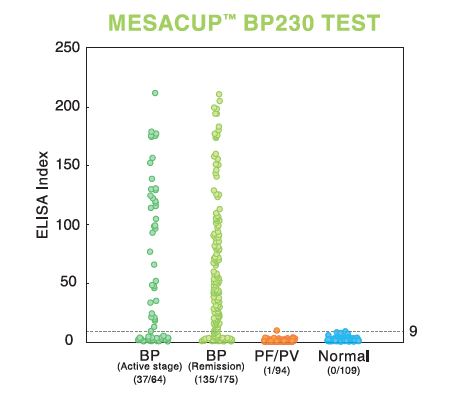
Bullous pemphigoid (BP)
Pemphigoid is a group of diseases characterised histologically by subepidermal blisters and immunopathologically by linear deposition of IgG and complement C3 at basement membrane zone (BMZ) in the skin from patients with circulating IgG against the molecules within the dermal-epidermal junction (DEJ). The target antigens recognised by autoantibodies in patients with bullous pemphigoid (BP) are BP180 (a 180 kDa transmembrane protein), and BP230 (a 230 kDa intracellular protein).
Detection of Polymyositis and Dermatomyositis (PM/DM)
Polymyositis and dermatomyositis (PM/DM) are systemic autoimmune disorders that involve muscle, skin and lungs. A number of autoantibodies are detected in PM/DM patient sera, some of which are specific to PM/DM (known as myostis-specific autoantibodies; MSAs).
In addition to well characterised MSAs, such as anti-aminoacyl tRNA synthetase (ARS), anti-signal recognition particle, and anti-Mi-2 antibodies, a number of additional DM specific antibodies have been recently described. These include antibodies against melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 (MDA5).

