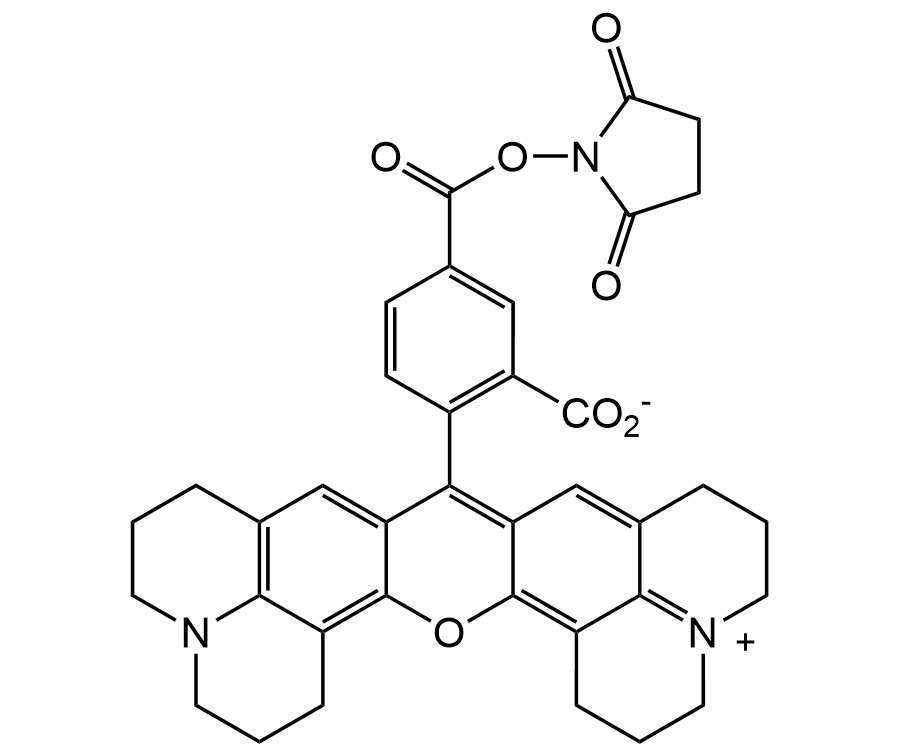
5-ROX N-succinimidyl ester
Product Code:
CDX-C0019
CDX-C0019
Regulatory Status:
RUO
RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Ambient
Storage:
Short term: +4°C. Long term: -20°C
Short term: +4°C. Long term: -20°C
No additional charges, what you see is what you pay! *
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| CDX-C0019-M005 | 5 mg | £301.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Stay in control of your spending. These prices have no additional charges to UK mainland customers, not even shipping!
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
Multibuy discounts available! Contact us to find what you can save.
This product comes from: Switzerland.
Typical lead time: 7-10 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
Typical lead time: 7-10 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
- Further Information
- Documents
- References
- Show All
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
5-Carboxy-X-rhodamine succinimidyl ester; 5-ROX SE ; 5-CXR SE
Appearance:
Dark violet powder.
CAS:
209734-74-7
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
solid
GHS Symbol:
GHS07
Handling Advice:
Protect from light and moisture.
Hazards:
H315-H319-H335
InChi:
InChi=1S/C37H33N3O7/c41-29-11-12-30(42)40(29)47-37(45)22-9-10-23(26(19-22)36(43)44)31-27-17-20-5-1-13-38-15-3-7-24(32(20)38)34(27)46-35-25-8-4-16-39-14-2-6-21(33(25)39)18-28(31)35/h9-10,17-19H,1-8,11-16H2
InChiKey:
BTTBJYLMDASSAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 209734-74-7. Formula: C37H33N3O7. MW: 631.67. 5-ROX N-succinimidyl ester (5-ROX-SE) is an amine-reactive long wavelength rhodamine dye. Derivatives made with the amine-reactive carboxy-X-rhodamine (ROX), succinimidyl ester are widely used for oligonucleotide labeling and automated DNA sequencing applications. Conjugates of this dye have longer-wavelength spectra than the spectra of Lissamine rhodamine B conjugates, but somewhat shorter-wavelength spectra than those of Texas Red conjugates. 5-ROX-SE derivatized compounds such as proteins, nucleic acids and drugs may be analyzed by fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) and fluorescence quenching applications. 5-ROX-SE is a labeling reagent for preparation of charge-modified dye-labeled ddNTPs to "direct-load" DNA sequencing. 5-ROX-SE is a single isomer of ROX and increasingly preferred for labeling peptides and nucleotides because it gives better resolution in HPLC purifications that are often required in bioconjugations. Variable ratios of the 5- and 6-isomers often cause complications in the interpretation of labeling results and assay performances. Spectral data: lambdaex=578nm; lambdaem=604nm; Extinction coefficient (cm-1M-1): 82000; Quantum yield: 0.94 (aqueous buffer pH 7.0).
MDL:
MFCD07437880
Molecular Formula:
C37H33N3O7
Molecular Weight:
631.67
Package Type:
Vial
Precautions:
P261-P264-P271-P280-P302+P352-P305+P351+P338
Product Description:
5-ROX N-succinimidyl ester (5-ROX-SE) is an amine-reactive long wavelength rhodamine dye. Derivatives made with the amine-reactive carboxy-X-rhodamine (ROX), succinimidyl ester are widely used for oligonucleotide labeling and automated DNA sequencing applications. Conjugates of this dye have longer-wavelength spectra than the spectra of Lissamine rhodamine B conjugates, but somewhat shorter-wavelength spectra than those of Texas Red conjugates. 5-ROX-SE derivatized compounds such as proteins, nucleic acids and drugs may be analyzed by fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) and fluorescence quenching applications. 5-ROX-SE is a labeling reagent for preparation of charge-modified dye-labeled ddNTPs to "direct-load" DNA sequencing. 5-ROX-SE is a single isomer of ROX and increasingly preferred for labeling peptides and nucleotides because it gives better resolution in HPLC purifications that are often required in bioconjugations. Variable ratios of the 5- and 6-isomers often cause complications in the interpretation of labeling results and assay performances. Spectral data: lambdaex=578nm; lambdaem=604nm; Extinction coefficient (cm-1M-1): 82000; Quantum yield: 0.94 (aqueous buffer pH 7.0).
Purity:
TLC-Test
Signal Word:
Warning
SMILES:
[O-]C(=O)c1cc(ccc1-c2c3cc4CCCN5CCCc(c45)c3[o+]c6c7CCCN8CCCc(cc26)c78)C(=O)ON9C(=O)CCC9=O
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMF, acetonitrile or DMSO.
Source / Host:
Synthetic
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Number:
41105331
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
Documents
References
(1) L.G. Lee, et al.; Nucl. Acids Res. 20, 2471 (1992) | (2) J. Ju, et al.; PNAS 92, 4347 (1995) | (3) S.-C. Hung, et al.; Anal. Biochem. 255, 32 (1998) | (4) Y. Yoshikawa, et al.; Anal. Biochem. 256, 82 (1998) | (5) P.J. Finn, et al.; Nucl. Acids Res. 30, 2877 (2002) | (6) T.S. Seo, et al.; PNAS 102, 5926 (2005)