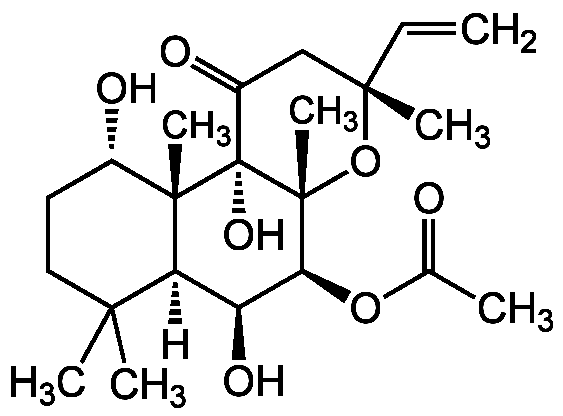
Forskolin
Product Code:
AG-CN2-0089
AG-CN2-0089
Regulatory Status:
RUO
RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Ambient
Storage:
Short term: +4°C. Long term: -20°C
Short term: +4°C. Long term: -20°C
No additional charges, what you see is what you pay! *
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-CN2-0089-M001 | 1 mg | £31.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CN2-0089-M005 | 5 mg | £51.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CN2-0089-M025 | 25 mg | £81.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CN2-0089-M050 | 50 mg | £106.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Stay in control of your spending. These prices have no additional charges to UK mainland customers, not even shipping!
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
Multibuy discounts available! Contact us to find what you can save.
This product comes from: Switzerland.
Typical lead time: 7-10 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
Typical lead time: 7-10 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
- Further Information
- Documents
- References
- Show All
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
Boforsin; Colforsin; Coleonol; NSC 357088; NSC 375489
Appearance:
White to off-white solid.
CAS:
66428-89-5 and 66575-29-9
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
GHS Symbol:
GHS07
Handling Advice:
Keep cool and dry.Protect from light.
Hazards:
H302
InChi:
InChI=1S/C22H34O7/c1-8-19(5)11-14(25)22(27)20(6)13(24)9-10-18(3,4)16(20)15(26)17(28-12(2)23)21(22,7)29-19/h8,13,15-17,24,26-27H,1,9-11H2,2-7H3/t13-,15-,16-,17-,19-,20-,21+,22-/m0/s1
InChiKey:
OHCQJHSOBUTRHG-KGGHGJDLSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 66428-89-5 and 66575-29-9. Formula: C22H34O7. MW: 410.5. Isolated from Coleus forskohlii. Potent, cell permeable adenylyl cyclase activator. Increases intracellular cAMP levels. Widely used tool to investigate cAMP as a second messenger. Inotropic and antihypertensive. Smooth muscle relaxant/vasodilator. Glucose transporter inhibitor. Platelet aggregation inhibitor. Stimulates lipolysis in fat cells. Non-competitive nicotinic acetylcholine receptors inhibitor. MAP kinase inhibitor. Upregulates mitochondrial uncoupling protein (UCP) mRNA levels in brown adipose tissue. Autophagy inhibitor. Hedgehog signaling inhibitor. Has antiglaucoma potential. Promotes neuronal differentiation of NSCs.
MDL:
MFCD00082317
Molecular Formula:
C22H34O7
Molecular Weight:
410.5
Other data:
Note: Do not dissolve in ethanol for activation of adenylyl cyclase.
Package Type:
Vial
Precautions:
P264, P280, P301, P312, P330
Product Description:
Potent, cell permeable adenylyl cyclase activator. Increases intracellular cAMP levels [1, 2, 6]. Widely used tool to investigate cAMP as a second messenger [15]. Inotropic and antihypertensive. Smooth muscle relaxant/vasodilator [3, 4, 6]. Glucose transporter inhibitor [4]. Platelet aggregation inhibitor [3, 10]. Stimulates lipolysis in fat cells [8]. Non-competitive nicotinic acetylcholine receptors inhibitor [9]. MAP kinase inhibitor [11]. Upregulates mitochondrial uncoupling protein (UCP) mRNA levels in brown adipose tissue [12]. Autophagy inhibitor [13]. Hedgehog signaling inhibitor [14]. Has antiglaucoma potential [16]. Promotes neuronal differentiation of NSCs [17]. Anti-neuroinflammatory and neuroprotective agent. Ameliorated Alzheimer?s disease symptoms, restoring impairment in nesting ability and sociability, and reducing neuroinflammation and amyloid beta deposition [18].
Purity:
>99% (HPLC)
Signal word:
Warning
SMILES:
[H][C@@]12[C@H](O)[C@H](OC(C)=O)[C@@]3(C)O[C@](C)(CC(=O)[C@]3(O)[C@@]1(C)[C@@H](O)CCC2(C)C)C=C
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in ethyl acetate, anhydrous DMSO or ethanol; very poorly soluble in water. DMSO is the recommended solvent for activation of cAMP.
Source / Host:
Isolated from Coleus forskohlii.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Natural Products/Extracts
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
Documents
References
The positive inotropic-acting forskolin, a potent adenylate cyclase activator: H. Metzger & E. Lindner; Arzneimittelforschung 31, 1248 (1981) | Forskolin: a unique diterpene activator of cyclic AMP-generating systems: K.B. Seamon & J.W. Daly; J. Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 7, 201 (1981) | Forskolin: a labdane diterpenoid with antihypertensive, positive inotropic, platelet aggregation inhibitory, and adenylate cyclase activating properties: N.J. de Souza, et al.; Med. Res. Rev. 3, 201 (1983) | Effects of forskolin on cerebral blood flow: Implications for a role of adenylate cyclase: D.G. Wysham, et al.; Stroke 17, 1299 (1986) | Forskolin inhibits insulin-stimulated glucose transport in rat adipose cells by a direct interaction with the glucose transporter: H.G. Joost & H.J. Steinfelder; Mol. Pharmacol. 31, 279 (1987) | Effect of forskolin on cytosolic Ca++ level and contraction in vascular smooth muscle: A. Abe & H. Karaki; J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 249, 895 (1989) | Forskolin: a specific stimulator of adenylyl cyclase or a diterpene with multiple sites of action?: A. Laurenza, et al.; TIPS 10, 442 (1989) (Review) | Relationship between cyclic AMP production and lipolysis induced by forskolin in rat fat cells: H. Okuda, et al.; J. Lipid Res. 33, 225 (1992) | Forskolin acts as a noncompetitive inhibitor of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: M.L. Aylwin & M.M. White; Mol. Pharmacol. 41, 908 (1992) | Forskolin inhibits platelet-activating factor binding to platelet receptors independently of adenylyl cyclase activation: S. Wong, et al.; Eur. J. Pharmacol. 245, 55 (1993) | Forskolin inhibits protein kinase C-induced mitogen activated protein kinase activity in MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts: S.R. Siddhanti, et al.; Endocrinol. 136, 4834 (1995) | Thermogenesis in brown adipose tissue with age: post-receptor activation by forskolin: P.J. Scarpace & M. Matheny; Pflugers Arch. 431, 388 (1996) | Role of the autophagic-lysosomal system on low potassium-induced apoptosis in cultured cerebellar granule cells: N. Canu, et al.; J. Neurochem. 92, 1228 (2005) | Forskolin, a Hedgehog signal inhibitor, inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in pediatric tumor cell lines: H. Yamanaka, et al.; Mol. Med. Rep. 3, 133 (2010) | Forskolin and derivatives as tools for studying the role of cAMP: R.H. Alasbahi & M.F. Melzig; Pharmazie 67, 5 (2012) (Review) | Forskolin: upcoming antiglaucoma molecule: V.D. Wagh, et al.; J. Postgrad. Med. 58, 199 (2012) (Review) | Functional neural differentiation of human adipose tissue-derived stem cells using bFGF and forskolin: S. Jang, et al.; BMC Cell Biol. 11, 1 (2010) | Protective effects of forskolin on behavioral deficits and neuropathological changes in a mouse model of cerebral amyloidosis: B.A. Owona, et al.; J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 75, 618 (2016)