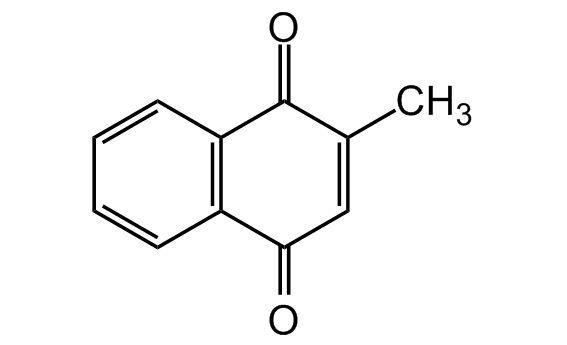
Menadione
Product Code:
AG-CR1-3631
AG-CR1-3631
Regulatory Status:
RUO
RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Ambient
Storage:
Short term: +4°C. Long term: -20°C
Short term: +4°C. Long term: -20°C
No additional charges, what you see is what you pay! *
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-CR1-3631-G001 | 1 g | £31.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CR1-3631-G005 | 5 g | £46.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Stay in control of your spending. These prices have no additional charges to UK mainland customers, not even shipping!
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
Multibuy discounts available! Contact us to find what you can save.
This product comes from: Switzerland.
Typical lead time: 7-10 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
Typical lead time: 7-10 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
- Further Information
- Documents
- References
- Show All
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
Vitamin K3; NSC4170; 2-Methyl-1,4-naphthalenedione
Appearance:
Off-white to yellow solid.
CAS:
58-27-5
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
GHS Symbol:
GHS07
Handling Advice:
Keep cool and dry.Keep under inert gas.Protect from light.
Hazards:
H302, H317, H319, H335
InChi:
InChI=1S/C11H8O2/c1-7-6-10(12)8-4-2-3-5-9(8)11(7)13/h2-6H,1H3
InChiKey:
MJVAVZPDRWSRRC-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 58-27-5. Formula: C11H8O2. MW: 172.2. Synthetic naphthoquinone without the isoprenoid side chain and biological activity, but can be converted to active vitamin K2 (menaquinone) after alkylation in vivo. The 1,4-naphthoquinone (NQ) moiety can form redox isomers by accepting one or two electrons respectively. The quinone redox cycling ability leads to the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) as well as arylation reactions. Anticancer compound. Apoptosis inducer in various cultured cells including leukemia through several modes of action. Free radical generator. Produces peroxide and superoxide radicals (ROS) leading to mitochondrial dysfunction. Cell cycle inhibitor. Glutathione (GSH) depletion results by direct arylation of cellular thiols. Once GSH is depleted, cellular macromolecules start to be alkylated, resulting in their inactivation. Protein tyrosine phosphatase inhibitor. Inhibitor of mitochondrial DNA polymerase gamma. Inhibitor of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) with an IC50 of ~1µM.
MDL:
MFCD00001681
Molecular Formula:
C11H8O2
Molecular Weight:
172.2
Package Type:
Vial
Precautions:
P261, P280, P301, P312, P302, P352, P305, P351, P338, P304, P340, P403, P233
Product Description:
Synthetic naphthoquinone without the isoprenoid side chain and biological activity, but can be converted to active vitamin K2 (menaquinone) after alkylation in vivo. The 1,4-naphthoquinone (NQ) moiety can form redox isomers by accepting one or two electrons respectively. The quinone redox cycling ability leads to the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) as well as arylation reactions. Anticancer compound. Apoptosis inducer in various cultured cells including leukemia through several modes of action. Free radical generator. Produces peroxide and superoxide radicals (ROS) leading to mitochondrial dysfunction. Cell cycle inhibitor. Glutathione (GSH) depletion results by direct arylation of cellular thiols. Once GSH is depleted, cellular macromolecules start to be alkylated, resulting in their inactivation. Protein tyrosine phosphatase inhibitor. Inhibitor of mitochondrial DNA polymerase gamma. Inhibitor of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) with an IC50 of ~1µM.
Purity:
>98%
Signal word:
Warning
SMILES:
O=C1C(C)=CC(C2=C1C=CC=C2)=O
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO (20mg/ml), ethanol (10mg/ml) or dimethylformamide (30mg/ml). Insoluble in water.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Biochemical Reagents
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
Documents
References
Vitamin K3 induces cell cycle arrest and cell death by inhibiting Cdc25 phosphatase: F.Y. Wu and T.P.; Eur. J. Cancer 35, 1388 (1999) | Apoptosis-inducing activity of vitamin C and vitamin K: H. Sakagami, et al.; Cell Mol. Biol. 46, 129 (2000) | Cytotoxic activity of vitamins K1, K2 and K3 against human oral tumor cell lines: H. Okayasu, et al.; Anticancer Res. 21, 2387 (2001) | 2-Methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone, vitamin K(3), decreases gap-junctional intercellular communication via activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor/extracellular signal-regulated kinase cascade: L.O. Klotz, et al.; Cancer Res. 62, 4922 (2002) | Signaling effects of menadione: from tyrosine phosphatase inactivation to connexin phosphorylation: K. Abdelmohsen, et al.; Methods Enzymol. 378, 258 (2004) (Review) | Vitamin K3 (menadione)-induced oncosis associated with keratin 8 phosphorylation and histone H3 arylation: G.K. Scott, et al.; Mol. Pharmacol. 68, 606 (2005) | Menadione-induced reactive oxygen species generation via redox cycling promotes apoptosis of murine pancreatic acinar cells: D.N. Criddle, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 281, 40485 (2006) | Activation of ErbB2 by 2-methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone (menadione) in human keratinocytes: role of EGFR and protein tyrosine phosphatises: J.I. Beier, et al.; FEBS Lett. 580, 1859 (2006) | Inhibition of PTEN and activation of Akt by menadione: K. Yoshikawa, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1770, 687 (2007) | Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase Is the Anticancer Target for a Novel Series of Potent Naphthoquinone-Based Inhibitors: S. Kumar, et al.; J. Med. Chem. 51, 1706 (2008) | DNA polymerase gamma inhibition by vitamin K3 induces mitochondria-mediated cytotoxicity in human cancer cells: R. Sasaki, et al.; Cancer Sci. 99, 1040 (2008) | Targeting cancer cells by an oxidant-based therapy: J. Verrax, et al.; Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 1, 80 (2008) (Review) | The phosphatase inhibitor menadione (vitamin K3) protects cells from EGFR inhibition by erlotinib and cetuximab: R. Perez-Soler, et al.; Clin. Cancer Res. 17, 6766 (2011) | 1,4-naphthoquinones: from oxidative damage to cellular and inter-cellular signalling: L.O. Klotz, et al.; Molecules 19, 14902 (2014) | Anticancer Vitamin K3 analogues: A review: K.D. Badave, et al.; Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 16, 1017 (2016)