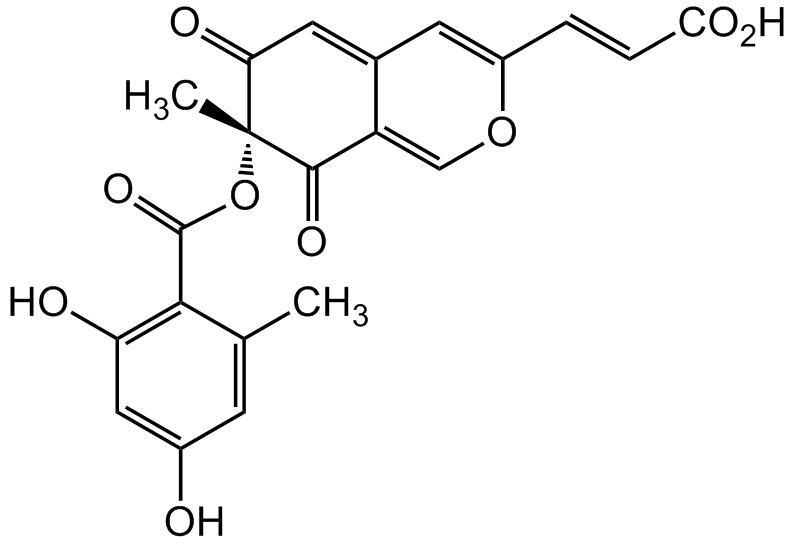
(-)-Mitorubrinic acid
Product Code:
AG-CN2-0505
AG-CN2-0505
Regulatory Status:
RUO
RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Ambient
Storage:
Short term: +4°C. Long term: -20°C
Short term: +4°C. Long term: -20°C
No additional charges, what you see is what you pay! *
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-CN2-0505-M001 | 1 mg | £181.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Stay in control of your spending. These prices have no additional charges to UK mainland customers, not even shipping!
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
Multibuy discounts available! Contact us to find what you can save.
This product comes from: Switzerland.
Typical lead time: 7-10 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
Typical lead time: 7-10 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
- Further Information
- Documents
- References
- Show All
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
(R,E)-3-(7-((2,4-Dihydroxy-6-methylbenzoyl)oxy)-7-methyl-6,8-dioxo-7,8-dihydro-6H-isochromen-3-yl)acrylic acid
Appearance:
Yellow solid.
CAS:
58958-07-9
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
solid
Handling Advice:
Keep cool and dry.
InChi:
InChI=1S/C21H16O9/c1-10-5-12(22)8-15(23)18(10)20(28)30-21(2)16(24)7-11-6-13(3-4-17(25)26)29-9-14(11)19(21)27/h3-9,22-23H,1-2H3,(H,25,26)/b4-3+/t21-/m1/s1
InChiKey:
ZJIWQCFXEQSFGR-YEFOHOTDSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 58958-07-9. Formula: C21H16O9. MW: 412.4. Isolated from Penicillium sp. Azaphilone fungal metabolite. Induces formation of chlamydospore-like cells in fungi. Trypsin inhibitor (IC50=16µg/ml). Mitorubrinic acid was shown to be a virulence factor of Penicillium marneffei by improving its intracellular survival in macrophages. P. marneffei is the most important thermal dimorphic fungus causing respiratory, skin and systemic mycosis in China and Southeast Asia. It is a common indicator disease of AIDS. Besides HIV positive patients, P. marneffei infections have been reported in other immunocompromised patients, such as transplant recipients, patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and on corticosteroid therapy.
MDL:
MFCD00238645
Molecular Formula:
C21H16O9
Molecular Weight:
412.4
Package Type:
Vial
Product Description:
Azaphilone fungal metabolite. Induces formation of chlamydospore-like cells in fungi. Trypsin inhibitor (IC50=16µg/ml). Mitorubrinic acid was shown to be a virulence factor of Penicillium marneffei by improving its intracellular survival in macrophages. P. marneffei is the most important thermal dimorphic fungus causing respiratory, skin and systemic mycosis in China and Southeast Asia. It is a common indicator disease of AIDS. Besides HIV positive patients, P. marneffei infections have been reported in other immunocompromised patients, such as transplant recipients, patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and on corticosteroid therapy.
Purity:
>90% (HPLC)
SMILES:
O=C1[C@@](C)(OC(C2=C(O)C=C(O)C=C2C)=O)C(C3=COC(/C=C/C(O)=O)=CC3=C1)=O
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO, ethanol or methanol.
Source / Host:
Isolated from Penicillium sp.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Natural Products/Extracts
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
Documents
References
(-)-Mitorubrinic acid, a morphogenic substance inducing chlamydospore-like cells, and its related new metabolite, (+)-mitorubrinic acid b, isolated from Penicillium funiculosum: M. Natsume, et al.; Agric. Biol. Chem. 49, 2517 (1985) | (-)-Mitorubrinic Acid, a New Metabolite of Penicillium vermiculatum DANG. F-852: B.Proksa, et al.; Chemical Papers 48, 429 (1994) | Production of (-)-mitorubrinic acid by Penicillium vermiculatum: B. Proksa, et al.; Folia Microbiol. 42, 133 (1997) | Factors affecting the production of (-)-mitorubrinic acid by Penicillium funiculosum: K. Lesova, et al.; J. Basic Microbiol. 40, 369 (2000) | First discovery of two polyketide synthase genes for mitorubrinic acid and mitorubrinol yellow pigment biosynthesis and implications in virulence of Penicillium marneffei: P.C. Woo, et al.; PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 6, e1871 (2012)