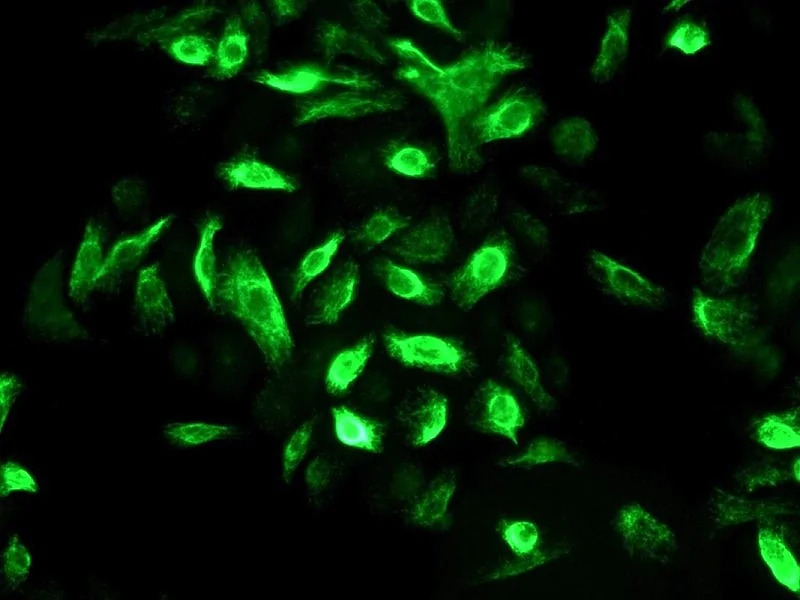
Human Oral Keratinocytes
Product Code:
SC-2610
SC-2610
Cell System:
Oral Cell system
Oral Cell system
Cell Type:
Keratinocytes
Keratinocytes
Species:
Human
Human
Regulatory Status:
RUO
RUO
No additional charges, what you see is what you pay! *
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| SC-2610 | 5 x 10^5 cells/vial | £809.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Stay in control of your spending. These prices have no additional charges to UK mainland customers, not even shipping!
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
Multibuy discounts available! Contact us to find what you can save.
This product comes from: United States.
Typical lead time: 10-14 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
Typical lead time: 10-14 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
- Further Information
- Documents
- References
- Related Products
- Show All
Further Information
Extra Description:
Isolated from human oral mucosa. HOK are cryopreserved at passage one and delivered frozen. Each vial contains >5 x 10^5 cells in 1 ml volume.
Long Description:
Oral keratinocytes act as the major barrier to physical, microbial, and chemical agents that may cause local cell injury. They are involved in the proinflammatory process through the production of cytokines either constitutively or after a variety of stimuli. Consequently, oral keratinocytes may potentially participate in controlling oral infections through an inflammatory process involving different interleukins, such as IL-1β and IL-18. Oral keratinocytes express a variety of differentiation markers, the expression of which is influenced by calcium-induced changes in the transcription of target genes. Oral keratinocytes share major structural and functional features with the well-characterized dermal keratinocyte and are a good model to study basic keratinocyte biology, as well as, processes of immortalization and malignant transformation.HOK from ScienCell Research Laboratories are isolated from human oral mucosa. HOK are cryopreserved at passage one and delivered frozen. Each vial contains >5 x 10^5 cells in 1 ml volume. HOK are characterized by immunofluorescence with antibodies specific to cytokeratin-18 and/or cytokeratin-19. HOK are negative for HIV-1, HBV, HCV, mycoplasma, bacteria, yeast and fungi. HOK are guaranteed to further expand for 10 population doublings under the conditions provided by ScienCell Research Laboratories.
Recommended Medium -
It is recommended to use Oral Keratinocyte Medium (OKM, Cat. No. 2611) for the culturing of HOK in vitro.
Documents
References
- https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0063295
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24079913/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23324604/
- https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0067985
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19643820/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18838522/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2885137/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16982811/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20206247/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17993289/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20337899/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2952253/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21656745/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23160375/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3887855/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22723337/
- http://journals.plos.org/plosone/article/asset?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0149618.PDF
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4694824/pdf/oncotarget-06-25188.pdf
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4594676/pdf/jcmm0019-2341.pdf
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4396206/pdf/ijcep0008-1364.pdf
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4359265/pdf/oncotarget-06-915.pdf
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4399078/
- http://journals.plos.org/plosone/article/asset?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0152526.PDF
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4637754/pdf/ijcep0008-11837.pdf
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4937741/pdf/ajcr00061396.pdf
- http://journals.plos.org/plosone/article/asset?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0158440.PDF