What is an Immune Checkpoint?
The immune system needs to differentiate between normal and abnormal cells. When the immune system identifies cells properly, it is able to destroy abnormal cells while not harming normal cells. Immune cells utilise checkpoints to perform this task. Immune checkpoints are cell surface proteins on T-cells that are able to bind homologous receptor proteins on other cells, such as an antigen-presenting cell (APC). Activation of the immune checkpoint pathways results in either immune suppression or stimulation. Immune checkpoint pathways play a vital role in regulating the immune system, ultimately balancing its function and maintaining homeostasis.
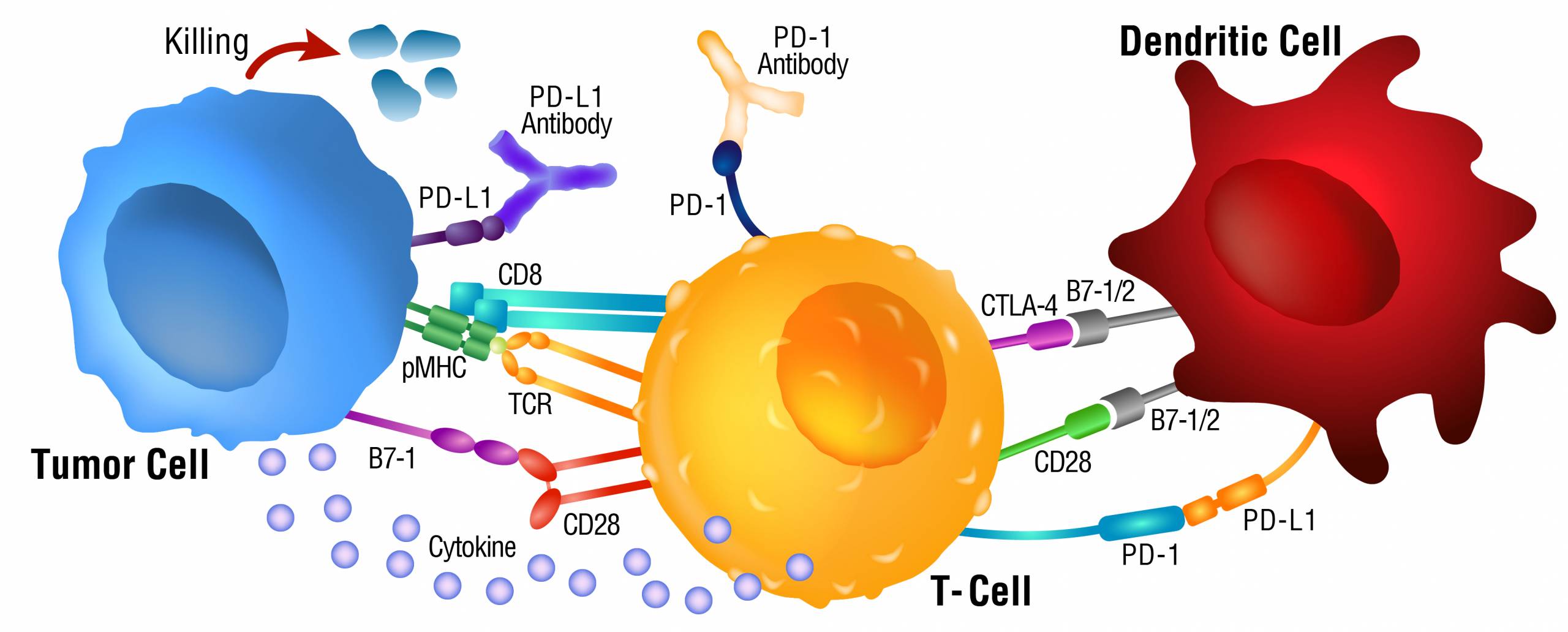
Anti-tumour Immunity and Cancer Progression
Tumour cells adapt by learning to exploit checkpoint mechanisms. Tumour cells confuse T-cells by presenting cell surface proteins that are recognised as normal by the T-cell, even though they are unwanted and should be eliminated by the immune system. Checkpoint pathway manipulation is one strategy tumour cells employ to outsmart the immune system, survive, and proliferate freely.
Cancer and Checkpoint Inhibitors
An example of tumour cells evading immune response can be understood through the PD-1 and PD-L1 interaction. PD-1 is a checkpoint protein on T-cells that recognises the cellular surface protein, PD-L1, which acts to prevent the attack of other cells. One strategy tumour cells employ to avoid an immune attack is through the expression of PD-L1. Upon binding of PD-1 to PD-L1, immune suppression signals are sent which indicates to the immune system not to attack the tumour cell.
Checkpoint inhibitors are a class of monoclonal antibodies designed to target and bind to checkpoint proteins and block checkpoint signals (immune activation or suppression). Checkpoint inhibitors can bind to proteins on T-cells, such as PD-1, or protein receptors on tumour cells, such as PD-L1. Whether the checkpoint inhibitor binds to PD-1 or PD-L1, the PD-1/PD-L1 interaction is prevented and the signal is blocked. The power of checkpoint inhibitors as an immunotherapeutic method is being diligently investigated. Checkpoint inhibitor drugs have been successful in treating some forms of cancer and show great promise as an effective treatment with fewer symptoms than traditional therapeutic methods.
Congratulations to James P. Allison and Tasuku Honjo for their pioneering work and discovery of immune checkpoint proteins and for winning the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine.
Originally posted by Leinco Technologies Inc. on: https://www.leinco.com/immune-checkpoint-antibody/
Caltag Medsystems is the distributor of Leinco Technologies’ products in the UK and Ireland. If you have any questions about these products, please contact us.
