 Understanding binding affinity is an important part of the drug discovery process, ensuring that therapeutic antibodies that bind their targets selectively and specifically. It also helps to understand the intermolecular interactions driving biological processes, structural biology, and structure-function relationships.
Understanding binding affinity is an important part of the drug discovery process, ensuring that therapeutic antibodies that bind their targets selectively and specifically. It also helps to understand the intermolecular interactions driving biological processes, structural biology, and structure-function relationships.
KD is the equilibrium dissociation constant, a calculated ratio of Koff/Kon, between the antibody and its antigen. The association constant (Kon) is used to characterise how quickly the antibody binds to its target. The dissociation constant (Koff) is used to measure how quickly an antibody dissociates from its target. KD and affinity are inversely related. A high affinity interaction is characterized by a low KD, a fast recognizing (high Kon) and a strong stability of formed complexes (low Koff).
Diaclone, represented by Caltag Medsystems, are a leading manufacturer of monoclonal antibodies, and their expertise can be used to further characterise your antibody. They measure KD using the SPR (Surface Plasmon Resonance) technology and the Octet instrument. This technique can help you to rank your antibodies but also to better understand the performance of your antibodies.
Case Study: ELISA antibody pair development
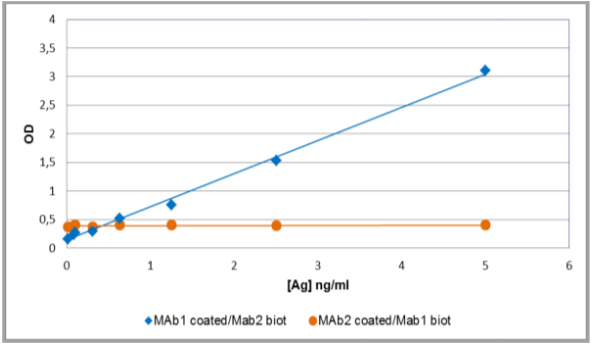
For example, during this ELISA development, Diaclone discovered that the antibody pair only worked when mAb1 is coated, and not the other way round (Fig.1).
The determination of KD and association/dissociation profiles of antibodies by Octet allowed Diaclone to discover why the pair works only in one way:
The mAb2 has a quick dissociation time (Fig. 2), so, when it’s coated and after all the washing steps, the antigen doesn’t stay on mAb2. Using this antibody as revelation avoids this dissociation which is linked to accumulated washing steps.
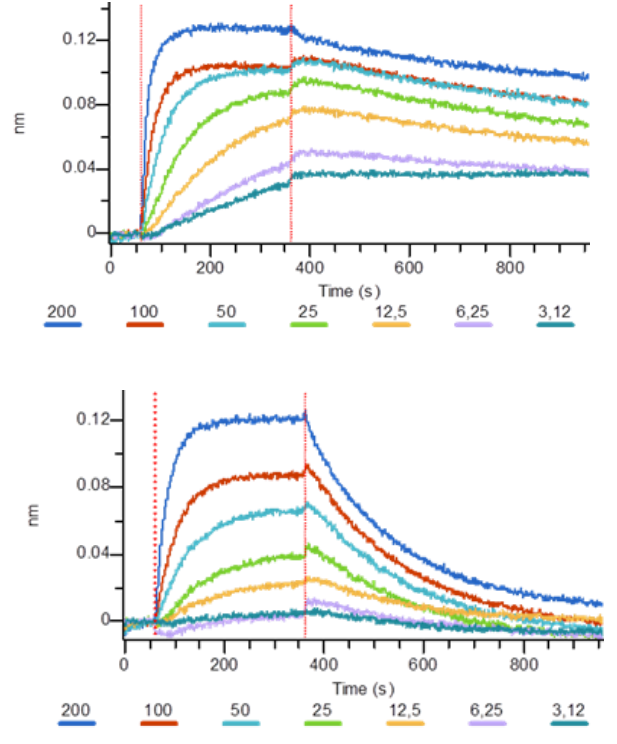
Octet analysis
The Octet technology is fully integrated into Diaclone’s custom monoclonal antibody development so that it can be implemented to further study monoclonal antibody candidates.
Diaclone utilise the Octet instrument to measure KD, but it can also help to validate the accessibility of tags (HIS, GST…), to study the interaction receptor-ligand and the potential inhibition of interaction with an antibody, and to perform epitope binning (also known as epitope mapping or pairing).
The advantage of Octet compared to the highly popular Biacore technique is the lower price, the rapid execution of experiments and the small amount of proteins required. Whatever the interaction to study, Octet is a valuable tool.
Make use of Diaclone’s expertise in antibody characterisation
Diaclone have over 30 years experience in the production of monoclonal antibody, ELISA, ELISpot & Multiplex assays. Their catalogue items are readily available, and target antigens in the areas of T cell Immunology, CD antigens, Cytokines, cytokine/chemokine receptors, adhesion molecules and apoptosis.
Diaclone also offer a large range of custom services, dedicated to your needs:
- Biological activity: agonist or antagonist, secretion enhancer, blocking signal transduction, cellular growth activation or inhibition (or any new model to design!)
- Effector activity: ADCC, ADCP or CDC
- Antibody applications: ELISA, Western Blotting, Flow cytometry…
- Antibody labeling
Contact us to discover how Diaclone can support your drug discovery activity!
Diaclone Products and Services are distributed in the UK by Caltag Medsystems Ltd.
